Abstract
Miocene volcanism was active in the city area of İzmir, Turkey, where volcanic deposits formed predominantly made of gray and pinkish colored andesite. These rocks have been widely used in the construction of many buildings in the region. In the northern part of Izmir, known as the Buca region, there is an area where andesite presents green color. The occurrence of the green andesite is rather rare, and historically this rock type has been used in the construction of ancient valuable architectonic structures including aqueducts, historical buildings, and mosques. Some of these structures date back to the beginning of the first century AD when the region was under the control of the Roman Empire. Interestingly, the recent survey of these structures showed that after all of these years, the green andesite still appears pretty much well preserved, only showing slight deterioration in the form of limited crumbling. Although these rocks were used in this particular region in the past, their material properties have not been investigated so far. The purpose of this study was therefore to identify mineralogical, chemical, physical, and mechanical properties of these rocks, which eventually determine their durability. The first phase of the research focused on detailed site investigation, which resulted in the definition of the geological extent of the green andesite and the identification of two historical quarries, from one of which representative samples was collected for laboratory investigation, which was the main task of the second phase of the research. The main cause for the green color of the andesite resulted the presence of celadonite, which is also accompanied by cristobalite. The presence of cristobalite in the pores as a secondary mineral appears to have contributed to the increased strength and durability of Buca andesite. Laboratory evaluation of the durability was in general agreement with field observations, although some test gave ambiguous results. This discrepancy revealed some weakness of laboratory tests to precisely assess durability of building stones.





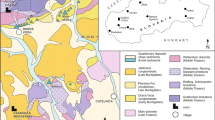
(modified after Uzel et al. 2012)

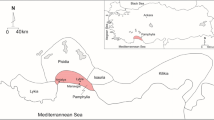
(modified after Kıncal 2004)





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrews AJ (1980) Saponite and celadonite in Layer 2 basalts, DSDP Leg 37. Contrib Miner Petrol 73:323–340
Anon (1979) Classification of rocks and soils for engineering geological mapping. Part 1. Rock and soil materials. Bull Int Assoc Eng Geol 19:364–371
ASTM 4404 (1984) Standard test method for determining the pore volume and volume distribution of soil and rock by mercury intrusion porosimetr. Annual Book of ASTM Standards. pp 744–748
ASTM C88 (1990). Standard test method for soundness of aggregates by the use of sodium sulfate or magnesium sulfate. Annual book of ASTM standards. American Society for Testing and Material pp 37–41
ASTM C 1113-90 (1990) Test method for thermal conductivity of refractories by hot wire, Platinum Resistance Thermometer Technique
Baker LL, Rember W, Sprenke KF, Strawn DG (2012) Celadonite in continental flood basalts of the Columbia River Basalt Group. Am Mineral 97:1284–1290
Bell FG (1980) Engineering Geology and Geotechnics. Butter Worth and Co., Ltd., London
Bell FG (1993) Engineering Geology. Blackwell Scientific Publica-tions, London
Benavente D, Garcia del Cura MA, Fort R, Ordonez S (2004) Durability estimation of porous building stones from pore structure and strength. Eng Geol 74:113–127
Bieniavski ZT (1975) Rock mass classification in rock engineering. In: Proceedings of the symposium exploration for rock engineering, Johannesburg. pp 97–106
Borsi S, Ferrara G, Innocenti F, Mazzuoli R (1972) Geochronology and petrology of recent volcanics in the eastern Aegean sea (west Anatolia and Lesbos Island). Bull Volc 36:473–496
Calcaterra D, Cappelletti P, Langella A, Colella A, Gennaro M (2004) The ornamental stones of Caserta province: the Campanian Ignimbrite in the medieval architecture of Casertavecchia. J Cult Herit 5(2):137–148
Dere DU, Miller RP (1966) Engineering classification and index properties for intact rock. Report AFWL-TR-65-116. Air Force Weapons Laboratory (WLDC) Kirtland Air Force Base, New Mexico
Drahor MG, Berge MA (2006) Geophysical investigations of the Seferihisar geothermal area, Western Anatolia, Turkey. Geothermics 35:302–320
Ercan T, Satır M, Steinitz G, Dora A. Sarıfakıoğlu, E, Walter HJ, Yıldırım T (1996) Biga Yarımadası ile Gökceada, Bozcaada ve Tavşan adalarındakı (KB Anadolu) Tersiyer volkanizmasının özellikleri (Characteristics of the Tertiary volcanics in Biga Peninsula, Gökceada, Bozcaada and Tavşan islands–NW Anatolia). Mineral Research and Exploration Institute of Turkey (MTA) Bulletin (in Turkish with English Abstract) 117: 55–86
Fitzner B, Snethlage R (1982) Über Zuzammenhange zwischen Salzcristallisationsdruck und Porenradienverteilung. GP News Lett 3:13–24
Fookes PG, Gourley CS, Ohikere C (1988) Rock weathering in engineering time. Q J Eng Geol 21:33–57
Gallahan WE, Duncan RA (1994) Spatial and temporal variability in crystallization of celadonites within the Troodos ophiolite, Cyprus: implications for low-temperature alteration of the oceanic crust. J Geophys Res 99:3147–3161
Genç SC, Altunkaynak Ş, Karacık Z, Yılmaz Y (2001) The Çubukludağ Graben, Karaburun Peninsula: its tectonic significance in the Neogene geological evolution of the western Anatolia. Geodin Acta 14:45–55
Gibbs RS (1965) Error due to segregation in quantitative clay mineral X-ray diffraction mounting techniques. Am Mineral 50:741–751
Gibbs RS (1968) Clay mineral mounting techniques for Xray diffraction analysis. A discussion. J Sediment Petrol 38:242–244
Hall K, Thorn C, Sumner P (2012) On the persistence of ‘weathering’. Geomorphology 149–150:1–10
ISRM (2007) In: Ulusay R, Hudson JA editors. The complete ISRM suggested methods for rock characterization, testing and monitoring: 1974–2006. Compilation arranged by the ISRM Turkish national group. International Society for Rock Mechanics, Ankara
Jamshidi A, Reza-Nikudel M, Nikudel Khamehchiyan M (2013) Predicting the long-term durability of building stones against freeze–thaw using a decay function model. Cold Reg Sci Tech 92:29–36
Jefferson DP (1993) Building stone: the geological dimension. Q J Eng Geo 26:305–319
Kaputoğlu S (2013) Buca yeşil andezitlerinin jeolojisi malzeme ve durabilite özelliklerinin araştırılması. Unpublished, Ms Thesis, D.E.U. Graduate School of Natural and Applied Sciences, Izmir, Turkey (in Turkish with English abstract)
Karaca Z, Deliormanlı AH, Elçi H, Pamukcu C (2010) Effect on freeze-thaw process on the abrasion loss value of stones. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 47(7):1027–1111
Kieslinger A (1931) Das Volumen des Eises. Geol Bauwesen 2:199–207
Kıncal C (2004) İzmir iç körfezi çevresinde yer alan birimlerin coğrafi bilgi sistemleri ve uzaktan algılama teknikleri kullanılarak mühendislik jeolojisi açısından değerlendirilmesi. Unpublished, PhD Thesis, D.E.U. Graduate School of Natural and Applied Sciences, Izmir, Turkey (in Turkish with English abstract)
Knöfel DK, Hoffman D, Snethlage R (1987) Physico-chemical weathering reactions as a formulary for time-lapsing ageing tests. Mater Struct 20:127–145
Koca MY (1995) Slope stability assessments of the abandoned andesite quarries in and around the İzmir city center. Unpublished, PhD Thesis, D.E.U. Graduate School of Natural and Applied Sciences, Izmir, Turkey
Koca Y, Kıncal C (2015) The relationships between the rock material properties and weathering grades of andesitic rocks around Izmir, Turkey. Bull Eng Geol Env. doi:10.1007/s10064-015-0813-y
Korkanç M (2013) Deterioration of different stones used in historical buildings within Nigde province, Cappadocia. Constr Build Mater 48:789–803
Le Maitre RW, Bateman P, Dudek A, Keller J, Lameyre J, Le Bas MJ, Sabine PA, Schmid R, Sorensen H, Streckeisen A, Woolley AR, Zanettin B (1989) A classification of igneous rocks and glossary of terms: recommendations of the international union of geological sciences subcommission on the systematics of igneous rocks. Blackwell Scientific Publications, Oxford
Lista-Friere DM, Fart R, Varas-Muriel MJ (2015) Freeze-Thaw fracturing in building granites. Cold Reg Sci Tech 113:40–51
Luquer LM (1985) The relative effects of frost and the sulfate of soda efflorescence tests on building stones. Trans Am Soc Civ Eng 33:235–256
Odin GS, Desprairies A, Fullagar PD, Bellon H, Decarreau A, Frohlish F, Zelvelder M (1988) Nature and geological significance of celadonite. In: Odin GS (ed) Developments in Sedimentology. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 337–398
Odom IE (1984) Glauconite and celadonite minerals. Rev Mineral 13:545–572
Olier C (1984) Weathering. Longman, Singapore, p 267
Ordonez S, Fort R, Garcia del Cura MA (1997) Pore size distribution and the durability of a porous limestone. Q J Eng Geol 30:221–230
Özgenç İ (1978) Cumaovası (İzmir) asit volkanitlerde saptanan iki ekstrüzyon aşaması arasındaki göreceli yaş ilişkisi (Relative age relationships between two extrusion phases of Cumaovası acidic volcanics (İzmir)). Geol Soc Turk Bull (in Turkish with English abstract) 21:31–34
Punuru AR, Chowdhury AN, Kulshreshtha NP, Gauri KL (1990) Control of porosity on durability of limestone at the Great Sphinx. Egypt. Envir Geol Water Sci 15:225–232
RILEM (1980) Recommended tests to measure the deterioration of stone and to assess the effectiveness of treatment methods. Commission 25-PEM. Mater Struct 3:175–253
Rivas-Brea T, Prieto Lamas B, Silva Hermo B (2008) Ensayos de alteración artificial aplicados a rocas graníticas. Mater Constr 58(289–290):179–189
Rossi-Dora PR (1985) Laboratory tests on artistic stonework. The deterioration and conservation of stone. Stud Doc Cult Herit 16:235–242
Rossi-Manaresi R (1976) Causes of decay and conservation treatments of the tuff of Castel dell’Ovo in Naples. In: Procceedings for the 2nd international symposium on the deterioration of building stones, Athens, pp 233–248
Ruedrich J, Kirchner D, Siegesmund S (2011) Physical weathering of building stones induced by freeze–thaw action: a laboratory long-term study. Environ Earth Sci 63:1573–1586
Savaşcın Y (1978) Foça-Urla Neojen Volkanitlerinin Mineralojik ve Jeokimyasal İncelenmesi ve Kökensel Yorumu (Mineralogical and Geochemical Investigation of Foça-Urla Neogene Volcanics and Their Origin). PhD Thesis (in Turkish with English abstract)
Seghedi L, Helvacı C, Pecskay Z (2014) Composite volcanoes in the south-eastern part of İzmir-Balıkesir Transfer Zone, Western Anatolia, Turkey. J Vol Geot Res 291:75
Siegesmund S, Snethlage R (2014) Stone in architecture. Springer, Berlin. ISBN 978-3-642-45154-6
Sims I (1991) Quality and durability of stone for construction. Q J Eng Geol 24:67–73
Stück H, Siegesmund S, Rüdrich J (2011) Weathering behavior and construction suitability of dimension stones from the Drei Gleichen area (Thuringia, Germany). Env Geol 63:1763–1786
Takarli M, Prince W, Siddique R (2008) Damage in granite under heating/cooling cycles and water freeze–thaw condition. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 45:1164–1175
Topal T, Doyuran V (1997a) Analyses of deterioration of the Cappadocian tuff, Turkey. Environ Geol 34:5–20
Topal T, Doyuran V (1997b) Engineering geological properties and durability assessment of the Cappadocian tuff. Eng Geol 47:175–187
Topal T, Doyuran V (1998) Analyses of deterioration of the Cappadocian tuff. Turkey. Environ Geol 34(1):5–20
Topal T, Kaya Y (2016) Assessment of deterioration and collapse mechanisms of dolomitic limestone at Hasankeyf Antique City before and after reservoir impounding (Turkey). Env Earth Sci 75:131. doi:10.1007/s12665-015-5062-7
Topal T, Sözen B (2003) Deterioration mechanism of tuffs in Midas monument. Eng Geol 68:201–233
Török A, Forgo LZ, Vogt T, Löbens S, Siegmund S, Weiss T (2007) The influence of lithology and pore size distribution on the durability of acid volcanic tuffs, Hungary. Building Stone from Diagnosis to Conservation. Geol. Soc., Special Publication, pp 251–259
TS EN 1097-1 (2000) Agregaların mekanik ve fiziksel özellikleri için deney Bölüm:1 Aşınmaya karşı direncin tayini (Micro-Deval). (Mechanical and physical properties of aggregates. Part.1 Determination of abrasion resistance of aggregates with Micro-Deval method) Ankara: Türk Standartları Enstitüsü (in Turkish), p 36
TS EN 1097-2 (2000) Agregaların mekanik ve fiziksel özellikleri için deneyler Bölüm:3 Parçalanma direncinin tayini için metodlar. (Mechanical and physical properties of aggregates. Part.2 Determination of abrasion resistance of aggregates with Los Angeles method) Ankara: Türk Standartları Enstitüsü (in Turkish), p 36
TS EN 12370 (2001) Doğal Taşlar-Deney Metodları-Tuz Kristallenmesi Direncinin Tayini (Natural stone test methods—determination of resistance to salt cystallization). Ankara; Türk Standartları Enstitüsü (in Turkish), p 3
TS EN 14157 (2005) Doğal taş-Aşınma direncinin tayini (Natural stone—Determination of the abrasion resistance). Ankara: Türk Standartları Enstitüsü (in Turkish), p 21
TS 699 (2009) Doğal Yapı Taşları-İnceleme ve Laboratuar Deney Metodları (Natural building Stones—methods of inspection and laboratory testing). Ankara: Türk Standartları Enstitüsü; (in Turkish), p 36
Tuğrul A (2004) The effect of weathering on pore geometry and compressive strength of selected rock types from Turkey. Eng Geol 75:215–227
Uzel B, Sözbilir H, Özkaymak Ç (2012) Neotectonic evolution of an actively growing superimposed Basin in Western Anatolia: the Inner Bay of İzmir, Turkey. Turk J Earth Sci 21:446–447
Velde B (2003) Green clay minerals. In: MacKenzie FT (ed) Sediments, Diagenesis and Sedimentary Rocks. Pergamon, Oxford, pp 309–324
Weaver CE (1989) Clays, muds and shales. Elsevier Science Publishers, Amsterdam, p 819
Whitney DL, Evans BW (2010) Abbreviations for names of rock-forming minerals. Am Mineral 95:185–187
Yavuz AB (2006) Deterioration of the volcanic kerb and pavement stones in a humid environment in the city centre of Izmir, Turkey. Environ Geol 51:211–227
Yavuz AB (2012) Durability assessment of the Alaçatı tuff (Izmir) in western Turkey. Environ Earth Sci 67(7):1909–1925
Yavuz AB, Topal T (2007) Thermal and salt crystallization effects on the marble deterioration: examples from Western Anatolia, Turkey. Eng Geol 80:30–40
Yavuz AB, Topal T (2016) Effects of different drying temperatures on the physical and mechanical properties of some marbles (Muğla, Turkey) during salt crystallization tests. Environ Earth Sci 75:982
Yu S, Oguchi TC (2010) Role of pore size distribution in salt uptake damage and predicting salt susceptibility of eight types of Japanese building stones. Eng Geol 115:226–236
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yavuz, A.B., Kaputoglu, S.A., Çolak, M. et al. Durability assessments of rare green andesites widely used as building stones in Buca (Izmir), Turkey. Environ Earth Sci 76, 211 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-017-6531-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-017-6531-y