Abstract
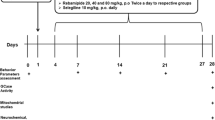
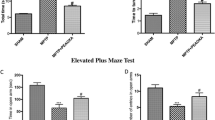
Many studies reported the neuroprotective effects of angiotensin II type 1 receptor (AT1R) antagonists in Parkinson’s disease (PD). However, the role of AT1R blockade on astroglial, in turn, dopaminergic functions in chronic PD is still to be studied. In the present study, telmisartan (TEL; 3 and 10 mg/kg/day; p.o), was used to study the effects AT1R blockade on astrocytic and dopaminergic functions in a chronic 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP) mouse model of Parkinsonism (250 mg/kg, i.p, in 10 equally divided doses at 3.5 days interval) in C57BL/6 J mice. TEL significantly downregulated glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP), inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), TNFα and IL1β expressions and nitric oxide (NO) content. Significant upregulation glial cell derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) expression and increased glutathione (GSH) content reveal the ameliorating effects of TEL on astroglial functions. On the other hand, TEL upregulated tyrosine hydroxylase (TH), dopamine transporter (DAT), and vesicular monoamine transporter 2 (VMAT2) expressions. Finally, TEL improved dopamine and its turnover and restored locomotor performance. Present experiment reveals that TEL has the potential to alleviate astroglial functions, apart from restoring dopaminergic functions, at least in part. To conclude, TEL may be a better disease-modifying therapeutic regimen in the management of Parkinsonism, acting primarily via astroglial-dopaminergic functions.









Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
15 December 2019
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-019-00127-6
References
Akama KT, Van Eldik LJ (2000) Beta-amyloid stimulation of inducible nitric-oxide synthase in astrocytes is interleukin-1beta- and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNFalpha)-dependent, and involves a TNFalpha receptor-associated factor- and NFkappaB-inducing kinase-dependent signaling mechanism. J Biol Chem 275:7918–7924
Araki T, Mikami T, Tanji H, Matsubara M, Imai Y, Mizugaki M, Itoyama Y (2001) Biochemical and immunohistological changes in the brain of 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP)-treated mouse. Eur J Pharm Sci 12:231–238
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Brahmachari S, Fung YK, Pahan K (2006) Induction of glial fibrillary acidic protein expression in astrocytes by nitric oxide. J Neurosci 26:4930–4939. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5480-05.2006
Cabezas R, Avila M, Gonzalez J, El-Bachá RS, Báez E, García-Segura LM, Jurado Coronel JC, Capani F, Cardona-Gomez GP, Barreto GE (2014) Astrocytic modulation of blood brain barrier: perspectives on Parkinson’s disease. Front Cell Neurosci 8(211). https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2014.00211
Canals S, Casarejos MJ, de Bernardo S, Rodríguez-Martín E, Mena MA (2001) Glutathione depletion switches nitric oxide neurotrophic effects to cell death in midbrain cultures: implications for Parkinson’s disease. J Neurochem 79:1183–1195
Chen Y, Vartiainen NE, Ying W, Chan PH, Koistinaho J, Swanson RA (2001) Astrocytes protect neurons from nitric oxide toxicity by a glutathione-dependent mechanism. J Neurochem 77:1601–1610
Chung YC, Kim SR, Jin BK (2010) Paroxetine prevents loss of nigrostriatal dopaminergic neurons by inhibiting brain inflammation and oxidative stress in an experimental model of Parkinson’s disease. J Immunol 185:1230–1237. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.1000208
Croisier E, Graeber MB (2006) Glial degeneration and reactive gliosis in alpha-synucleinopathies: the emerging concept of primary gliodegeneration. Acta Neuropathol 112:517–530. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-006-0119-z
Dringen R, Gutterer JM, Hirrlinger J (2000) Glutathione metabolism in brain metabolic interaction between astrocytes and neurons in the defense against reactive oxygen species. Eur J Biochem 267:4912–4916
Duncan AJ, Heales SJR (2005) Nitric oxide and neurological disorders. Mol Asp Med 26:67–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mam.2004.09.004
Eng LF, Ghirnikar RS (1994) GFAP and astrogliosis. Brain Pathol 4:229–237
Fellner L, Jellinger KA, Wenning GK, Stefanova N (2011) Glial dysfunction in the pathogenesis of α-synucleinopathies: emerging concepts. Acta Neuropathol 121:675–693. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-011-0833-z
Fernagut PO, Diguet E, Labattu B, Tison F (2002) A simple method to measure stride length as an index of nigrostriatal dysfunction in mice. J Neurosci Methods 113:123–130
Gallagher PE, Chappell MC, Ferrario CM, Tallant EA (2006) Distinct roles for ANG II and ANG-(1-7) in the regulation of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 in rat astrocytes. Am J Physiol, Cell Physiol 290:C420–C426. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpcell.00409.2004
Garrido-Gil P, Joglar B, Rodriguez-Perez AI, Guerra MJ, Labandeira-Garcia JL (2012) Involvement of PPAR-γ in the neuroprotective and anti-inflammatory effects of angiotensin type 1 receptor inhibition: effects of the receptor antagonist telmisartan and receptor deletion in a mouse MPTP model of Parkinson’s disease. J Neuroinflammation 9:38. https://doi.org/10.1186/1742-2094-9-38
Giasson BI, Duda JE, Murray IV, Chen Q, Souza JM, Hurtig HI, Ischiropoulos H, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM (2000) Oxidative damage linked to neurodegeneration by selective alpha-synuclein nitration in synucleinopathy lesions. Science 290:985–989
Gohlke P, Weiss S, Jansen A, Wienen W, Stangier J, Rascher W, Culman J, Unger T (2001) AT1 receptor antagonist telmisartan administered peripherally inhibits central responses to angiotensin II in conscious rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 298:62–70
González-Hernández T, Cruz-Muros I, Afonso-Oramas D, Salas-Hernandez J, Castro-Hernandez J (2010) Vulnerability of mesostriatal dopaminergic neurons in Parkinson’s disease. Front Neuroanat 4:140. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnana.2010.00140
Green LC, Wagner DA, Glogowski J, Skipper PL, Wishnok JS, Tannenbaum SR (1982) Analysis of nitrate, nitrite, and [15N]nitrate in biological fluids. Anal Biochem 126:131–138
Heales SJR, Lam AAJ, Duncan AJ, Land JM (2004) Neurodegeneration or neuroprotection: the pivotal role of astrocytes. Neurochem Res 29:513–519. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:NERE.0000014822.69384.0f
Khasnavis S, Ghosh A, Roy A, Pahan K (2013) Castration induces Parkinson disease pathologies in young male mice via inducible nitric-oxide synthase. J Biol Chem 288:20843–20855. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M112.443556
Klivenyi P, Siwek D, Gardian G, Yang L, Starkov A, Cleren C, Ferrante RJ, Kowall NW, Abeliovich A, Beal MF (2006) Mice lacking alpha-synuclein are resistant to mitochondrial toxins. Neurobiol Dis 21:541–548. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2005.08.018
Lee H-J, Patel S, Lee S-J (2005) Intravesicular localization and exocytosis of alpha-synuclein and its aggregates. J Neurosci 25:6016–6024. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0692-05.2005
Liberatore GT, Jackson-Lewis V, Vukosavic S, Mandir AS, Vila M, McAuliffe WG, Dawson VL, Dawson TM, Przedborski S (1999) Inducible nitric oxide synthase stimulates dopaminergic neurodegeneration in the MPTP model of Parkinson disease. Nat Med 5:1403–1409. https://doi.org/10.1038/70978
Liu B, Gao H-M, Wang J-Y, Jeohn G-H, Cooper CL, Hong J-S (2002) Role of nitric oxide in inflammation-mediated neurodegeneration. Ann N Y Acad Sci 962:318–331
Luchtman DW, Shao D, Song C (2009) Behavior, neurotransmitters and inflammation in three regimens of the MPTP mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Physiol Behav 98:130–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physbeh.2009.04.021
McKinley MJ, Albiston AL, Allen AM, Mathai ML, May CN, McAllen RM, Oldfield BJ, Mendelsohn F a O, Chai SY (2003) The brain renin-angiotensin system: location and physiological roles. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 35:901–918
Mirza B, Hadberg H, Thomsen P, Moos T (2000) The absence of reactive astrocytosis is indicative of a unique inflammatory process in Parkinson’s disease. Neuroscience 95:425–432
Moron MS, Depierre JW, Mannervik B (1979) Levels of glutathione, glutathione reductase and glutathione S-transferase activities in rat lung and liver. Biochim Biophys Acta 582:67–78
National Research Council (1996) Guide for the care and use of laboratory animals. The National Academies Press, Washington, DC https://doi.org/10.17226/5140
Pang T, Wang J, Benicky J, Sánchez-Lemus E, Saavedra JM (2012) Telmisartan directly ameliorates the neuronal inflammatory response to IL-1β partly through the JNK/c-Jun and NADPH oxidase pathways. J Neuroinflammation 9(102). https://doi.org/10.1186/1742-2094-9-102
Paxinos G, Franklin KBJ (2001) The mouse brain in stereotaxic coordinates, 2nd ed. Academic Press, San Diego
Peña LL, Nieto AI, Pérez-Alenza D, Cuesta P, Castaño M (1998) Immunohistochemical detection of Ki-67 and PCNA in canine mammary tumors: relationship to clinical and pathologic variables. J Vet Diagn Investig 10:237–246. https://doi.org/10.1177/104063879801000303
Saavedra A, Baltazar G, Duarte EP (2008) Driving GDNF expression: the green and the red traffic lights. Prog Neurobiol 86:186–215. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pneurobio.2008.09.006
Sagara JI, Miura K, Bannai S (1993) Maintenance of neuronal glutathione by glial cells. J Neurochem 61:1672–1676
Sathiya S, Ranju V, Kalaivani P, Priya RJ, Sumathy H, Sunil AG, Babu CS (2013) Telmisartan attenuates MPTP induced dopaminergic degeneration and motor dysfunction through regulation of α-synuclein and neurotrophic factors (BDNF and GDNF) expression in C57BL/6J mice. Neuropharmacology 73:98–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2013.05.025
Schallert T (2006) Behavioral tests for preclinical intervention assessment. NeuroRx 3:497–504. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nurx.2006.08.001
Silva KC, Rosales MAB, de Faria JBL, de Faria JML (2010) Reduction of inducible nitric oxide synthase via angiotensin receptor blocker prevents the oxidative retinal damage in diabetic hypertensive rats. Curr Eye Res 35:519–528. https://doi.org/10.3109/02713681003664923
Stephenson D, Ramirez A, Long J, Barrezueta N, Hajos-Korcsok E, Matherne C, Gallagher D, Ryan A, Ochoa R, Menniti F, Yan J (2007) Quantification of MPTP-induced dopaminergic neurodegeneration in the mouse substantia nigra by laser capture microdissection. J Neurosci Methods 159:291–299. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneumeth.2006.07.027
Stewart VC, Sharpe MA, Clark JB, Heales SJ (2000) Astrocyte-derived nitric oxide causes both reversible and irreversible damage to the neuronal mitochondrial respiratory chain. J Neurochem 75:694–700
Wang S, Hu L, Zhang Y, Sun T, Sun Y, Liu S, Ding J, Wu J, Hu G (2006) Effects of systemic administration of iptakalim on extracellular neurotransmitter levels in the striatum of unilateral 6-hydroxydopamine-lesioned rats. Neuropsychopharmacology 31:933–940. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.npp.1300857
Zang G-Q, Zhou X-Q, Yu H, Xie Q, Zhao G-M, Wang B, Guo Q, Xiang Y-Q, Liao D (2000) Effect of hepatocyte apoptosis induced by TNF-alpha on acute severe hepatitis in mouse models. World J Gastroenterol 6:688–692
Zawada WM, Banninger GP, Thornton J, Marriott B, Cantu D, Rachubinski AL, Das M, Griffin WS, Jones SM (2011) Generation of reactive oxygen species in 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium (MPP+) treated dopaminergic neurons occurs as an NADPH oxidase-dependent two-wave cascade. J Neuroinflammation 8:129
Zhang Y, Schlussman SD, Rabkin J, Butelman ER, Ho A, Kreek MJ (2013) Chronic escalating cocaine exposure, abstinence/withdrawal, and chronic re-exposure: effects on striatal dopamine and opioid systems in C57BL/6J mice. Neuropharmacology 67:259–266. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2012.10.015
Acknowledgements
This project was funded by Scientific and Engineering Research Board (SERB), Project Sanction No. SB/FT/LS-293/2012, Department of Science & Technology, Govt. of India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Participated in research design: Chidambaram
Conducted experiments: Sekar, Mani and Rajamani
Contributed new reagents or analytic tools: Chidambaram
Performed data analysis: Sekar, and Chidambaram
Wrote or contributed to the writing of the manuscript: Sekar, Bhat, Ray, Thamilarasan, Guillemin, Essa, Chidambaram
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sekar, S., Mani, S., Rajamani, B. et al. Telmisartan Ameliorates Astroglial and Dopaminergic Functions in a Mouse Model of Chronic Parkinsonism. Neurotox Res 34, 597–612 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-018-9921-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-018-9921-3