Abstract
Aim
To compare treatment outcome of arthroplasty followed by distraction osteogenesis (AFD) and distraction osteogenesis followed by arthroplasty (DFA) in the management of mandibular deficiencies in temporomandibular joint (TMJ) ankylosis.
Materials and methods
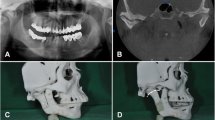
A total of 20 patients with TMJ Ankylosis were included in the study. Patients were randomly divided into two groups. Group 1 consisted of patients for whom arthroplasty was done prior to distraction osteogenesis (AFD) for the correction of deficient mandible. Group 2 included patients where distraction osteogenesis was performed prior to arthroplasty (DFA). The treatment outcome was assessed based on maximum interincisal distance, overjet, corpus length, ramus height, upper airway, lower airway, duration of the procedure and the complications for the treatment at the end of 3, 6 and 12 months.
Results
After the treatment was ended, the patients of both groups had increase in mouth opening and appearance was improved remarkably. There was general increase in all the parameters in both the groups. But at the end of 12 months, airway and the ramus height were more stable and the control of the proximal segment was superior in DFA group. Open bite was noticed in 2 cases of AFD group which was treated by elastics. There required additional surgery for the removal of distractors in the AFD Group. Establishing the airway during the surgery was easier in AFD group.
Conclusion
The study concludes that distraction followed by arthroplasty was a better procedure for the management of TMJ ankylosis owing to its stable results and less number of surgeries.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Giraddi GB, Arora K, Sai Anusha AJ (2016) Distraction in the treatment of temporomandibular joint ankylosis with mandibular micrognathia. AnnMaxillofac Surg 6:68–74
Katsnelson A, Markiewicz MR, Keith DA, Dodson TB (2012) Operative management of temporomandibular joint ankylosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 70(3):531–536. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joms.2011.10.003Epub 2011 Dec 30
Loveless TP, Bjornland T, Dodson TB, Keith DA (2010) Efficacy of temporomandibular joint ankylosis surgical treatment. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 68(6):1276–1282. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joms.2009.10.014Epub 2010 Mar 20
Feiyun P, Wei L, Jun C, Xin X, Zhuojin S, Fengguo Y (2010) Simultaneous correction of bilateral temporomandibular joint ankylosis with mandibular micrognathia using internal distraction osteogenesis and 3-dimensional craniomaxillofacial models. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 68(3):571–577. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joms.2009.07.022Epub 2009 Dec 2
Kaban LB, Bouchard C, Troulis MJ (2009) A protocol for management of temporomandibular joint ankylosis in children. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 67(9):1966–1978. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joms.2009.03.071
Burston CJ, James RB et al (1978) Cephalometrics for orthognathic surgery. J Oral Surg. 36(4):269–277
Brian P, Judith D et al (2004) Cephalometric evaluation and measurement of the upper airway. SeminOrthod 10(1):3–15
Bansal V, Singh S, Garg N, Dubey P (2014) Transport distraction osteogenesis as a method of reconstruction of the temporomandibular joint following gap arthroplasty for post-traumatic ankylosis in children: a clinical and radiological prospective assessment of outcome. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 43:227–236
Hegab AF et al (2015) Outcome of surgical protocol for the treatment of temporomandibular joint ankylosis based on the pathogenesis of ankylosis and re-ankylosis. A prospective clinical study of 14 patients. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 73:2300–2311
Lopez EN, Dogliotti PL (2004) Treatment of temporomandibular joint ankylosis in children: Is it necessary to perform mandibular distraction simultaneously? J CraniofacSurg 15:879–884
Kwon TG, Park HS, Kim JB, Shin HI (2006) Staged surgical treatment for temporomandibular joint ankylosis: intraoral distraction after temporalis muscle flap reconstruction. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 64:1680–1683
Sadakah AA, Elgazzar RF, Abdelhady AI (2006) Intraoral distraction osteogenesis for the correction of facial deformities following temporomandibular joint ankylosis: a modified technique. Int J Oral MaxillofacSurg 35:399–406
Shang H, Xue Y, Liu Y, Zhao J, He L (2012) Modified internal mandibular distraction osteogenesis in the treatment of micrognathia secondary to temporomandibular joint ankylosis: 4-year follow-up of a case. J CraniomaxillofacSurg 40:373–378
Zhu S, Wang D, Yin Q, Hu J (2013) Treatment guidelines for temporomandibular joint ankylosis with secondary dentofacial deformities in adults. J CraniomaxillofacSurg 41:117–127
Shirani G, Arshad M, Mahmoudi X (2018) A new method of treatment of temporomandibular joint ankylosis with osteodistraction using the Sh-device: a case report. J Dent (Tehran) 15(1):63–68
Neelam NA, Kanchan RR (2009) Management of patients with obstructive sleep apnoea induced by temporomandibular joint ankylosis: a novel 2-stage surgical protocol and report of 5 cases. Asian J Oral Maxillofac Surg 21:27–32
Andrade NN, Kalra R, Shetye SP (2012) New protocol to prevent TMJ reankylosis and potentially life-threatening complications in triad patients. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 41(12):1495–1500. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijom.2012.06.012Epub 2012 Jul 21
Neelam NA, Paul M, Sriram G, Neha A, Kamil R, Trupti N (2018) Pre-arthroplastic mandibular distraction osteogenesis for the correction of OSA in TMJ ankylosis: a prospective observational study of 25 cases. OralMaxillofac Surg 22(4):409–418
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Dr. G Harsha, Dr. Aditya Mohan Alwala, Dr. Ramesh K, Dr. Srilatha Tunkimetla, Dr. Rathod Prakash, and Dr. Zainuddinelyaskhan Y declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Ethical Clearance
Obtained from Institutional Ethical Committee.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gorrela, H., Alwala, A.M., Ramesh, K. et al. Arthroplasty Followed by Distraction Osteogenesis Versus Distraction Osteogenesis Followed by Arthroplasty in the Management of TMJ Ankylosis: A Comparative Study. J. Maxillofac. Oral Surg. 20, 674–679 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12663-020-01463-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12663-020-01463-3