Abstract
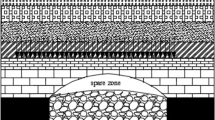
According to the borehole drilling detection results of a superhigh-fill highway subgrade that crossed an open-pit coal mined-out area with an underground coal fire (UCF) in Urumqi, China, a numerical model of the subgrade and substrata was established. The variations of the stability characteristics of the highway pavement and the subgrade slope with respect to the substrata properties under the effects of coal-seam combustion were analyzed via thermal-stress coupled calculations using the finite-difference software FLAC3D. When the coal body underlying the subgrade underwent burnout and the combustion cavity formed, the bearing capacity of the strata decreased significantly. Under the effect of the heavy self-weight of the high-fill subgrade body and other external loads, such as the vehicle load on the pavement, collapse was likely, followed by the formation of a large sink basin on the surface of the subgrade. The displacement of the highway suffering from UCF increased gradually. The displacement development was divided into two stages: the swelling stage due to rock-mass expansion and the collapse stage due to the burnout of the coal body. The concrete geocell had a good reinforcement effect on the subgrade in which the settlement of the basin occurred under the effects of the UCF. When part of the geocell was deformed under external loads, the loads were transferred to the neighboring concrete geocell located in the stable region. Thus, the concrete geocell in the stable region constrained the geocell in the unstable region from deforming. Furthermore, a parametric analysis with varying combustion conditions indicated that a higher heat-release intensity, wider combustion region, and shallower combustion depth lead to greater stability hazards for the overlying subgrade.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdulagatova Z, Abdulagatov IM, Emirov VN (2009) Effect of temperature and pressure on the thermal conductivity of sandstone. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 46:1055–1071. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2009.04.011
Benmebarek S, Berrabah F, Benmebarek N (2015) Effect of geosynthetic reinforced embankment on locally weak zones by numerical approach. Comput Geotech 65:115–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compgeo.2014.12.004
Cao Y (1992) The ductility deformation mechanism and distinguished marks of Coa. J Jiaoz Min Instit (3):39–44
Deng J, Ren S, Xiao Y, Li Q, Shu C (2018) Thermal properties of coals with different metamorphic levels in air atmosphere. Appl Therm Eng 143:542–549. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2018.07.117
Deng J, Ren S, Xiao Y, Shu C (2019) Mechanical properties of coal and rock mass under thermo-mechanical coupling. Arab J Geosci 12:398. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-019-4565-z
Derghoum R, Meksaouine M (2019) Coupled finite element modelling of geosynthetic reinforced embankment slope on soft soils considering small and large displacement analyses. Arab J Sci Eng 44:4555–4573. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-018-3461-2
Elick JM (2011) Mapping the coal fire at Centralia, Pa using thermal infrared imagery. Int J Coal Geol 87:197–203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coal.2011.06.018
Huang J, Bruining J, Wolf KHAA (2001) Modeling of gas flow and temperature fields in underground coal fires. Fire Saf J 36:477–489. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0379-7112(01)00003-0
Itasca Consulting Group I (2012) Online manual of fast lagrangian analysis of continua in 3 dimensions. Minneapolis
Jamsawang P, Yoobanpot N, Thanasisathit N, Voottipruex P, Jongpradist P (2016) Three-dimensional numerical analysis of a DCM column-supported highway embankment. Comput Geotech 72:42–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compgeo.2015.11.006
Kong B, Li Z, Yang Y, Liu Z, Yan D (2017) A review on the mechanism, risk evaluation, and prevention of coal spontaneous combustion in China. Env Sci Pollut Res 24:23453–23470. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0209-6
Kuenzer C, Stracher GB (2012) Geomorphology of coal seam fires. Geomorphology 138:209–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2011.09.004
Lai H, Zheng J, Zhang J, Zhang R, Cui L (2014) DEM analysis of “soil”-arching within geogrid-reinforced and unreinforced pile-supported embankments. Comput Geotech 61:13–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compgeo.2014.04.007
Lin M (1990) Thermal physics of rock and its engineering applications. Chongqing University Press, Beijing
Liu J (2018) High temperature and high pressure deformation experiment and ductile deformation mechanism of coal—A case study of bituminous coal from suxian mining area doctor, China University of Mining and Technology
MATLAB (2017) Curve Fitting Toolbox™ User's guide. MathWorks, Inc. https://www.mathworks.com/help/releases/R2017b/pdf_doc/curvefit/curvefit.pdf
Profession standard of the people's republic of china. Code for design of highway reinforced concrete and prestressed concrete bridges and culverts. JTG D62–2004. Beijing: China communications press 10–3
Profession recommended standard of the People's Republic of China. Guidelines for design and construction of highway engineering in the mined-out area. JTG/T D31–03 -2011 Beijing: China communications press, 21–6
Qiao S, Xu P, Teng J, Sun X (2020) Numerical study of optimal parameters on the high filling embankment landslide reinforced by the portal anti-slide pile. KSCE J Civil Eng. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-020-1743-1
Reisen F, Gillett R, Choi J, Fisher G, Torre P (2017) Characteristics of an open-cut coal mine fire pollution event. Atmos Environ 151:140–151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2016.12.015
Selvi P (2015) Fatigue and rutting strain analysis on lime stabilized subgrades to develop a pavement design chart. Transport Geotech 2:86–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trgeo.2014.11.001
Song Z, Kuenzer C (2014) Coal fires in China over the last decade: a comprehensive review. Int J Coal Geol 133:72–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coal.2014.09.004
Stracher GB (2004) Coal fires burning around the world: a global catastrophe. Int J Coal Geol 59:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coal.2004.01.001
Stracher GB, Taylor TP (2004) Coal fires burning out of control around the world: thermodynamic recipe for environmental catastrophe. Int J Coal Geol 59:7–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coal.2003.03.002
Sun Q, Lü C, Cao L, Li W, Geng J, Zhang W (2016) Thermal properties of sandstone after treatment at high temperature. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 85:60–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2016.03.006
Tong L, Liu L, Yu Q (2014) Highway construction across heavily mined ground and steep topography in southern China. Bull Eng Geol Env 73:43–60. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-013-0503-6
Wang Z, Luo Y, Tang S (2008) Mechanism and calculation method of rheological settlement of high-filled embankment. J Central South Univ Technol 15:381–385. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-008-0384-1
Wu JT, Ye X, Li J, Li GW (2019) Field and numerical studies on the performance of high embankment built on soft soil reinforced with PHC piles. Comput Geotech 107:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compgeo.2018.11.019
Xiao Y (2013) Study on the mechanical characteristics of CoaI-rock mass of coalfield fires with thermo-hydro-mechanical coupling for fissure seepage. Doctor, Xi`an University Of Science And Technology
Yu Z, Sherong H, Jichao P, Tongtong Z, Jin L (2016) Metamorphic products of coal combustion and its macroscopic models in North China. J China Coal Soc 41:1798–1805
Yu L, Li G, Su H, Jing H, Zhang T (2017) Experimental study on static and dynamic mechanical properties of anthracite after high temperature heating Chinese. J Rock Mech Eng 36:2712–2719
Zhang L, Mao X, Lu A (2009) Experimental study on the mechanical properties of rocks at high temperature. Sci China Ser E: Technol Sci 52:641–646. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-009-0063-y
Zhao M, Guo W, Chen L, Wang S (2019) Experiment on the frost resistance of modified phospho gypsum: a case used to improve baozhong railway subgrade loess. J Mount Sci 16:2920–2930. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-018-5014-2
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, CHD (Grant No. 300102219208), the Traffic Construction Research Funds of Shaanxi Province (Grant Nos. 2017-1-4, 2018-1-3), the Science and Technology Program of Transportation Department of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region (Grant No. 2014-09), and the Tianshan Cedar Plan of the Science and Technology Department of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region (Grant No. 2017XS13), Science and Technology Major Project of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region (Grant No. 2020A03003-7).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bao, W., Wang, H., Lai, H. et al. Numerical stability analysis of superhigh-fill subgrade underlying acute inclined mined-out area with underground coal fire. Environ Earth Sci 80, 88 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-020-09346-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-020-09346-z