Abstract
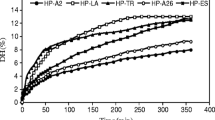
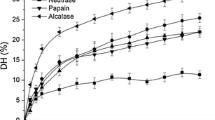
The present study reports the surface and antioxidant properties, as well as the angiotensin-I converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory activity of protein hydrolysates (HHPHs) from European hake (Merluccius merluccius) heads and obtained with Savinase®. Hake heads protein hydrolysates contained high protein content between 84.75 and 87.92% and a high percentage of essential amino acids. They have a high nutritional value and could be used as supplement in poorly balanced dietary proteins. All protein hydrolysates possessed interesting surface properties, which were governed by their concentrations Hake heads protein hydrolysates displayed a high ACE inhibitory activity. The IC50 values recorded for the ACE inhibitory activity of all HHPHs varied between 0.24 and 1.4 mg/mL. Therefore, HHPHs can be used as a promising source of functional peptides with good surface and biological properties.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sila, A., Bougatef, A.: Antioxidant peptides from marine by-products: isolation, identification and application in food systems. A review. J. Funct. Foods 21, 10–26 (2016)
Sila, A., Nedjar-Arroume, N., Hedhili, K., Chataigné, G., Balti, R., Nasri, M., Dhulster, P., Bougatef, A.: Antibacterial peptides from barbel muscle protein hydrolysates: Activity against some pathogenic bacteria. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 55, 183–188 (2014a)
Zhao, Y., Li, B., Dong, S., Liu, Z., Zhao, X., Wang, J., Zeng, M.: A novel ACE inhibitory peptide isolated from Acaudina molpadioidea hydrolysate. Peptides 30, 1028–1033 (2009)
Lahl, W.J., Braun, S.D.: Enzymatic production of protein hydrolysates for food use. Food Technol. 48, 68–71 (1994)
Bougatef, A., Balti, R., Haddar, A., Jellouli, K., Souissi, N., Nasri, M.: Protein hydrolysates from bluefin tuna (Thunnus thynnus) heads as influenced by the extent of enzymatic hydrolysis. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 17, 841–852 (2012)
Balti, R., Bougatef, A., Sila, A., Guillochon, D., Dhulster, P., Nedjar-Arroume, N.: Nine novel angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptides from cuttlefish (Sepia officinalis) muscle protein hydrolysates and antihypertensive effect of the potent active peptide in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Food Chem. 170, 519–525 (2015)
Sayari, N., Sila, A., Haddar, A., Balti, R., Ellouz-Chaabouni, S., Bougatef, A.: Valorisation of smooth hound (Mustelus mustelus) waste biomass through recovery of functional, antioxidative and antihypertensive bioactive peptides. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 23, 366–376 (2016)
FAO.: The state of world fisheries and aquaculture 2016, The FAO Fisheries and Aquaculture Department, Rome (2016)
DGPA.: Directorate-general for fisheries and aquaculture, Ministry of Agriculture, Water Ressources and Fisherie, Tunisia, (2015)
Khoufi, W., Elleboode, R., Jaziri, H., El Fehri, S., Bellamy, E., Meriem, Ben, Romdhane, S., Mahé, M.S.: K.: Growth of hake juveniles (Merluccius merluccius) from the Northern coast of Tunisia, determined from otolith microstructure. Bull. Soc. Zool. Fr. 37, 245–256 (2012)
Adler-Nissen, J.: A review of food hydrolysis specific area. In: Enzymatic hydrolysis of food proteins, pp. 57–109. Elsevier, Copenhagen (1986)
AOAC.: Official methods of analysis. (17th edn.). Association of Official Analytical, Gaithersburg (2000)
Lin, M.H.Y., Humbert, E.S., Sosulki, F.W.: Certain functional properties of sunflower meal products. J. Food Sci. 39, 368–370 (1974)
Shahidi, F., Han, X.Q., Synowiecki, J.: Production and characteristics of protein hydrolysates from capelin (Mallotus villosus). Food Chem. 53, 285–293 (1995)
Pearce, K.N., Kinsella, J.E.: Emulsifying properties of proteins: evaluation of a turbidimetric technique. J. Agric. Food Chem. 26, 716–723 (1978)
Bersuder, P., Hole, M., Smith, G.: Antioxidants from a heated histidine glucose model system. I: Investigation of the antioxidant role of histidine and isolation of antioxidants by high performance liquid chromatography. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 75, 181–187 (1998)
Koleva, I.I., Van Beek, T.A., Linssen, J.P.H., de Groot, A., Evstatieva, L.N.: Screening of plant extracts for antioxidant activity: a comparative study on three testing methods. Phytochem. Anal. 13, 8–17 (2002)
Yildirim, A., Mavi, A., Kara, A.A.: Determination of antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of Rumex crispus L. extracts. J. Agric. Food Chem. 49, 4083–4089 (2001)
Nakamura, Y., Yamamoto, N., Sakai, K., Okubo, A., Yamazaki, S., Takano, T.: Purification and characterization of angiotensin I-converting-enzyme inhibitors from sour milk. J. Dairy Sci. 78, 777–783 (1995)
Dathe, M., Schumann, M., Wieprecht, T., Winkler, A., Beyermann, M., Krause, E., Matsuzaki, K., Murase, O., Bienert, M.: Peptide helicity and membrane surface charge modulate the balance of electrostatic and hydrophobic interactions with lipid bilayers and biological membranes. BioChemistry 35, 12612–12620 (1996)
Kristinsson, H.G., Rasco, B.A.: Fish protein hydrolysates: production, biochemical and functional properties. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 40, 43–81 (2000)
Klomklao, S., Kishimura, H., Benjakul, S.: Use of viscera extract from hybrid catfish (Clarias macrocephalus × Clarias gariepinus) for the production of protein hydrolysate from toothed ponyfish (Gazza minuta) muscle. Food Chem. 136, 1006–1012 (2013)
Benjakul, S., Morrissey, M.T.: Protein hydrolysates from Pacific whiting solid wastes. J. Agric. Food Chem. 45, 3423–3430 (1997)
Usydus, Z., Szlinder-Richert, J., Adamczyk, M.: Protein quality and amino acid profiles of fish products available in Poland. Food Chem. 112, 139–145 (2009)
Nikoo, M., Benjakul, S., Rahmanifarah, K.: Hydrolysates from marine sources as cryoprotective substances in seafoods and seafood products. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 57, 40–51 (2016)
Shahidi, F., Ambigaipalan, P.: Novel functional food ingredients from Marine Sources. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2, 123–129 (2015)
Atef, M., Ojagh, S.M.: Health benefits and food applications of bioactive compounds from fish byproducts: a review. J. Funct. Foods 35, 673–681 (2017)
Chalamaiah, M., Dinesh-kumar, B., Hemalatha, R., Jyothirmayi, T.: Fish protein hydrolysates: proximate composition, amino acid composition, antioxidant activities and applications: a review. Food Chem. 135, 3020–3038 (2012)
Kim, S.K., Mendis, E.: Bioactive compounds from marine processing byproducts—a review. Food Res. Interface 39, 383–393 (2006)
Chi, Z., Liu, G.L., Lu, Y., Jiang, H., Chi, Z.M.: Bio-products produced by marine yeasts and their potential applications. Bioresour. Technol. 202, 244–252 (2016)
Sila, A., Sayari, N., Balti, R., Martinez-Alvarez, O., Nedjar-Arroume, N., Nasri, M., Bougatef, A.: Biochemical and antioxidant properties of peptidic fraction of carotenoproteins generated from shrimp by-products by enzymatic hydrolysis. Food Chem. 148, 445–452 (2014b)
Kong, X., Zhou, H., Qian, H.: Enzymatic preparation and functional properties of wheat gluten hydrolysates. Food Chem. 101, 615–620 (2007)
Jost, R., Monti, J.C., Pahud, J.J.: Partial enzymatic hydrolysis of whey protein by trypsin. J. Dairy Sci. 60, 1387–1393 (1977)
Fonkwe, L.G., Singh, R.K.: Protein recovery from mechanically deboned turkey residue by enzymic hydrolysis. Process Biochem. 31, 605–616 (1996)
Klompong, V., Benjakul, S., Kantachote, D., Shahidi, F.: Antioxidative activity and functional properties of protein hydrolysate of yellow stripe trevally (Selaroides leptolepis) as influenced by the degree of hydrolysis and enzyme type. Food Chem. 102, 1317–1327 (2007)
Faithong, N., Benzakul, S., Phatcharat, S., Binsan, W.: Chemical composition and antioxidative activity of Thai traditional fermented shrimp and krill products. Food Chem. 119, 133–140 (2010)
Kittiphattanabawon, P., Benjakul, S., Visessanguan, W., Shahidi, F.: Inhibition of angiotensin converting enzyme, human LDL cholesterol and DNA oxidation by hydrolysates from blacktip shark gelatin. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 51, 177–182 (2013)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Karoud, W., Sila, A., Krichen, F. et al. Characterization, Surface Properties and Biological Activities of Protein Hydrolysates Obtained from Hake (Merluccius merluccius) Heads. Waste Biomass Valor 10, 287–297 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-017-0069-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-017-0069-9