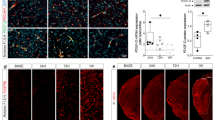
Abstract
Currently, brain stroke is one of the leading causes of death and disabilities. It results in depletion of oxygen and glucose in certain areas of the brain, leading to neuronal death. Re-oxygenation has been proven to attenuate neuronal damage; however, sudden oxygen supply may also cause oxidative stress and subsequent inflammation. Hence, therapies to suppress re-oxygenation-induced oxidative damage are urgently needed. Interleukin (IL)-35, an immunomodulator secreted by regulatory T cells and regulatory B cells, is proven to be a strong immune-repressive cytokine. Here, we investigated the potential role of IL-35 in a disease model of oxygen glucose deprivation/re-oxygenation (OGD/R) and found that M2 macrophage-derived IL-35 significantly alleviated inflammatory response induced by oxidative stress. Our results also showed that IL-35 treatment decreased OGD/R-induced neuronal cell death and inflammatory response. Additionally, we demonstrated that IL-35 suppresses inflammatory response via the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Hence, our findings indicate that IL-35 therapy has great potential in the treatment of OGD/R-induced oxidative damage and related inflammatory diseases.







Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of Data and Materials
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article and its additional files.
References
Amruta N, Bix G (2021) ATN-161 ameliorates ischemia/reperfusion-induced oxidative stress, fibro-inflammation, mitochondrial damage, and apoptosis-mediated tight junction disruption in bEnd. Cells 3:1–18
Bettini M, Castellaw AH, Lennon GP, Burton AR, Vignali DA (2012) Prevention of autoimmune diabetes by ectopic pancreatic β-cell expression of interleukin-35. Diabetes 61:1519–1526
Celik M, Labuz D, Keye J, Glauben R, Machelska H (2020) IL-4 induces M2 macrophages to produce sustained analgesia via opioids. JCI Insight 5:e133093
Chen YD, Huang PY, Chiang CS, Huang YS, Tang SC (2021) Generation and role of calpain-cleaved 17-kDa tau fragment in acute ischemic stroke. Mol Neurobiol 58:5814–5825
Collison LW, Chaturvedi V, Henderson AL et al (2010) IL-35-mediated induction of a potent regulatory T cell population. Nat Immunol 11:1093–1101
Collison LW, Delgoffe GM, Guy CS et al (2012) The composition and signaling of the IL-35 receptor are unconventional. Nat Immunol 13:290–299
Collison LW, Workman CJ, Kuo TT et al (2007) The inhibitory cytokine IL-35 contributes to regulatory T-cell function. Nature 450:566–569
Cua DJ, Sherlock J, Chen Y et al (2003) Interleukin-23 rather than interleukin-12 is the critical cytokine for autoimmune inflammation of the brain. Nature 421:744–748
Devergne O, Hummel M, Koeppen H et al (1996) A novel interleukin-12 p40-related protein induced by latent Epstein-Barr virus infection in B lymphocytes. J Virol 70:1143–1153
Devisscher L, Verhelst X, Colle I, Van Vlierberghe H, Geerts A (2016) The role of macrophages in obesity-driven chronic liver disease. J Leukoc Biol 99:693–698
Dijkstra CD, De Groot CJ, Huitinga I (1992) The role of macrophages in demyelination. J Neuroimmunol 40:183–188
Egwuagu CE, Yu CR (2015) Interleukin 35-producing B cells (i35-Breg): a new mediator of regulatory B-cell functions in CNS autoimmune diseases. Crit Rev Immunol 35:49–57
Egwuagu CE, Yu CR, Sun L, Wang R (2015) Interleukin 35: Critical regulator of immunity and lymphocyte-mediated diseases. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 26:587–593
Fei H, Xiang P, Luo W et al (2021) CTRP1 Attenuates cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury via the PERK signaling pathway. Front Cell Dev Biol 9:700854
Fukui M, Zhu BT (2010) Mitochondrial superoxide dismutase SOD2, but not cytosolic SOD1, plays a critical role in protection against glutamate-induced oxidative stress and cell death in HT22 neuronal cells. Free Radic Biol Med 48:821–830
Gimenez-Barcons M, Clotet B, Martinez MA (2007) Endoribonuclease-prepared short interfering RNAs induce effective and specific inhibition of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 replication. J Virol 81:10680–10686
Gwak J, Hwang SG, Park HS et al (2012) Small molecule-based disruption of the Axin/β-catenin protein complex regulates mesenchymal stem cell differentiation. Cell Res 22:237–247
Imai T, Matsubara H, Nakamura S, Hara H, Shimazawa M (2020) The mitochondria-targeted peptide, bendavia, attenuated ischemia/reperfusion-induced stroke damage. Neuroscience 443:110–119
Jablonski KA, Amici SA, Webb LM et al (2015) Novel markers to delineate murine M1 and M2 macrophages. PLoS One 10:e0145342
Jiang Y, Wang J, Li H, Xia L (2020) IL-35 promotes microglial M2 polarization in a rat model of diabetic neuropathic pain. Arch Biochem Biophys 685:108330
Kanai K, Park AM, Yoshida H, Tsunoda I (2017) IL-35 Suppresses lipopolysaccharide-induced airway eosinophilia in EBI3-deficient mice. 198:119–127
Lee CC, Lin JC (2018) Macrophage-secreted interleukin-35 regulates cancer cell plasticity to facilitate metastatic colonization. 9:3763
Li X, Liu X, Wang W (2021a) IL-35: a novel immunomodulator in hepatitis B virus-related liver diseases. Front Cell Dev Biol 9:614847
Li Y, Yuan L, Jiang S et al (2019) Interleukin-35 stimulates tumor necrosis factor-α activated osteoblasts differentiation through Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in rheumatoid arthritis. Int Immunopharmacol 75:105810
Li YJ, Zhan Y, Li C, Sun J, Yang C (2021b) CPI-1189 protects neuronal cells from oxygen glucose deprivation/re-oxygenation-induced oxidative injury and cell death. Aging (albany NY) 13:6712–6723
Liu N, Peng A, Sun H et al (2021) LncRNA AC136007.2 alleviates cerebral ischemic-reperfusion injury by suppressing autophagy. Aging (albany NY) 13:19587–19597
Liu P, Peng J, Han GH et al (2019) Role of macrophages in peripheral nerve injury and repair. Neural Regen Res 14:1335–1342
Liu X, Liu J, Zhao S et al (2016) Interleukin-4 is essential for microglia/macrophage M2 polarization and long-term recovery after cerebral ischemia. Stroke 47:498–504
Martinez FO, Gordon S (2014) The M1 and M2 paradigm of macrophage activation: time for reassessment. F1000Prime Rep 6:13
Martinez FO, Helming L, Gordon S (2009) Alternative activation of macrophages: an immunologic functional perspective. Annu Rev Immunol 27:451–483
Medzhitov R (2008) Origin and physiological roles of inflammation. Nature 454:428–435
Morán J, Perez-Basterrechea M, Garrido P et al (2017) Effects of estrogen and phytoestrogen treatment on an in vitro model of recurrent stroke on HT22 neuronal cell line. Cell Mol Neurobiol 37:405–416
Mosser DM, Edwards JP (2008) Exploring the full spectrum of macrophage activation. Nat Rev Immunol 8:958–969
Murray PJ, Allen JE, Biswas SK et al (2014) Macrophage activation and polarization: nomenclature and experimental guidelines. Immunity 41:14–20
Niida A, Hiroko T, Kasai M et al (2004) DKK1, a negative regulator of Wnt signaling, is a target of the beta-catenin/TCF pathway. Oncogene 23:8520–8526
Ohashi W, Yamamine N, Imura J, Hattori Y (2017) SKL2001 suppresses colon cancer spheroid growth through regulation of the E-cadherin/β-Catenin complex. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 493:1342–1348
Olson BM, Sullivan JA, Burlingham WJ (2013) Interleukin 35: a key mediator of suppression and the propagation of infectious tolerance. Front Immunol 4:315
Orecchioni M, Ghosheh Y, Pramod AB, Ley K (2019) Macrophage polarization: different gene signatures in M1(LPS+) vs. classically and M2(LPS-) vs. aalternatively activated macrophages. Front Immunol 10:1084
Prabhakaran S, Naidech AM (2012) Ischemic brain injury after intracerebral hemorrhage: a critical review. Stroke 43:2258–2263
Ryou MG, Mallet RT (2018) An in vitro oxygen-glucose deprivation model for studying ischemia-reperfusion injury of neuronal cells. Methods Mol Biol 1717:229–235
Shen P, Roch T, Lampropoulou V et al (2014) IL-35-producing B cells are critical regulators of immunity during autoimmune and infectious diseases. Nature 507:366–370
Sica A, Bronte V (2007) Altered macrophage differentiation and immune dysfunction in tumor development. J Clin Invest 117:1155–1166
Spence JD, Azarpazhooh MR, Larsson SC, Bogiatzi C, Hankey GJ (2020) Stroke prevention in older adults: recent advances. Stroke 51:3770–3777
Sun L, He C, Nair L, Yeung J, Egwuagu CE (2015) Interleukin 12 (IL-12) family cytokines: role in immune pathogenesis and treatment of CNS autoimmune disease. Cytokine 75:249–255
Sun X, Wang D, Zhang T et al (2020) Eugenol attenuates cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury by enhancing autophagy via AMPK-mTOR-P70S6K Pathway. Front Pharmacol 11:84
Tian Y, Zhu P, Liu S et al (2019) IL-4-polarized BV2 microglia cells promote angiogenesis by secreting exosomes. Adv Clin Exp Med 28:421–430
Wang RX, Yu CR, Dambuza IM et al (2014) Interleukin-35 induces regulatory B cells that suppress autoimmune disease. Nat Med 20:633–641
Xin PL, Jie LF, Cheng Q, Bin DY, Dan CW (2021) Pathogenesis and function of interleukin-35 in rheumatoid arthritis. Front Pharmacol 12:655114
Xu C, Zhu H, Shen R, Feng Q, Zhou H, Zhao Z (2018) IL-35 is a Protective Immunomodulator in Brain Ischemic Injury in Mice. Neurochem Res 43:1454–1463
Xu S, Li Y, Chen JP et al (2020) Oxygen glucose deprivation/re-oxygenation-induced neuronal cell death is associated with Lnc-D63785 m6A methylation and miR-422a accumulation. Cell Death Dis 11:816
Yoshizaki A, Miyagaki T, DiLillo DJ et al (2012) Regulatory B cells control T-cell autoimmunity through IL-21-dependent cognate interactions. Nature 491:264–268
Zheng Y, Zhao P, Lian Y, Li S, Chen Y, Li L (2020) MiR-340–5p alleviates oxygen-glucose deprivation/reoxygenation-induced neuronal injury via PI3K/Akt activation by targeting PDCD4. Neurochem Int 134:104650
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Tao Xiao and Juan Wan conceived and designed the study. Tao Xiao, Hongtao Qu, and Zhiqing Zeng collected the data. Chuanghua Li analyzed the data. Tao Xiao wrote the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript for publication.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Statement
Not appropriate.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiao, T., Qu, H., Zeng, Z. et al. Interleukin-35 from Interleukin-4-Stimulated Macrophages Alleviates Oxygen Glucose Deprivation/Re-oxygenation-Induced Neuronal Cell Death via the Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway. Neurotox Res 40, 420–431 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-022-00478-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-022-00478-7