Abstract
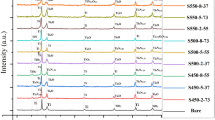
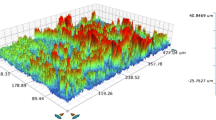
The hardness, wettability, and electrochemical properties of Ti6Al4V alloy surfaces treated with anodic oxidation and plasma oxidation as well as the viabilities of the different cell lines on the obtained surfaces were investigated. The anodic oxidation was performed for 10 min under 100 V potential, and it resulted in a 0.95 µm thick nanoporous anatase-TiO2 structure. On the other hand, plasma oxidation was carried out at 650°C for 1 h and resulted in a dense rutile-TiO2 structure with a thickness of 1.2 µm. While a hardness of HV0.025 823 and roughness of ∼220 nm were obtained by plasma oxidation, those obtained by anodic oxidation were HV0.025 512 and ∼130 nm, respectively. The anodic oxidation process created a more hydrophilic surface with a contact angle of 87.2°. Both oxidation processes produced similar properties in terms of corrosion behavior and showed better resistance than the as-received state in a certain range of potential. Moreover, the surface treatments led to no significant change in the protein adsorption levels, which indicates that the difference in viability between the osteoblast and fibroblast cells was not due to the difference in surface protein adsorption. Given all the factors, the surfaces obtained by anodic oxidation treatment revealed higher cell viability than those obtained by plasma oxidation (p = 0.05).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S.B. Goodman, Z.Y. Yao, M. Keeney, and F. Yang, The future of biologic coatings for orthopaedic implants, Biomaterial, 34(2013), No. 13, p. 3174.
C. Oldani and A. Dominguez, Titanium as a biomaterial for implants, [in] S. Fokter, ed., Recent Advances in Aetheoplasty, InTechOpen, London, 2012, p. 149.
M. Saini, Y. Singh, P. Arora, V. Arora and K. Jain, Implant biomaterials: A comprehensive review, Woeld J. Clin. Cases, 3(2015), No. 1, p. 52.
K. Wang, The use of titanium for medical applications in the USA, Matee. Sci. Eng. A, 213(1996), No. 1–2, p. 134.
A. Zieliński, S. Sobieszczyk, T. Seramak, W. Serbiński, B. Świeczko-Żurek, and A. Ossowska, Biocompatibility and bioactivity of load-bearing metallic implants, Adv. Matee. Sci., 10(2010), No. 4, p. 21.
A.F. Yetim, F. Yildiz, Y. Vangolu, A. Alsaran, and A. Celik, Several plasma diffusion processes for improving wear properties of Ti6Al4V alloy, Wear, 267(2009), No. 12, p. 2179.
P. Stratton and M. Graf, Wear of diffusion hardened Ti-6Al-4V sliding against tool steel, Wear, 268(2010), No. 3–4, p. 612.
X.Y. Liu, P.K. Chu, and C.X. Ding, Surface modification of titanium, titanium alloys, and related materials for biomedical applications, Mater. Sci. Eng. R, 47(2004), No. 3–4, p. 49.
S. Minagar, C.C. Berndt, J. Wang, E. Ivanova, and C.E. Wen, A review of the application of anodization for the fabrication of nanotubes on metal implant surfaces, Acta Biomater., 8(2012), No. 8, p. 2875.
B.E. Rapuano, H. Singh, A.L. Boskey, S.B. Doty, and D.E. MacDonald, Heat and radiofrequency plasma glow discharge pretreatment of a titanium alloy: Eveidence for enhanced osteoinductive properties, J. Cell. Biochem., 114(2013), No. 8, p. 1917.
D.E. MacDonald, B.E. Rapuano, P. Vyas, J.M. Lane, K. Meyers, and T. Wright, Heat and radiofrequency plasma glow discharge pretreatment of a titanium alloy promote bone formation and osseointegration, J. Cell. Biochem., 114(2013), No. 10, p. 2363.
K.L. Anderson, E.E. Apolinario, S.R. MacAuley, and K.R. Sowers, A 5′ leader sequence regulates expression of methanosarcinal CO dehydrogenase/acetyl coenzyme A synthase, J. Bacteriol., 191(2009), No. 22, p. 7123.
A. Pizzoferrato, G. Ciapetti, S. Stea, E. Cenni, C.R. Arciola, and D. Granchi, Cell culture methods for testing biocompatibility, Clin. Mater., 15(1994), No. 3, p. 173.
J.M. Anderson, Future challenges in the in vitro and in vivo evaluation of biomaterial biocompatibility, Regen. Biomater., 3(2016), No. 2, p. 73.
M. Rinner, J. Gerlach, and W. Ensinger, Formation of titanium oxide films on titanium and Ti6Al4V by O2-plasma immersion ion implantation, Surf. Coat. Technol., 132(2000), No. 2–3, p. 111.
M.A.M. Silva, A.E. Martinelli, C. Alves, R.M. Nascimento, M.P. Távora, and C.D. Vilar, Surface modification of Ti implants by plasma oxidation in hollow cathode discharge, Surf. Coat. Technol., 200(2006), No. 8, p. 2618.
F. Borgioli, E. Galvanetto, F.P. Galliano, and T. Bacci, Air treatment of pure titanium by furnace and glow-discharge processes, Surf. Coat. Technol., 141(2001), No. 1, p. 103.
S. Uttiya, D. Contarino, S. Prandi, M.M. Carnasciali, G. Gemme, L. Mattera, R. Rolandi, M. Canepa, and O. Cavalleri, Anodic oxidation of titanium in sulphuric acid and phosphoric acid electrolytes, J. Mater. Sci. Nanotechnol., 1(2014), No. 1, p. S106.
W. Asumpinwong, K. Saengkiettiyut, and V. Srimaneepong, Different constant voltages of anodization on the corrosion behavior of Ti-6Al-4V alloy, Chiang Mai J. Sci., 42(2015), No. 1, p. 239.
A.K. Sharma, Anodizing titanium for space applications, Thin Solid Films, 208(1992), No. 1, p. 48.
A. Lasia, Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy and its applications, [in] B.E. Conway, J.O. Bockris, and R.E. White, eds., Modern Aspects of Electrochemistry, Springer, Boston, 2002.
H.A. Acciari, D.P.S. Palma, E.N. Codaro, Q.Y. Zhou, J.P. Wang, Y.H. Ling, J.Z. Zhang, and Z.J. Zhang, Surface modifications by both anodic oxidation and ion beam implantation on electropolished titanium substrates, Appl. Surf. Sci., 487(2019), p. 1111.
H.D. Traid, M.L. Vera, A.E. Ares, and M.I. Litter, Porous titanium dioxide coatings obtained by anodic oxidation for photocatalytic applications, Procedia Mater. Sci., 9(2015), p. 619.
T.A. Soares, H. Mozaffari, and H. Reinecke, Generation of microstructures on a Ti-6Al-4V substrate through anodization, Surf. Coat. Technol., 278(2015), p. 64.
K. Satoh, S. Sato, and K. Wagatsuma, Formation mechanism of toxic-element-free oxide layer on Ti-6Al-4V alloy in d.c. glow discharge plasma with pure oxygen gas, Surf. Coat. Technol., 302(2016), p. 82.
A. Çelik, M. Aslan, A.F. Yetim, and Ö. Bayrak, Wear behavior of plasma oxidized CoCrMo alloy under dry and simulated body fluid conditions, J. Bionic Eng., 11(2014), No. 2, p. 303.
M. Aslan, O. Çomaklı, M. Yazıcı, A.F. Yetim, Ö. Bayrak, and A. Çelik, The effect of plasma oxidation and nitridation on corrosion behavior of CoCrMo alloy in SBF solution, Surf. Rev. Lett., 25(2018), No. 08, art. No. 1950024.
A. Çelik, Ö. Bayrak, A. Alsaran, İ. Kaymaz, and A.F. Yetim, Effects of plasma nitriding on mechanical and tribological properties of CoCrMo alloy, Surf. Coat. Technol., 202(2008), No. 11, p. 2433.
A. Yli-Pentti, Electroplating and electroless plating, [in] S. Hashmi, G.F. Batalha, C.J.V. Tyne, and B. Yilbas, eds., Comprehensive Materials Processing, Elsevier, 2014.
A.C. Alves, F. Wenger, P. Ponthiaux, J.P. Celis, A.M. Pinto, L.A. Rocha, and J.C.S. Fernandes, Corrosion mechanisms in titanium oxide-based films produced by anodic treatment, Electrochim. Acta, 234(2017), p. 16.
D. Veys-Renaux, Z.A.E. Haj, and E. Rocca, Corrosion resistance in artificial saliva of titanium anodized by plasma electrolytic oxidation in Na3PO4, Surf. Coat. Technol., 285(2016), p. 214.
K. Elagli, M. Traisnel, and H.F. Hildebrand, Electrochemical behaviour of titanium and dental alloys in artificial saliva, Electrochim. Acta, 38(1993), No. 13, p. 1769.
K.Y. Cai, J. Bossert, and K.D. Jandt, Does the nanometre scale topography of titanium influence protein adsorption and cell proliferation?, Colloids Surf. B, 49(2006), No. 2, p. 136.
B.E. Li, J. Li, C.Y. Liang, H.P. Li, L.T. Guo, S.M. Liu, and H.S. Wang, Surface roughness and hydrophilicity of titanium after anodic oxidation, Rare Met. Mater. Eng., 45(2016), No. 4, p. 858.
M. Lukaszewska-Kuska, P. Wirstlein, R. Majchrowski, and B. Dorocka-Bobkowska, Osteoblastic cell behaviour on modified titanium surfaces, Micron, 105(2018), p. 55.
A. Wennerberg and T. Albrektsson, Effects of titanium surface topography on bone integration: A systematic review, Clin. Oral Implan. Res., 20(2009), No. s4, p. 172.
M. Bachle and R.J. Kohal, A systematic review of the influence of different titanium surfaces on proliferation, differentiation and protein synthesis of osteoblast-like MG63 cells, Clin. Oral Implan. Res., 15(2004), No. 6, p. 683.
L.L. Guehennec, M.A. Lopez-Heredia, B. Enkel, P. Weiss, Y. Amouriq, and P. Layrolle, Osteoblastic cell behaviour on different titanium implant surfaces, Acta Biomater., 4(2008), No. 3, p. 535.
L. Crespo, M. Hierro-Oliva, S. Barriuso, V. Vadillo-Rodríguez, M.Á. Montealegre, L. Saldaña, E. Gomez-Barrena, J.L. González-Carrasco, M.L. González-Martín, and N. Vilaboa, On the interactions of human bone cells with Ti6Al4V thermally oxidized by means of laser shock processing, Biomed. Mater., 11(2016), No. 1, art. No. 015009.
C.H. Ku, D.P. Pioletti, M. Browne, and P.J. Gregson, Effect of different Ti-6Al-4V surface treatments on osteoblasts behaviour, Biomaterials, 23(2002), No. 6, p. 1447.
J. Chen, S. Mwenifumbo, C. Langhammer, J.P. McGovern, M. Li, A. Beye, and W.O. Soboyejo, Cell/surface interactions and adhesion on Ti-6Al-4V: Effects of surface texture, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B, 82(2007), No. 2, p. 360.
W. de Melo Silva, C.A. Ribeiro, C.S. Marques, A.S. Tabata, M.J. Saeki, L.I. Medeiros, and D.E. de Oliveira, Fibroblast and pre-osteoblast cell adhesive behavior on titanium alloy coated with diamond film, Mater. Res., 20(2017), No. 2 suppl, p. 284.
Y. Shibata and Y. Tanimoto, A review of improved fixation methods for dental implants Part I: Surface optimization for rapid osseointegration, J. Prosthodont. Res., 59(2015), No. 1, p. 20.
J.H. Park, R. Olivares-Navarrete, R.E. Baier, A.E. Meyer, R. Tannenbaum, B.D. Boyan, and Z. Schwartz, Effect of cleaning and sterilization on titanium implant surface properties and cellular response, Acta Biomater., 8(2012), No. 5, p. 1966.
E. Czarnowska A. Sowinska, B. Cukrowska, J.R. Sobiecki, and T. Wierzchoñ, Response of human osteoblast-like cells and fibroblasts to titanium alloy nitrided under glow discharge conditions, Mater. Sci. Forum, 475–479(2005), p. 2415.
E. Czarnowska, T. Wierzchoñ, and A. Maranda-Niedbala Properties of the surface layers on titanium alloy and their biocompatibility in in vitro eetts, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 92–93(1999), p. 190.
S. Bruni, M. Martinesi, M. Stio, C. Treves, T. Bacci, and F. Borgioli, Effects of surface treatment of Ti-6A1-4V titanium alloy on biocompatibility in cultured human umbilical vein endothelial cells, Acta Biomater., 1(2005), No. 2, p. 223.
C. Treves, M. Martinesi, M. Stio, A. Gutiérrez, J.A. Jiménez, and M.F. López, In vitro biocompatibility evaluation of surface-modified titanium alloys, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A, 92(2010), No. 4, p. 1623.
C.F. Huang, H.C. Cheng, C.M. Liu, C.C. Chen, and K.L. Ou, Microstructure and phase transition of biocompatible titanium oxide film on titanium by plasma discharging, J. Alloys Compd., 476(2009), No. 1–2, p. 683.
A. El-Ghannam, L. Starr, and J. Jones, Laminin-5 coating enhances epithelial cell attachment, spreading, and hemidesmosome assembly on Ti-6Al-4V implant material in vitro, J. Biomed. Mater. Res., 41(1998), No. 1, p. 30.
M. Martinesi, S. Bruni, M. Stio, C. Treves, and F. Borgioli, In vitro interaction between surface-treated Ti-6Al-4V titanium alloy and human peripheral blood mononuclear cells, J. Boomed. Mater. Res. Part A, 74(2005), No. 2, p. 197.
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by Erzincan Binali Yıldırım University Research Fund (No. FBA-2018-547). Authors acknowledge Prof. Dr. Bora Garipcan for enabling the authors to Biomaterials Laboratory of Biomedical Engineering Institute, Boǧaziçi University and Prof. Dr. Ayhan Çelik for permitting the use of glow discharge plasma oxidation at Mechanical Engineering Laboratory in Ataturk University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bayrak, Ö., Ghahramanzadeh Asl, H. & Ak, A. Protein adsorption, cell viability and corrosion properties of Ti6Al4V alloy treated by plasma oxidation and anodic oxidation. Int J Miner Metall Mater 27, 1269–1280 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-020-2020-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-020-2020-5