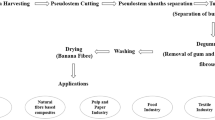
Abstract
Proteins are renewable resources rich in animals and plants and can be extracted from the agricultural and breeding industry byproducts and wastes. Collagen, keratin, zein and soy proteins are found in these byproducts and are extensively studied for protein-based hydrogels, which are especially attractive as a promising biomaterial due to their excellent biocompatibility, biodegradability, nontoxicity and low immune response. In recent years, hydrogels have been playing an increasingly important role in tissue engineering, drug delivery, nutrient encapsulation, controlled release of pesticides and other fields. The diversity of the amino acid composition of proteins leads to significant differences in their processing strategies, and the properties of the resultant hydrogels. This review covers the extraction methods for collagen, keratin, zein and soy proteins from various industrial byproducts, the synthesis of hydrogels from these protein sources, as well as their potential applications.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hoffman, A.S.: Hydrogels for biomedical applications. Adv. Drug Del. Rev. 54(1), 3–12 (2002)
Campoccia, D., Doherty, P., Radice, M., Brun, P., Abatangelo, G., Williams, D.F.: Semisynthetic resorbable materials from hyaluronan esterification. Biomaterials 19(23), 2101–2127 (1998)
Prestwich, G.D., Marecak, D.M., Marecek, J.F., Vercruysse, K.P., Ziebell, M.R.: Controlled chemical modification of hyaluronic acid: synthesis, applications, and biodegradation of hydrazide derivatives. J. Control. Release 53(1), 93–103 (1998)
Lee, K.Y., Mooney, D.J.: Hydrogels for tissue engineering. Chem. Rev. 101(7), 1869–1880 (2001)
Demitri, C., Del Sole, R., Scalera, F., Sannino, A., Vasapollo, G., Maffezzoli, A., Ambrosio, L., Nicolais, L.: Novel superabsorbent cellulose-based hydrogels crosslinked with citric acid. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 110(4), 2453–2460 (2008)
Yu, L., Yan, D., Sun, G., Gu, L.: Preparation and characterization of pH-sensitive hydrogel fibers based on hydrolyzed-polyacrylonitrile/soy protein. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 108(2), 1100–1108 (2008)
Anderson, T.J., Lamsal, B.P.: Development of new method for extraction of α-Zein from corn gluten meal using different solvents. Cereal Chem. 88(4), 356 (2011)
Zhong, Q., Tian, H., Zivanovic, S.: Encapsulation of fish oil in solid zein particles by liquid-liquid dispersion. J. Food Process. Preserv. 33(2), 255–270 (2009)
Kopeček, J.: Hydrogel biomaterials: a smart future? Biomaterials 28(34), 5185–5192 (2007)
Shi, W., Dumont, M.-J., Ly, E.B.: Synthesis and properties of canola protein-based superabsorbent hydrogels. Eur. Polym. J. 54, 172–180 (2014)
van Hest, J.C.: Protein-based materials, toward a new level of structural control. Chem. Commun. 19, 1897–1904 (2001)
Kaplan, D., McGrath, K.: Protein-Based Materials, pp. 133–177. Springer, Berlin (2012)
Ma, L., Yang, Y., Yao, J., Shao, Z., Huang, Y., Chen, X.: Selective chemical modification of soy protein for a tough and applicable plant protein-based material. J. Mater. Chem. B 3, 5241–5248 (2015)
Bai, X., Zheng, H., Fang, R., Wang, T., Hou, X., Li, Y., Chen, X., Tian, W.: Fabrication of engineered heart tissue grafts from alginate/collagen barium composite microbeads. Biomed. Mater. 6(4), 045002 (2011)
Pace, L.A., Plate, J.F., Mannava, S., Barnwell, J.C., Koman, L.A., Li, Z., Smith, T.L., Van Dyke, M.: A human hair keratin hydrogel scaffold enhances median nerve regeneration in nonhuman primates: an electrophysiological and histological study. Tissue Eng. pt. A 20(3–4), 507–517 (2014)
Vallejos, N., Gonzalez, G., Troncoso, E., Zuniga, R.N.: Acid and enzyme-aided collagen extraction from the byssus of chilean mussels (mytilus chilensis): effect of process parameters on extraction performance. Food Biophys. 9(4), 322–331 (2014)
Chien, K.B., Chung, E.J., Shah, R.N.: Investigation of soy protein hydrogels for biomedical applications: materials characterization, drug release, and biocompatibility. J. Biomater. Appl. 28(7), 1085–1096 (2014)
Wang, N., Lin, W., Mu, C.-D.: Progress in extraction and purification of collagen from animal skin. Leather Sci. Eng. 16(2), 42–47 (2006)
Walters, B.D., Stegemann, J.P.: Strategies for directing the structure and function of three-dimensional collagen biomaterials across length scales. Acta Biomater. 10(4), 1488–1501 (2014)
Liu, D., Wei, G., Li, T., Hu, J., Lu, N., Regenstein, J.M., Zhou, P.: Effects of alkaline pretreatments and acid extraction conditions on the acid-soluble collagen from grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella) skin. Food Chem. 172, 836–843 (2015)
Zhang, Y., Olsen, K., Grossi, A., Otte, J.: Effect of pretreatment on enzymatic hydrolysis of bovine collagen and formation of ACE-inhibitory peptides. Food Chem. 141(3), 2343–2354 (2013)
Bella, J., Eaton, M., Brodsky, B., Berman, H.M.: Crystal and molecular structure of a collagen-like peptide at 1.9 A resolution. Science 266(5182), 75–81 (1994)
Foegeding, E., Lanier, T., Hultin, H.: Characteristics of edible muscle tissues. Food Chem. 3(15), 902 (1996)
Gómez-Guillén, M., Giménez, B., López-Caballero, M.A., Montero, M.: Functional and bioactive properties of collagen and gelatin from alternative sources: a review. Food Hydrocolloid. 25(8), 1813–1827 (2011)
Meschia, M., Pifarotti, P., Bernasconi, F., Magatti, F., Riva, D., Kocjancic, E.: Porcine skin collagen implants to prevent anterior vaginal wall prolapse recurrence: a multicenter, randomized study. J. Urol. 177(1), 192–195 (2007)
Gómez-Estaca, J., Montero, P., Fernández-Martín, F., Gómez-Guillén, M.: Physico-chemical and film-forming properties of bovine-hide and tuna-skin gelatin: a comparative study. J. Food Eng. 90(4), 480–486 (2009)
Mori, H., Tone, Y., Shimizu, K., Zikihara, K., Tokutomi, S., Ida, T., Ihara, H., Hara, M.: Studies on fish scale collagen of Pacific saury (Cololabis saira). Mater. Sci. Eng., C 33(1), 174–181 (2013)
Yaxin, S., Huan, W.C.W.S.R.: Study on the preparation of collagen chelating calcium using shellfish. J. Chin. Inst. Food Sci. Technol. 5, 056 (2012)
Madry, H., Rey-Rico, A., Venkatesan, J.K., Johnstone, B., Cucchiarini, M.: Transforming growth factor beta- releasing scaffolds for cartilage tissue engineering. Tissue Eng. pt. B-Rev. 20(2), 106–125 (2014)
Auger, F., Rouabhia, M., Goulet, F., Berthod, F., Moulin, V., Germain, L.: Tissue-engineered human skin substitutes developed from collagen-populated hydrated gels: clinical and fundamental applications. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 36(6), 801–812 (1998)
Seliktar, D., Black, R.A., Vito, R.P., Nerem, R.M.: Dynamic mechanical conditioning of collagen-gel blood vessel constructs induces remodeling in vitro. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 28(4), 351–362 (2000)
Kaufmann, P., Heimrath, S., Kim, B., Mooney, D.: Highly porous polymer matrices as a three-dimensional culture system for hepatocytes. Cell Transplant. 6(5), 463–468 (1997)
Doillon, C.J., Drouin, R., Côte, M.F., Dallaire, N., Pageau, J.F., Laroche, G.: Chemical inactivators as sterilization agents for bovine collagen materials. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 37(2), 212–221 (1997)
Sanborn, T., Gibbs, H., Brinker, J., Knopf, W., Kosinksi, E., Roubin, G.: A multicenter randomized trial comparing a percutaneous collagen hemostasis device with conventional manual compression after diagnostic angiography and angioplasty. J. Invasive Cardiol. 11, 6B–13B (1999)
Dunn, M.W., Miyata, T., Rubin, A.L., Stenzel, K.H.: Collagen soft contact lens. U.S. Patent 4223984, Sep 23, 1980
Miyata, T.: Collagen contact lens. U.S. Patent 4264155, Apr 28, 1981
Chen, D.-C., Lai, Y.-L., Lee, S.-Y., Hung, S.-L., Chen, H.-L.: Osteoblastic response to collagen scaffolds varied in freezing temperature and glutaraldehyde crosslinking. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 80A(2), 399–409 (2007)
Sahiner, M., Alpaslan, D., Bitlisli, B.O.: Collagen-based hydrogel films as drug-delivery devices with antimicrobial properties. Polym. Bull. 71(11), 3017–3033 (2014)
Cheng, Y., Lu, J., Liu, S., Zhao, P., Lu, G., Chen, J.: The preparation, characterization and evaluation of regenerated cellulose/collagen composite hydrogel films. Carbohydr. Polym. 107, 57–64 (2014)
Zheng, W., Zhang, W., Jiang, X.: Biomimetic collagen nanofibrous materials for bone tissue engineering. Adv. Eng. Mater. 12(9), B451–B466 (2010)
Gómez-Guillén, M., Pérez-Mateos, M., Gómez-Estaca, J., López-Caballero, E., Giménez, B., Montero, P.: Fish gelatin: a renewable material for developing active biodegradable films. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 20(1), 3–16 (2009)
Cansu, Ü., Boran, G.: Optimization of a multi-step procedure for isolation of chicken bone collagen. Korean J. Food. Sci. Anim. 35(4), 431–440 (2015)
Chen, S., Ikoma, T., Ogawa, N., Migita, S., Kobayashi, H., Hanagata, N.: In vitro formation and thermal transition of novel hybrid fibrils from type I fish scale collagen and type I porcine collagen. Sci. Technol. Adv, Mat (2016)
Francis, G., Thomas, J.: Isolation and chemical characterization of collagen in bovine pulmonary tissues. Biochem. J. 145(2), 287–297 (1975)
Kittiphattanabawon, P., Benjakul, S., Visessanguan, W., Shahidi, F.: Isolation and properties of acid- and pepsin-soluble collagen from the skin of blacktip shark (Carcharhinus limbatus). Eur. Food Res. Technol. 230(3), 475–483 (2010)
Nalinanon, S., Benjakul, S., Visessanguan, W., Kishimura, H.: Use of pepsin for collagen extraction from the skin of bigeye snapper (Priacanthus tayenus). Food Chem. 104(2), 593–601 (2007)
Rajan, N., Habermehl, J., Coté, M.-F., Doillon, C.J., Mantovani, D.: Preparation of ready-to-use, storable and reconstituted type I collagen from rat tail tendon for tissue engineering applications. Nat. Protoc. 1(6), 2753–2758 (2006)
DeVictor, P., Allard, R., Perrier, E., Huc, A.: Unpigmented fish skin, particularly from flat fish, as a novel industrial source of collagen, extraction method, collagen and biomaterial thereby obtained. U.S. Patent 5420248, May 30, 1995
Antoine, E.E., Vlachos, P.P., Rylander, M.N.: Review of collagen i hydrogels for bioengineered tissue microenvironments: characterization of Mechanics, Structure, and Transport. Tissue Eng. pt. B-Rev. 20(6), 683–696 (2014)
Zhu, h., Zhang, h., Wang, S., Teng, X.: Preparation method of low molecular weight collagen peptide effervescent tablet.C.N. Patent 102888436, Jun 4, 2014
Wang, Y.: Method for extracting collagens from bovine achilles tendon.C.N. Patent 103468771, Jul 15, 2015
Candage, R., Jones, K., Luchette, F.A., Sinacore, J.M., Vandevender, D., Reed Ii, R.L.: Use of human acellular dermal matrix for hernia repair: Friend or foe? Surgery 144(4), 703–711 (2008)
Patton Jr., J.H., Berry, S., Kralovich, K.A.: Use of human acellular dermal matrix in complex and contaminated abdominal wall reconstructions. Am. J. Surg. 193(3), 360–363 (2007)
Livesey, S.A., Herndon, D.N., Hollyoak, M.A., Atkinson, Y.H., Nag, A.: Transplanted acellular allograft dermal matrix: potential as a template for the reconstruction of viable dermis. Transplantation 60(1), 1–9 (1995)
Takami, Y., Matsuda, T., Yoshitake, M., Hanumadass, M., Walter, R.: Dispase/detergent treated dermal matrix as a dermal substitute. Burns 22(3), 182–190 (1996)
Griffey, E.S., Livesey, S.A., Schiff, C.M., Boerboom, L.E.: Particulate acellular tissue matrix. U.S Patent 7358284, Apr 15, 2008
Barrows, T.H., MacIntyre, P., Washenik, K.J.: Hair follicle graft from tissue engineered skin. U.S. Patent 9023380, May 5, 2015
Fisher, J., Ingham, E.: Ultrasonic modification of soft tissue matrices. U.S. Patent 7754232, Jul 13, 2010
Gough, J.E., Scotchford, C.A., Downes, S.: Cytotoxicity of glutaraldehyde crosslinked collagen/poly(vinyl alcohol) films is by the mechanism of apoptosis. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 61(1), 121–130 (2002)
Weadock, K.S., Miller, E.J., Bellincampi, L.D., Zawadsky, J.P., Dunn, M.G.: Physical crosslinking of collagen fibers: comparison of ultraviolet irradiation and dehydrothermal treatment. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 29(11), 1373–1379 (1995)
Zhang, X., Zhang, Y., Chen, W., Xu, L., Wei, S., Zheng, Y., Zhai, M.: Biological behavior of fibroblast on contractile collagen hydrogel crosslinked by gamma-irradiation. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 102(8), 2669–2679 (2014)
Chandran, P.L., Paik, D.C., Holmes, J.W.: Structural mechanism for alteration of collagen gel mechanics by glutaraldehyde crosslinking. Connect. Tissue Res. 53(4), 285–297 (2012)
Bou-Akl, T., Banglmaier, R., Miller, R., VandeVord, P.: Effect of crosslinking on the mechanical properties of mineralized and non-mineralized collagen fibers. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 101A(9), 2507–2514 (2013)
Ahn, J.-I., Kuffova, L., Merrett, K., Mitra, D., Forrester, J.V., Li, F., Griffith, M.: Crosslinked collagen hydrogels as corneal implants: effects of sterically bulky vs. non-bulky carbodiimides as crosslinkers. Acta Biomater. 9(8), 7796–7805 (2013)
Sanami, M., Sweeney, I., Shtein, Z., Meirovich, S., Sorushanova, A., Mullen, A.M., Miraftab, M., Shoseyov, O., O’Dowd, C., Pandit, A., Zeugolis, D.I.: The influence of poly(ethylene glycol) ether tetrasuccinimidyl glutarate on the structural, physical, and biological properties of collagen fibers. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B 104B, 1–9 (2015)
Solorio, L., Zwolinski, C., Lund, A.W., Farrell, M.J., Stegemann, J.P.: Gelatin microspheres crosslinked with genipin for local delivery of growth factors. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 4(7), 514–523 (2010)
Zeugolis, D.I., Paul, R.G., Attenburrow, G.: The influence of a natural cross-linking agent (Myrica rubra) on the properties of extruded collagen fibres for tissue engineering applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C. Mater. Biol. Appl. 30(1), 190–195 (2010)
He, L., Mu, C., Shi, J., Zhang, Q., Shi, B., Lin, W.: Modification of collagen with a natural cross-linker, procyanidin. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 48(2), 354–359 (2011)
Albu, M., Ghica, M., Leca, M., Popa, L., Borlescu, C., Cremenescu, E., Giurginca, M., Trandafir, V.: Doxycycline delivery from collagen matrices crosslinked with tannic acid. Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 523(1), 97–105 (2010)
Usha, R., Ramasami, T.: Effect of crosslinking agents (basic chromium sulfate and formaldehyde) on the thermal and thermomechanical stability of rat tail tendon collagen fibre. Thermochim. Acta 356(1–2), 59–66 (2000)
Cai, W., Kwok, S.W., Taulane, J.P., Goodman, M.: Metal-assisted assembly and stabilization of collagen-like triple helices. JACS 126(46), 15030–15031 (2004)
Przybyla, D.E., Chmielewski, J.: Metal-triggered radial self-assembly of collagen peptide fibers. JACS 130(38), 12610–12611 (2008)
Pires, M.M., Przybyla, D.E., Chmielewski, J.: A metal-collagen peptide framework for three-dimensional cell culture. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 48(42), 7813–7817 (2009)
Xu, G., Wang, X., Deng, C., Teng, X., Suuronen, E.J., Shen, Z., Zhong, Z.: Injectable biodegradable hybrid hydrogels based on thiolated collagen and oligo(acryloyl carbonate)–poly(ethylene glycol)–oligo(acryloyl carbonate) copolymer for functional cardiac regeneration. Acta Biomater. 15, 55–64 (2015)
Barnes, A.L., Genever, P.G., Rimmer, S., Coles, M.C.: Collagen–Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) Hydrogels with Tunable Properties. Biomacromolecules 17(3), 723–734 (2016)
Mirazul Islam, M., Cėpla, V., He, C., Edin, J., Rakickas, T., Kobuch, K., Ruželė, Ž., Bruce Jackson, W., Rafat, M., Lohmann, C.P., Valiokas, R., Griffith, M.: Functional fabrication of recombinant human collagen–phosphorylcholine hydrogels for regenerative medicine applications. Acta Biomater. 12, 70–80 (2015)
Kim, J., Lin, B., Kim, S., Choi, B., Evseenko, D., Lee, M.: TGF-β1 conjugated chitosan collagen hydrogels induce chondrogenic differentiation of human synovium-derived stem cells. J. Biol. Eng. 9(1), 1 (2015)
Bendtsen, S.T., Wei, M.: Synthesis and characterization of a novel injectable alginate–collagen–hydroxyapatite hydrogel for bone tissue regeneration. J. Mater. Chem. 3(15), 3081–3090 (2015)
Yu, H.S., Jin, G.Z., Won, J.E., Wall, I., Kim, H.W.: Macrochanneled bioactive ceramic scaffolds in combination with collagen hydrogel: a new tool for bone tissue engineering. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A. 100(9), 2431–2440 (2012)
Alarcon, E.I., Udekwu, K.I., Noel, C.W., Gagnon, L.B.-P., Taylor, P.K., Vulesevic, B., Simpson, M.J., Gkotzis, S., Islam, M.M., Lee, C.-J.: Safety and efficacy of composite collagen–silver nanoparticle hydrogels as tissue engineering scaffolds. Nanoscale 7(44), 18789–18798 (2015)
Rouse, J.G., Van Dyke, M.E.: A review of keratin-based biomaterials for biomedical applications. Materials 3(2), 999–1014 (2010)
Shi, W., Dumont, M.-J.: Review: bio-based films from zein, keratin, pea, and rapeseed protein feedstocks. J. Mater. Sci. 49(5), 1915–1930 (2013)
Karthikeyan, R., Balaji, S., Sehgal, P.K.: Industrial applications of keratins—a review. J. Sci. Ind. Res. India. 66(9), 710–715 (2007)
Strnad, P., Usachov, V., Debes, C., Gräter, F., Parry, D.A., Omary, M.B.: Unique amino acid signatures that are evolutionarily conserved distinguish simple-type, epidermal and hair keratins. J. Cell Sci. 124(24), 4221–4232 (2011)
Lee, H., Noh, K., Lee, S.C., Kwon, I.-K., Han, D.-W., Lee, I.-S., Hwang, Y.-S.: Human hair keratin and its-based biomaterials for biomedical applications. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 11(4), 255–265 (2014)
Rad, Z.P., Tavanai, H., Moradi, A.: Production of feather keratin nanopowder through electrospraying. J. Aerosol Sci. 51, 49–56 (2012)
Dowling, L., Crewther, W., Parry, D.: Secondary structure of component 8c-1 of alpha-keratin. An analysis of the amino acid sequence. Biochem. J. 236, 705–712 (1986)
Wrześniewska-Tosik, K., Adamiec, J.: Biocomposites with a content of keratin from chicken feathers. Fibres Text. East. Eur. 15(1), 60 (2007)
Richter, J.R., de Guzman, R.C., Greengauz-Roberts, O.K., Van Dyke, M.: Structure–property relationships of meta-kerateine biomaterials derived from human hair. Acta Biomater. 8(1), 274–281 (2012)
Cardamone, J.M., de Tunick, M.H., Onwulata, C.K.: Keratin sponge/hydrogel: I. Fabrication and characterization. Text. Res. J. 83(7), 661–670 (2013)
Reichl, S.: Films based on human hair keratin as substrates for cell culture and tissue engineering. Biomaterials 30(36), 6854–6866 (2009)
Martelli, S.M., Laurindo, J.B.: Chicken feather keratin films plasticized with polyethylene glycol. Int. J. Polymer. Mater. 61(1), 17–29 (2012)
Remadnia, A., Dheilly, R., Laidoudi, B., Quéneudec, M.: Use of animal proteins as foaming agent in cementitious concrete composites manufactured with recycled PET aggregates. Constr. Build. Mater. 23(10), 3118–3123 (2009)
Wei, P.-B., Wang, H.-R.: Modification of feather keratin and its application in leather filling process. China Leather 3, 003 (2006)
Ozaki, Y., Takagi, Y., Mori, H., Hara, M.: Porous hydrogel of wool keratin prepared by a novel method: an extraction with guanidine/2-mercaptoethanol solution followed by a dialysis. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 42, 146–154 (2014)
Sierpinski, P., Garrett, J., Ma, J., Apel, P., Klorig, D., Smith, T., Koman, L.A., Atala, A., Van Dyke, M.: The use of keratin biomaterials derived from human hair for the promotion of rapid regeneration of peripheral nerves. Biomaterials 29(1), 118–128 (2008)
Zucherman, J.F., Hsu, K.Y., Yerby, S., Smith, R.A.: Implantable prosthetic or tissue expanding device. U.S. Patent 6783546, Aug 31, 2004
Schrooyen, P.M., Dijkstra, P.J., Oberthür, R.C., Bantjes, A., Feijen, J.: Partially carboxymethylated feather keratins. 1. Properties in aqueous systems. J. Agric. Food Chem. 48(9), 4326–4334 (2000)
Thompson, E., O’donnell, I.: Studies on reduced wool V. A comparison of the two major components. Aust. J. Biol. Sci. 18(6), 1207–1226 (1965)
Eslahi, N., Dadashian, F., Nejad, N.H.: An investigation on keratin extraction from wool and feather waste by enzymatic hydrolysis. Prep. Biochem. Biotechnol. 43(7), 624–648 (2013)
Hill, P., Brantley, H., Van Dyke, M.: Some properties of keratin biomaterials: kerateines. Biomaterials 31(4), 585–593 (2010)
Kakkar, P., Madhan, B., Shanmugam, G.: Extraction and characterization of keratin from bovine hoof: a potential material for biomedical applications. SpringerPlus 3, 596 (2014)
Xu, S., Zhang, C., Zhang, A., Wang, H., Rao, H., Zhang, Z.: Fabrication and biological evaluation in vivo of an injectable keratin hydrogel as filler materials. J. Bioact. Compat. Pol. 31(2), 179–190 (2015)
AjaySharma, L., Ali, M.A., Love, R.M., Wilson, M.J., Dias, G.J.: Novel keratin preparation supports growth and differentiation of odontoblast-like cells. Int. Endod. J. 49(5), 471–482 (2015)
Campbell, D.I., Duncan, W.J.: The effect of a keratin hydrogel coating on osseointegration: an histological comparison of coated and non-coated dental titanium implants in an ovine model. J. Maxillofac. Oral Surg. 13(2), 159–164 (2014)
Van Dyke, M., Blanchard, C., Timmons, S., Siller-Jackson, A., Smith, R.: Implantable prosthetic or tissue expanding device.U.S. Patent 6849092, Feb 1, 2005
Apel, P.J., Garrett, J.P., Sierpinski, P., Ma, J., Atala, A., Smith, T.L., Koman, L.A., Van Dyke, M.E.: Peripheral nerve regeneration using a keratin-based scaffold: long-term functional and histological outcomes in a mouse model. J. Hand. Surg. 33(9), 1541–1547 (2008)
Bai, X., Lü, S., Cao, Z., Gao, C., Duan, H., Xu, X., Sun, L., Gao, N., Feng, C., Liu, M.: Self-reinforcing injectable hydrogel with both high water content and mechanical strength for bone repair. Chem. Eng. J. 288, 546–556 (2016)
Tachibana, A., Nishikawa, Y., Nishino, M., Kaneko, S., Tanabe, T., Yamauchi, K.: Modified keratin sponge: binding of bone morphogenetic protein-2 and osteoblast differentiation. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 102(5), 425–429 (2006)
de Guzman, R.C., Saul, J.M., Ellenburg, M.D., Merrill, M.R., Coan, H.B., Smith, T.L., Van Dyke, M.E.: Bone regeneration with BMP-2 delivered from keratose scaffolds. Biomaterials 34(6), 1644–1656 (2013)
Xu, H., Cai, S., Xu, L., Yang, Y.: Water-stable three-dimensional ultrafine fibrous scaffolds from keratin for cartilage tissue engineering. Langmuir 30(28), 8461–8470 (2014)
Yuan, J., Geng, J., Xing, Z., Shim, K.-J., Han, I., Kim, J.-C., Kang, I.-K., Shen, J.: Novel wound dressing based on nanofibrous PHBV–keratin mats. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 9(9), 1027–1035 (2015)
Tachibana, A., Furuta, Y., Takeshima, H., Tanabe, T., Yamauchi, K.: Fabrication of wool keratin sponge scaffolds for long-term cell cultivation. J. Biotechnol. 93(2), 165–170 (2002)
Kurimoto, A., Tanabe, T., Tachibana, A., Yamauchi, K.: Keratin sponge: immobilization of lysozyme. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 96(3), 307–309 (2003)
Shukla, R., Cheryan, M.: Zein: the industrial protein from corn. Ind. Crop. Prod. 13(3), 171–192 (2001)
Delcour, J., Hoseney, R.: Principles of Cereal Science and Technology, 3rd edn, pp. 40–85. AACC International. Inc, St. Paul (2010)
Bräuer, S., Meister, F., Gottlöber, R.-P., Nechwatal, A.: Preparation and thermoplastic processing of modified plant proteins. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 292(2), 176–183 (2007)
Sousa, F., Luzardo-Álvarez, A., Blanco-Méndez, J., Martín-Pastor, M.: NMR techniques in drug delivery: application to zein protein complexes. Int. J. Pharm. 439(1), 41–48 (2012)
Dong, F., Padua, G.W., Wang, Y.: Controlled formation of hydrophobic surfaces by self-assembly of an amphiphilic natural protein from aqueous solutions. Soft Matter 9(25), 5933–5941 (2013)
De Vries, A., Nikiforidis, C.V., Scholten, E.: Natural amphiphilic proteins as tri-block Janus particles: Self-sorting into thermo-responsive gels. Epl 107(5) (2014)
Tihminlioglu, F., Atik, İ.D., Özen, B.: Water vapor and oxygen-barrier performance of corn–zein coated polypropylene films. J. Food Eng. 96(3), 342–347 (2010)
Reyes, P.I., Li, J., Duan, Z., Yang, X., Cai, Y., Huang, Q., Lu, Y.: ZnO surface acoustic wave sensors built on zein-coated flexible food packages. Sensor Lett. 11(3), 539–544 (2013)
Esen, A.: A proposed nomenclature for the alcohol-soluble proteins (zeins) of maize (Zea mays L). J. Cereal Sci. 5(2), 117–128 (1987)
Esen, A.: An immunodominant site of γ-zein1 is in the region of tandem hexapeptide repeats. J. Protein Chem. 9(4), 453–460 (1990)
Argos, P., Pedersen, K., Marks, M., Larkins, B.: A structural model for maize zein proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 257(17), 9984–9990 (1982)
Mannheim, A., Cheryan, M.: Water-soluble zein by enzymatic modification in organic solvents. Cereal Chem. 70, 115 (1993)
Danzer, L.A., Ades, H., Rees, E.D.: The helical content of zein, a water insoluble protein, in non-aqueous solvents. BBA-Protein Struct. M 386(1), 26–31 (1975)
Watson, S., Yahal, K.: Comparison of the wet-milling properties of opaueu-2 high-lysine corn and normal corn. Corn Products Co. pp. 488–498 (1967)
Singh, N., Cheryan, M.: Extraction of oil from corn distillers dried grains with solubles. T. ASAE 41(6), 1775–1778 (1998)
Luo, Y., Wang, Q.: Zein-based micro-and nano-particles for drug and nutrient delivery: A review. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 131(16), 40696 (2014)
Huang, G., Yang, X.: Studies on zein as delayed-release skeleton material of aspirin. Chem. Bioeng. 9, 48–50 (2005)
Hurtado-Lopez, P., Murdan, S.: Formulation and characterisation of zein microspheres as delivery vehicles. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 15(4), 267–272 (2005)
Zhong, Q., Jin, M.: Nanoscalar structures of spray-dried zein microcapsules and in vitro release kinetics of the encapsulated lysozyme as affected by formulations. J. Agric. Food Chem. 57(9), 3886–3894 (2009)
Mukhidinov, Z.K., Kasimova, G.F., Bobokalonov, D.T., Khalikov, D.K., Teshaev, K.I., Khalikova, M.D., Liu, L.S.: Pectin-zein microspheres as drug delivery systems. Pharm. Chem. J. 44(10), 564–567 (2011)
Yan, F.: Delivery of a probiotic-derived protein by pectin/zein hydrogels for colitis prevention and treatment. Abstr. Pap. Am. Chem. S. 244 (2012)
O’brien, R.D.: Fats and oils: formulating and processing for applications. CRC Press, Boca Raton (2010)
Quispe-Condori, S., Saldana, M.D.A., Temelli, F.: Microencapsulation of flax oil with zein using spray and freeze drying. Lwt-Food Sci. Technol. 44(9), 1880–1887 (2011)
Wu, S., Myers, D.J., Johnson, L.A.: Factors affecting yield and composition of zein extracted from commercial corn gluten meal 1. Cereal Chem. 74(3), 258–263 (1997)
Anderson, T.J., Lamsal, B.P.: Zein extraction from corn, corn products, and coproducts and modifications for various applications: a review. Cereal Chem. 88(2), 159–173 (2011)
Roy, C., Roy, R.D.: Low temperature solvent extraction process for producing high purity zein. U.S Patent 3535305, Oct 20, 1970 (1970)
Wolf, W.J., Lawton, J.W.: Isolation and characterization of zein from corn distillers’ grains and related fractions. Cereal Chem. 74(5), 530–536 (1997)
Xu, W., Reddy, N., Yang, Y.: An acidic method of zein extraction from DDGS. J. Agric. Food Chem. 55(15), 6279–6284 (2007)
Wang, Q., Yin, L., Padua, G.W.: Effect of hydrophilic and lipophilic compounds on zein microstructures. Food Biophys. 3(2), 174–181 (2008)
Wang, Y., Padua, G.W.: Formation of zein microphases in ethanol-water. Langmuir 26(15), 12897–12901 (2010)
Wang, Y., Padua, G.W.: Formation of zein spheres by evaporation-induced self-assembly. Colloid Polym. Sci. 290(15), 1593–1598 (2012)
Fu, J.-X., Wang, H.-J., Zhou, Y.-Q., Wang, J.-Y.: Antibacterial activity of ciprofloxacin-loaded zein microsphere films. Mat. Sci. Eng. C-Bio. S. 29(4), 1161–1166 (2009)
Seville, P.C., Kellaway, I.W., Birchall, J.C.: Preparation of dry powder dispersions for non-viral gene delivery by freeze-drying and spray-drying. J. Gene. Med. 4(4), 428–437 (2002)
Desobry, S.A., Netto, F.M., Labuza, T.P.: Comparison of spray-drying, drum-drying and freeze-drying for β-carotene encapsulation and preservation. J. Food Sci. 62(6), 1158–1162 (1997)
Liu, L., Fishman, M.L., Hicks, K.B.: Pectin in controlled drug delivery—a review. Cellulose 14(1), 15–24 (2007)
Liu, L., Fishman, M.L., Hicks, K.B., Kende, M., Ruthel, G.: Pectin/zein beads for potential colon-specific drug delivery: synthesis and in vitro evaluation. Drug Deliv. 13(6), 417–423 (2006)
Chen, L., Subirade, M.: Elaboration and characterization of soy/zein protein microspheres for controlled nutraceutical delivery. Biomacromolecules 10(12), 3327–3334 (2009)
Moros, E., Darnoko, D., Cheryan, M., Perkins, E., Jerrell, J.: Analysis of xanthophylls in corn by HPLC. J. Agric. Food Chem. 50(21), 5787–5790 (2002)
Paliwal, R., Palakurthi, S.: Zein in controlled drug delivery and tissue engineering. J. Control Release 189, 108–122 (2014)
Perkins, E.G.: Composition of soybeans and soybean products. Practical handbook of soybean processing and utilization. AOCS Press, Urbana (1995)
Su, J.-F., Yuan, X.-Y., Huang, Z., Wang, X.-Y., Lu, X.-Z., Zhang, L.-D., Wang, S.-B.: Physicochemical properties of soy protein isolate/carboxymethyl cellulose blend films crosslinked by Maillard reactions: Color, transparency and heat-sealing ability. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 32(1), 40–46 (2012)
Caillard, R., Remondetto, G., Mateescu, M., Subirade, M.: Characterization of amino cross-linked soy protein hydrogels. J. Food Sci. 73(5), 283–291 (2008)
Kinsella, J.E.: Functional properties of soy proteins. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 56(3), 242–258 (1979)
Maruyama, N., Adachi, M., Takahashi, K., Yagasaki, K., Kohno, M., Takenaka, Y., Okuda, E., Nakagawa, S., Mikami, B., Utsumi, S.: Crystal structures of recombinant and native soybean β-conglycinin β homotrimers. Eur. J. Biochem. 268(12), 3595–3604 (2001)
Maruyama, N., Salleh, M.R.M., Takahashi, K., Yagasaki, K., Goto, H., Hontani, N., Nakagawa, S., Utsumi, S.: The effect of the N-linked glycans on structural features and physicochemical functions of soybean β-conglycinin homotrimers. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 79(2), 139–144 (2002)
Kang, H.G., Lee, S.B., Lee, Y.M.: Novel preparative method for porous hydrogels using overrun process. Polym. Int. 54(3), 537–543 (2005)
Caillard, R., Remondetto, G., Subirade, M.: Physicochemical properties and microstructure of soy protein hydrogels co-induced by Maillard type cross-linking and salts. Food Res. Int. 42(1), 98–106 (2009)
Meikle, S.T., Standen, G., Salvage, J., De Santis, R., Nicolais, L., Ambrosio, L., Santin, M.: Synthesis and characterization of soybean-based hydrogels with an intrinsic activity on cell differentiation. Tissue Eng. pt. A 18(17–18), 1932–1939 (2012)
Santin, M., Ambrosio, L.: Soybean-based biomaterials: preparation, properties and tissue regeneration potential. Expert Rev. Med. Devices 5(3), 349–358 (2008)
Zohuriaan-Mehr, M.J., Pourjavadi, A., Salimi, H., Kurdtabar, M.: Protein- and homo poly(amino acid)-based hydrogels with super-swelling properties. Polym. Adv. Technol. 20(8), 655–671 (2009)
Utsumi, S., Kinsella, J.E.: Forces involved in soy protein gelation: effects of various reagents on the formation, hardness and solubility of heat-induced gels made from 7S, 11S, and soy isolate. J. Food Sci. 50(5), 1278–1282 (1985)
Puppo, M.C., Añón, M.C.: Structural properties of heat-induced soy protein gels as affected by ionic strength and pH. J. Agric. Food Chem. 46(9), 3583–3589 (1998)
Li, Y.-D., Zeng, J.-B., Wang, X.-L., Yang, K.-K., Wang, Y.-Z.: Structure and properties of soy protein/poly (butylene succinate) blends with improved compatibility. Biomacromolecules 9(11), 3157–3164 (2008)
Rhim, J.-W., Gennadios, A., Weller, C.L., Cezeirat, C., Hanna, M.A.: Soy protein isolate–dialdehyde starch films. Ind. Crop. Prod. 8(3), 195–203 (1998)
Sacks, F.M., Lichtenstein, A., Van Horn, L., Harris, W., Kris-Etherton, P., Winston, M.: Soy protein, isoflavones, and cardiovascular health an American Heart Association science advisory for professionals from the nutrition committee. Circulation 113(7), 1034–1044 (2006)
Cassidy, A., Bingham, S., Setchell, K.: Biological effects of a diet of soy protein rich in isoflavones on the menstrual cycle of premenopausal women. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 60(3), 333–340 (1994)
Lee, J.-S.: Effects of soy protein and genistein on blood glucose, antioxidant enzyme activities, and lipid profile in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Life Sci. 79(16), 1578–1584 (2006)
Lai, Y.P., Mondor, M., Moresoli, C., Drolet, H., Gros-Louis, M., Ippersiel, D., Lamarche, F., Arcand, Y.: Production of soy protein isolates with low phytic acid content by membrane technologies: impact of the extraction and ultrafiltration/diafiltration conditions. J. Food Eng. 114(2), 221–227 (2013)
Deak, N.A., Johnson, L.A.: Effects of extraction temperature and preservation method on functionality of soy protein. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 84(3), 259–268 (2007)
Tang, C.H., Wu, H., Yu, H.P., Li, L., Chen, Z., Yang, X.Q.: Coagulation and gelation of soy protein isolates induced by microbial transglutaminase. J. Food Biochem. 30(1), 35–55 (2006)
Alting, A.C., de Jongh, H.H., Visschers, R.W., Simons, J.-W.F.: Physical and chemical interactions in cold gelation of food proteins. J. Agric. Food Chem. 50(16), 4682–4689 (2002)
Maltais, A., Remondetto, G.E., Gonzalez, R., Subirade, M.: Formation of soy protein isolate cold-set gels: protein and salt effects. J. Food Sci. 70(1), C67–C73 (2005)
Hwang, D.C., Damodaran, S.: Metal-chelating properties and biodegradability of an ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid dianhydride modified soy protein hydrogel. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 64(5), 891–901 (1997)
Brännvall, K., Bergman, K., Wallenquist, U., Svahn, S., Bowden, T., Hilborn, J., Forsberg-Nilsson, K.: Enhanced neuronal differentiation in a three-dimensional collagen-hyaluronan matrix. J. Neurosci. Res. 85(10), 2138–2146 (2007)
Hwang, D.C., Damodaran, S.: Metal-chelating properties and biodegradability of an ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid dianhydride modified soy protein hydrogel. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 64(5), 891–901 (1997)
Damodaran, S., Hwang, D.C.: Carboxyl-modified superabsorbent protein hydrogel. U.S. Patent 5847089, Dec 8, 1998
Guo, J., Jin, Y.-C., Yang, X.-Q., Yu, S.-J., Yin, S.-W., Qi, J.-R.: Computed microtomography and mechanical property analysis of soy protein porous hydrogel prepared by homogenizing and microbial transglutaminase cross-linking. Food Hydrocolloid. 31(2), 220–226 (2013)
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the funding provided by the Fonds de Recherche du Québec—Nature et Technologies (FRQNT).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ni, N., Dumont, MJ. Protein-Based Hydrogels Derived from Industrial Byproducts Containing Collagen, Keratin, Zein and Soy. Waste Biomass Valor 8, 285–300 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-016-9684-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-016-9684-0