Abstract
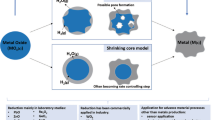
Iron ore powder was isothermally reduced at 1023–1373K with hydrogen/carbon monoxide gas mixture (from 0vol%H2/100vol%CO to 100vol%H2/0vol%CO). Results indicated that the whole reduction process could be divided into two parts that proceed in series. The first part represents a double-step reduction (Fe2O3→Fe3O4→FeO), in which the kinetic condition is more feasible compared with that in the second part representing a single-step reduction (FeO→Fe). The influence of hydrogen partial pressure on the reduction rate gradually increases as the reaction proceeds. The average reduction rate of hematite ore with pure hydrogen is about three and four times higher than that with pure carbon monoxide at 1173 and 1373 K, respectively. In addition, the logarithm of the average rate is linear to the composition of the gas mixture. Hydrogen can prominently promote carbon deposition to about 30% at 1023 K. The apparent activation energy of the reduction stage increases from about 35.0 to 45.4 kJ/mol with the increase in hydrogen content from 20vol% to 100vol%. This finding reveals that the possible rate-controlling step at this stage is the combined gas diffusion and interfacial chemical reaction.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M.C. Xie, G. Zhao, J.W. Chen, and K.L. Cao, Analysis of industrial metabolic flux in blast furnace ironmaking system, IOP Conf. Ser.: Earth Environ. Sci., 358(2019), No. 3, art. No. 032034.
Y. Kawashiri, T. Nouchi, and H. Matsuno, Effect of nitrogenless reducing atmosphere on permeability of cohesive layer in blast furnace, Tetsu-to-Hagane, 104(2018), No. 9, p. 467.
J. Tang, M.S. Chu, F. Li, C. Feng, Z.G. Liu, and Y.S. Zhou, Development and progress on hydrogen metallurgy, Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater., 27(2020), No. 6, p. 713.
W.H. Kim, S. Lee, S.M. Kim, and D.J. Min, The retardation kinetics of magnetite reduction using H2 and H2-H2O mixtures, Int. J. Hydrog. Energy, 38(2013), No. 10, p. 4194.
J. Dang, Y.J. Wu, Z.P. Lv, Z.X. You, S.F. Zhang, and X.W. Lv, A new kinetic model for hydrogen reduction of metal oxides under external gas diffusion controlling condition, Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater., 77(2018), p. 90.
R. Zhang, J. Dang, D. Liu, Z.P. Lv, G.Q. Fan, and L.W. Hu, Reduction of perovskite-geikielite by methane-hydrogen gas mixture: Thermodynamic analysis and experimental results, Sci. Total Environ., 699(2020), art. No. 134355.
A.A. El-Geassy and V. Rajakumar, Influence of particle size on the gaseous reduction of wustite at 900–1100°C, ISIJ Int., 25(1985), No. 12, p. 1202.
M.M. Sun, J.L. Zhang, K.J. Li, K. Guo, Z.M. Wang, and C.H. Jiang, Gasification kinetics of bulk coke in the CO2/CO/H2/H2O/N2 system simulating the atmosphere in the industrial blast furnace, Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater., 26(2019), No. 10, p. 1247.
M.N.A. Tahari, F. Salleh, T.S.T. Saharuddin, et al., Influence of hydrogen and various carbon monoxide concentrations on reduction behavior of iron oxide at low temperature, Int. J. Hydrog. Energy, 44(2019), No. 37, p. 20751.
R.A.D. Rodriguez, A.N. Conejo, and E.B. Bedolla, Kinetics of reduction of Fe2O3 particles with H2-CO mixtures at low temperatures, Iron & Steelmaker, 30(2003), No. 1, p. 25.
A. Bonalde, A. Henriquez, and M. Manrique, Kinetic analysis of the iron oxide reduction using hydrogen-carbon monoxide mixtures as reducing agent, ISIJ Int., 45(2005), No. 9, p. 1255.
A. Steinfeld, A. Frei, and P. Kuhn, Thermoanalysis of the combined Fe3O4-reduction and CH4-reforming processes, Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 26(1995), No. 3, p. 509.
N. Towhidi and J. Szekely, The influence of carbon deposition on the reduction kinetics of commercial grade hematite pellets with CO, H2, and N2, Metall. Trans. B, 14(1983), No. 3, p. 359.
P. Garg, X.J. Hu, Y. Li, K.J. Li, S. Nag, and J.L. Zhang, Kinetics of iron oxide reduction in H2/H2O gas mixture: Global and stepwise reduction, Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 53(2022), No. 3, p. 1759.
A.A. El-Geassy and M.I. Nasr, Influence of original structure on the kinetics and mechanisms of carbon monoxide reduction of hematite compacts, ISIJ Int., 30(1990), No. 6, p. 417.
W.E. Garner, Chemistry of the Solid State, Academic Press, New York, 1955.
A. Khawam and D.R. Flanagan, Solid-state kinetic models: Basics and mathematical fundamentals, J. Phys. Chem. B, 110(2006), No. 35, p. 17315.
A.A. El-Geassy and V. Rajakumar, Gaseous reduction of wustite with H2, CO and H2-CO mixtures, ISIJ Int., 25(1985), No. 6, p. 449.
X.J. Zuo, J.S. Wang, X.W. An, X.F. She, and Q.G. Xue, Reduction behaviors of pellets under different reducing potentials, J. Iron Steel Res. Int., 20(2013), No. 12, p. 12.
R.J. Fruehan, The rate of carburization of iron in CO-H2 atmospheres: Part I. Effect of temperature and CO and H2-pressures, Metall. Trans., 4(1973), No. 9, p. 2123.
S.H. Geng, Fundamental Research on Gas-based Direct Reduc- tion of Iron Ore with Reformed Coke Oven Gas [Dissertation], Shanghai University, Shanghai, 2018, p. 113.
A. Khawam and D.R. Flanagan, Complementary use of modelfree and modelistic methods in the analysis of solid-state kinetics, J. Phys. Chem. B, 109(2005), No. 20, p. 10073.
A.K. Galwey and M.E. Brown, Application of the Arrhenius equation to solid state kinetics: Can this be justified? Thermochim. Acta, 386(2002), No. 1, p. 91.
A. Khawam and D.R. Flanagan, Role of isoconversional methods in varying activation energies of solid-state kinetics: I. isothermal kinetic studies, Thermochim. Acta, 429(2005), No. 1, p. 93.
H. Tanaka, Thermal analysis and kinetics of solid state reactions, Thermochim. Acta, 267(1995), p. 29.
A. Ortega, The kinetics of solid-state reactions toward consensus—Part I: Uncertainties, failures, and successes of conventional methods, Int. J. Chem. Kinet., 33(2001), No. 6, p. 343.
B. Janković, B. Adnađević, and J. Jovanović, Application of model-fitting and model-free kinetics to the study of non-isothermal dehydration of equilibrium swollen poly (acrylic acid) hydrogel: Thermogravimetric analysis, Thermochim. Acta, 452(2007), No. 2, p. 106.
G. Munteanu, P. Budrugeac, L. Ilieva, T. Tabakova, D. Andreeva, and E. Segal, Kinetics of temperature programmed reduction of Fe3O4 promoted with copper: Application of iso-conversional methods, J. Mater. Sci., 38(2003), No. 9, p. 1995.
M.I. Nasr, A.A. Omar, M.H. Khedr, and A.A. El-Geassy, Effect of nickel oxide doping on the kinetics and mechanism of iron oxide reduction, ISIJ Int., 35(1995), No. 9, p. 1043.
Acknowledgements
The authors were very grateful for the financial support provided by Tata Steel Limited and State Key Laboratory of Advanced Metallurgy (USTB).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no potential conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mao, X., Garg, P., Hu, X. et al. Kinetic analysis of iron ore powder reaction with hydrogen—carbon monoxide. Int J Miner Metall Mater 29, 1882–1890 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-022-2512-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-022-2512-6