Abstract
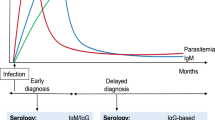
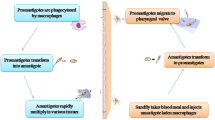
Human trichinellosis is a worldwide foodborne public health threat. Detecting circulating antigens of Trichinella spiralis “T. spiralis” allows for an early diagnosis before larval encystation develops in skeletal muscles. For the first time, the present study aimed to formulate an effective nanomagnetic beads based-ELISA and -latex agglutination test (NMB-ELISA and NMB-LAT) to recognize T. spiralis adult worm crude extract antigen (AWCEA) in sera of experimentally infected mice. The study included thirty-eight mice classified into 3 groups; T. spiralis-infected group (GI) which was euthanized 6, 8, 10, 12, 14 days post-infection (dpi), other parasitic infections group (GII) and healthy control group (GIII). Rabbit anti-T. spiralis polyclonal antibodies (pAbs) were utilized to detect AWCEA in serum samples by sandwich ELISA, NMB-ELISA, and NMB-LAT. Using NMB-ELISA, AWCEA was detected in sera collected at 6 and 8 dpi, with a sensitivity of 50% and 75%, respectively, and a specificity of 100%. Whereas, sandwich ELISA and NMB-LAT couldn’t detect the antigen at the same time intervals. Both ELISA formats were able to detect the antigen in samples collected at 10, 12, and 14 dpi with a sensitivity of 100% for NMB-ELISA and 25%, 75%, and 100% respectively, for sandwich-ELISA. Yet, NMB-LAT couldn't detect AWCEA until 12 dpi with a sensitivity of 50% and specificity of 75%. In conclusion, NMB-ELISA is a promising sensitive tool for early and specific diagnosis of acute trichinellosis. The use of NMB-LAT could be a helpful screening procedure in field surveys.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data analyzed in this study is included in the article.
References
Ahmed A, El Amir A, Rabee I, El Deeb S (2012) Effective diagnosis of schistosomiasis haematobium by immunomagnetic bead ELISA technique using super-paramagnetic nanoparticles. J Am Sci 8(9):833–841
Ali A, Shah T, Ullah R, Zhou P, Guo M, Ovais M, Tan Z, Rui Y (2021) Review on recent progress in magnetic nanoparticles: synthesis, characterization, and diverse applications. Front Chem 9:629054–629079. https://doi.org/10.3389/fchem.2021.629054
Aly IR, Zalat R, El Aswad BEDW, Moharm IM, Masoud BM, Diab T (2014) Novel nanomagnetic beads based latex agglutination assay for rapid diagnosis of human schistosomiasis haematobium. Int J Health Med Sci 7(12):977–983. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.1336230
Aly NS, Bayoumi I, Selem R, Kardoush M, Rashed G, Moharam A (2018) A novel nano magnetic beads dot ELISA immunoassay and its application on the detection of giardia lamblia coproantigen. Iran J Parasitol 13(4):532–540
Ascoli CA, Aggeler B (2018) Overlooked benefits of using polyclonal antibodies. Biotechniques 65(3):127–136. https://doi.org/10.2144/btn-2018-0065
Brice-Profeta S, Arrio MA, Tronc E, Menguy N, Letard I, Cartie dit MoulinNoguèsChanéacJolivetSainctavit CMCJPPh (2005) Magnetic order in γ-Fe2O3 nanoparticles a XMCD study. J Magnetism Magnetic Mater 288:354–365
Bruschi F, Dupouy-Camet J (2014): Trichinellosis. In: Bruschi, F. (Ed), Helminth Infections and their Impact on Global Public Health. Springer, Vienna. pp. 229–273. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-7091-1782-8_8
Carpenter AB (1992) Enzyme linked immunoassays. In: Rose NR, De Macario EC, Fahey JL, Friedman H, Penn GM (eds) Manual of clinical laboratory immunology, 4th edn. American Society for Microbiology Washington, D.C., pp 2–9
ConcatoVM AJP, Gonçalves MD, Carloto ACM, Conchon-Costa I, Pavanelli WR, Melanda FN, Costa IN (2017) Nanomedicine advances in toxoplasmosis: diagnostic, treatment, and vaccine applications. Parasitol Res 116(6):1603–1615. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-017-5458-2
Cui J, Liu RD, Wang L, Zhang X, Jiang P, Liu MY, Wang ZQ (2013) Proteomic analysis of surface proteins of Trichinella spiralis muscle larvae by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis and mass spectrometry. Parasites Vectors 6(355):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1186/1756-3305-6-355
Cui J, Li LG, Jiang P, Liu RD, Yang X, Liu LN, Liu P, Zhang Sh, Wang ZQ (2015) Biochemical and functional characterization of the glutathione S-transferase from Trichinella spiralis. Parasitol Res 114:2007–2013. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-015-4410-6
Devi CS, Parija SC (2003) A new serum hydatid antigen detection test for diagnosis of cystic echinococcosis. Am J Trop Med Hyg 69(5):525–528
Diaz JH, Warren RJ, Oster MJ (2020) The Disease ecology, epidemiology, clinical manifestations, and management of trichinellosis linked to consumption of wild animal meat. Wilderness Environ Med 31(2):235–244. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wem.2019.12.003
Ding N, Zhao H, Peng W, He Y, Zhou Y, Yuan L, Zhang Y (2012) A simple colorimetric sensor based on anti-aggregation of gold nanoparticles for Hg2+ detection. colloid. Surface A Physico Chem Eng Aspects 395:161–167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2011.12.024
Dupouy-Camet J, Raffetin A, Rosca EC, Yera H (2021) Clinical picture and diagnosis of human trichinellosis (Chapter 10). In: Bruschi, F. (Ed.), Trichinella and Trichinellosis. Academic Press, pp. 333–352. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-821209-7.00010-X
Eid A, Abdel-Hamid K, Abdel-Hafez M, Hosainy A, Aly IR (2020) Efficacy of iron oxide nanoparticles in diagnosis of schistosomiasis. Al-Azhar Int Med J 1:219–224
Enzel P, Adelman N, Beckman KJ, Campbell DJ, Ellis AB, Lisensky GC (1999) Preparation of an aqueous-based ferrofluid. J Chem Educ 76(7):943–948. https://doi.org/10.1021/ed076p943
Gajadhar AA, Noeckler k, Boireau P, Rossi P, Scandrett B, Gamble HR (2019) International commission on trichinellosis: recommendations for quality assurance in digestion testing programs for Trichinella. Food Waterborne Parasitol 16:e00059–e000126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fawpar.2019.e00059
Goel S, England CG, Chen F, Cai W (2017) Positron emission tomography and nanotechnology: a dynamic duo for cancer theranostics. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 113:157–176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2016.08.001
Gomaa MM (2020) Early diagnosis of experimental Trichinella spiralis infection by nano-based enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (nano-based ELISA). Exp Parasitol 212:107867–107874. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exppara.2020.107867
Grzelak S, Moskwa B, Bień J (2018) Trichinella britovi muscle larvae and adult worms: stage-specific and common antigens detected by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis-based immunoblotting. Parasite Vectors 11:584–601. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13071-018-3177-x
Gudikandula K, Maringanti SC (2016) Synthesis of silver nanoparticles by chemical and biological methods and their antimicrobial properties. J Exp Nanosci 11(9):714–721. https://doi.org/10.1080/17458080.2016.113919
Hegazy Sh, Farid A, Rabae I, El-Amir A (2014) Noval IMB-ELISA assay for rapid diagnosis of human toxoplasmosis using SAG1 antigens. Japan J Infect Dis 68(6):474–480. https://doi.org/10.7883/yoken.JJID.2014.444
Hikal WM, Bratovcic A, Baeshen RS, Tkachenko KG, Said-Al Ahl HAH (2021) Nanobiotechnology for the detection and control of waterborne parasites. Open J Ecol (OJE) 11:203–223. https://doi.org/10.4236/oje.2021.113016
Kefeni KK, Msagati TAM, Mamba BB (2017) Ferrite nanoparticles: synthesis, characterization and applications in electronic device. Mater Sci Eng, B 215:37–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mseb.2016.11.002
Khayyal AE, Mahmoud MSE, Ibrahim RB, Bayoumi IR, Badawy AF (2022) Diagnosis of human cystic echinococcosis by detecting antigen B in serum and urine using nanomagnetic beads-enzyme linked immunosorbent assay. J Egypt Soc Parasitol 52(3):491–500
Koura EA, Rabee I, Ahmed RO, Mohamed WA (2015) Using of paramagnetic nanoparticles with immunomagnetic bead ELISA in diagnosis of hydatidosis (Echinococcus granulosus). World J Pharm Sci 3(12):2292–2514
Lipman NS, Jackson LR, Trudel LJ, Weis-Garcia F (2005) Monoclonal versus polyclonal antibodies: distinguishingcharacteristics, applications, and information resources. ILAR J 46(3):258–268. https://doi.org/10.1093/ilar.46.3.258
Liu LN, Jing FJ, Cui J, Fu GY, Wang ZQ (2013) Detection of circulating antigen in serum of mice infected with Trichinella spiralis by an IgY-IgM mAb sandwich ELISA. Exp Parasitol 133(2):150–155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exppara.2012.11.001
Liu RD, Qi X, Sun G, Jiang P, Zhang X, Wang LA, Liu XL, Wang ZQ, Cui J (2016) Proteomic analysis of Trichinella spiralis adult worm excretory-secretory proteins recognized by early infection sera. Vet Parasitol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetpar.2016.10.008
Mayer-Scholl A, Pozio E, Gayda J, Thaben N, Bahn P, Nöckler K (2017) Magnetic stirrer method for the detection of Trichinella larvae in muscle samples. J Vis Exp 121:55354. https://doi.org/10.3791/55354
Morais V, Berasain P, Massaldi H (2014) Immunoglobulin purification by caprylic acid. Methods Mol Biol 1129:173–142. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-62703-977-2_13
Muñoz-Carrillo JL, Maldonado-Tapia C, López-Luna A, Muñoz-Escobedo JJ, Flores-De La Torre JA, Moreno-García A (2018): Current Aspects in Trichinellosis. In: Bastidas, G (Ed.) Parasites and Parasitic Diseases. https://dx.doi.org/https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen
Pozio E (2019) Trichinella and trichinellosis in Europe. Vet Glas 73(2):65–84. https://doi.org/10.2298/VETGL190411017P
Rainova I, Kaftandjiev I, Harizanov R, Tsvetkova N, Jordanova D, Marinova I, Kurdova R, Kantardjiev T, Lalkovski N (2016) Outbreaks of human trichinellosis, still a challenge for the public health authorities in Bulgaria. J Public Health 24:291–297. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10389-016-0724-9
Sun G, Wang Z, Liu C, Jiang P, Liu R, Wen H, Qi X, Wang L, Cui J (2015) Early serodiagnosis of trichinellosis by ELISA using excretory–secretory antigens of Trichinella spiralis adult worms. Parasites Vectors 8(484):1–8. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13071-015-1094-9
Sundar Sh, Singh A (2018) Chemotherapeutic of visceral leishmaniasis: present and future developments. Parasitol 145(4):481–489. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0031182017002116
Taher EE, Méabed EMH, El Akkad D, Kamel NO, Sabry MA (2017) Modified dot-ELISA for diagnosis of human trichinellosis. Exp Parasitol 177:40–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exppara.2017.04.002
Vashist SK (2013) Magnetic nanoparticles-based biomedical and bioanalytical applications. J Nanomed Nanotechol 4(2):e130–e132. https://doi.org/10.4172/2157-7439.1000e130
Wang ZQ, Shi YL, Liu RD, Jiang P, Guan YY, Chen YD, Cui J (2017) New insights on serodiagnosis of trichinellosis during window period: early diagnostic antigens from Trichinella spiralis intestinal worms. Infect Dis Poverty 6(1):41–45. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40249-017-0252-z
Wingfield PT (2016) Protein precipitation using ammonium sulfate. Curr Protoc Protein Sci. https://doi.org/10.1002/0471140864.psa03fs84
Yang J, Pan W, Sun X, Zhao X, Yuan G, Sun Q, Huang J, Zhu X (2015) Immunoproteomic profile of Trichinella spiralis adult worm proteins recognized by early infection sera. Parasit Vectors 8:20–31. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13071-015-0641-8
Yang Y, Cai YN, Tong MW, Sun N, Xuan YH, Kang YJ, Vallée I, Boireau P, Cheng ShP, Liu MY (2016) Serological tools for detection of Trichinella infection in animals and humans. One Health 2:25–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.onehlt.2015.11.005
Yew YP, Shameli K, Miyake M, Khairudin NBA, Mohamad SE, Naiki T, Lee KX (2018) Green biosynthesis of superparamagnetic magnetite Fe3O4 nanoparticles and biomedical applications in targeted anticancer drug delivery system: a review. Arab J Chem 13(1):2287–2308. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2018.04.013
Zumaquero-Ríos JL, García-Juarez J, De-la-Rosa-Arana JL, Marcet R, Sarracent-Pérez J (2012) Trichinella spiralis: monoclonal antibody against the muscular larvae for the detection of circulating and fecal antigens in experimentally infected rats. Exp Parasitol 132(4):444–449. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exppara.2012.09.016
Funding
No funds, grants, or other support were received for conducting this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The study conception and design were performed by Hanan Hussein Kamel and Noha Abdel Fattah Elleboudy. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by Aml Nabil Hasan and Ibrahim Rabea Ali. The draft of the manuscript was written by Omnia Sobhi Mohammad. All authors read, reviewed, and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Ethical approval
This study was performed in line with the principles and regulations of the Egyptian ministry of higher education and Helsinki declaration. The animal experiment was carried out according to the ILARC (Institute of Laboratory Animal Resources Commission) guidelines and principles for the care and use of laboratory animals. Approval was granted by the Ethics Committee of Faculty of Medicine, Ain Shams University (MS 597/2020).
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kamel, H.H., Elleboudy, N.A.F., Hasan, A.N. et al. Nano magnetic-based ELISA and nano magnetic-based latex agglutination test for diagnosis of experimental trichinellosis. J Parasit Dis 47, 400–409 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12639-023-01583-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12639-023-01583-w