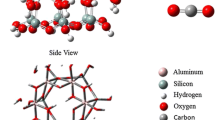
Abstract
Mineral aerosols play a significant role in gas–solid interfacial and atmospheric chemistry. Carbonation of olivine aerosol, which takes place in a multiphase reaction processes, can be an effective means to reduce the concentration of atmospheric carbon dioxide. Due to the presence of a huge reserve of silicate minerals in nature, olivine aerosol could be an ideal potential raw material for mineral carbonation for its higher reactivity with H2O and CO2. However, quantitative information about the carbonation process on the surface of natural olivine aerosol is not available. In this paper, calculations on the carbonation reaction processes with and without a H2O molecule using a periodic olivine model has been carried out via the density functional theory. The pathways and their corresponding energies and structures in the carbonation reactions have been established, and the effect of water as means to reduce the energy barriers and stabilize the carbonated structures by forming hydrogen bonds has been confirmed.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen JP, Parker SC, Price DW (2009) Atomistic simulation of the surface carbonation of calcium and magnesium oxide surfaces. J Phys Chem C 113:8320–8328
Andreas F, Reinhard Trettin HF (2013) DFT study on the effect of water on the carbonation of portlandite. Ind Eng Chem Res 52:2169–2173
Bian HS, Zender CS (2003) Mineral dust and global tropospheric chemistry: relative roles of photolysis and heterogeneous uptake. J Geophys Res Atmos 108:4672
Brodholt J (1997) Ab initio calculations on point defects in forsterite (Mg2SiO4) and implications for diffusion and creep. Am Mineral 82:1049–1053
Chen S, Navrotsky A (2009) Calorimetric study of the surface energy of forsterite. Am Mineral 95(1):112–117
Couling DJ, Das U, Green WH (2012) Analysis of hydroxide sorbents for CO2 capture from warm syngas. Ind Eng Chem Res 51(41):13473–13481
Dana ES (1941) A textbook of mineralogy. Wiley, New York
Delley B (2000) From molecules to solids with the DMol3 approach. J Chem Phys 113(18):7756–7764
Fricker KJ, Park A-HA (2013) Effect of H2O on Mg(OH)2 carbonation pathways for combined CO2 capture and storage. Chem Eng Sci 100:332–341
Gunter WD, Perkins EH, McCann TJ (1993) Aquifer disposal of CO2-rich gases: reaction design for added capacity. Energy Convers Manag 34(9–11):941–948
IPCC (2005) Ab initio calculations on point defects in forsterite (Mg2SiO4) and implications for diffusion and creep. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Kudoh Y, Takeuchi Y (1985) The crystal structure of forsterite Mg2SiO4 under high pressure up to 149kpa. Z Kristallogr 171:291–302
Kwon S, Fan M, Dacosta HFM, Russell AG, Tsouris C (2011) Correction to “reaction kinetics of CO2 carbonation with Mg-rich minerals”. J Phys Chem A 115(26):7638–7644
Kwon S, Choi JI, Lee SG, Jang SS (2014) A density functional theory (DFT) study of CO2 adsorption on Mg-rich minerals by enhanced charge distribution. Comput Mater Sci 95:181–186
Lackner KS, Wendt CH, Butt DP, Joyce EL, Sharp DH (1995) Carbon dioxide disposal in carbonate minerals. Energy 20(11):1153–1170
Lin P-C, Huang C-W, Hsiao C-T, Teng H (2008) Magnesium hydroxide extracted from a magnesium-rich mineral for CO2 Sequestration in a gas–solid system. Environ Sci Technol 42(8):2748–2752
Mikkelsen M, Jorgensen M, Krebs FC (2010) The teraton challenge. A review of fixation and transformation of carbon dioxide. Energy Environ Sci 3(1):43–81
Mohammad SA, Gasem KAM (2012) Modeling the competitive adsorption of CO2 and water at high pressures on wet coals. Energy Fuels 26(1):557–568
Pan SY, Chang EE, Chiang PC (2012) CO2 capture by accelerated carbonation of alkaline wastes: a review on its principles and applications. Aerosol Air Qual Res 12(5):770–791
Perdew JP, Burke K, Ernzerhof M (1998) Perdew, burke, and ernzerhof reply. Phys Rev Lett 80(4):891
Prigiobbe V, Suarez Negreira A, Wilcox J (2013) Interaction between olivine and water based on density functional theory calculations. J Phys Chem C 117(41):21203–21216
Shih SM, Ho CS, Song YS, Lin JP (1999) Kinetics of the reaction of Ca(OH)2 with CO2 at low temperature. Ind Eng Chem Res 38(4):1316–1322
Smyth JR, Hazen RMA (1973) The crystal structure and hortonolite at several temperature up to 900 °C. Am Mineral 58:588–593
Xie HP (2010a) CO2 storage and climate change. Sci Technol Rev 28(18):3 (in Chinese)
Xie HP (2010b) Developing low-carbon technology and promoting green economy. Energy of China 32(9):5–10 (in Chinese)
Xie HP, Liu H, Wu G (2012a) Simultaneous recovery of national resources and mineralization of CO2: a new CCU method. Energy of China 34(10):15–18 (in Chinese)
Xie HP, Xie LZ, Wang YF, Zhu JH, Liang B, Ju Y (2012b) CCU: a more feasible and economic strategy than CCS for reducing CO(2) emissions. J Sichuan Univ Eng Sci Ed 44(4):1–5
Xie HP, Wang YF, Ju Y, Liang B, Zhu JH, Zhang R, Xie LZ, Liu T, Zhou XG, Zeng HM (2013) Simultaneous mineralization of CO2 and recovery of soluble potassium using earth-abundant potassium feldspar. Chin Sci Bull 58(1):128–132
Xie HP, Wang YF, Chu W, Ju Y (2014a) Mineralization of flue gas CO2 with coproduction of valuable magnesium carbonate by means of magnesium chloride. Chin Sci Bull 59(23):2882–2889
Xie HP, Wang YF, He Y, Gou ML, Liu T, Wang JL, Tang L, Jiang W, Zhang R, Xie LZ (2014b) Generation of electricity from CO2 mineralization: principle and realization. Sci China Technol Sci 57(12):2335–2343
Xie H, Jiang W, Wang Y, Liu T, Wang R, Liang B, He Y, Wang J, Tang L, Chen J (2015a) Thermodynamics study on the generation of electricity via CO2-mineralization cell. Environ Earth Sci 74(8):6481–6488
Xie HP, Jiang W, Xue Y, Hou ZM, Wang Y, Wu DL, Liu T, Wang JL, Tang L (2015b) Effect of water on carbonation of mineral aerosol surface models of kaolinite: a density functional theory study. Environ Earth Sci 73(11):7053–7060
Xie H, Tang L, Wang Y, Liu T, Hou Z, Wang J, Wang T, Jiang W, Were P (2016) Feedstocks study on CO2. Environ Earth Sci 75(7):1–9
Yang HQ, Xu ZH, Fan MH, Gupta R, Slimane RB, Bland AE, Wright I (2008) Progress in carbon dioxide separation and capture: a review. J Environ Sci 20(1):14–27
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (Programs Nos. 21573153, 51254002, and 21336004) and the National Basic Research Program of China (No. 2013BAC12B03).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xie, H., Jiang, W., Hou, Z. et al. DFT study of the carbonation on mineral aerosol surface models of olivine: effect of water. Environ Earth Sci 76, 732 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-017-6988-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-017-6988-8