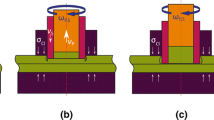
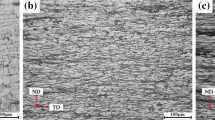
Abstract
In this study, we used the stop-action technique to experimentally investigate the material flow and microstructural evolution of al-clad 2A12-T4 aluminum alloy during refill friction stir spot welding. There are two material flow components, i.e., the inward- or outward-directed spiral flow on the horizontal plane and the upward- or downward-directed flow on the vertical plane. In the plunge stage, the flow of plasticized metal into the cavity is similar to that of a stack, whereby the upper layer is pushed upward by the lower layer. In the refill stage, this is process reversed. As such, there is no obvious vertical plasticized metal flow between adjacent layers. Welding leads to the coarsening of S (Al2CuMg) in the thermo-mechanically affected zone and the diminishing of S in the stir zone. Continuous dynamic recrystallization results in the formation of fine equiaxed grains in the stir zone, but this process becomes difficult in the thermo-mechanically affected zone due to the lower deformation rate and the pinning action of S precipitates on the dislocations and sub-grain boundaries, which leads to a high fraction of low-angle grain boundaries in this zone.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
G.H. Li, L. Zhou, W.L. Zhou, X.G. Song, and Y.X. Huang, Influence of dwell time on microstructure evolution and mechanical properties of dissimilar friction stir spot welded aluminum-copper metals, J. Mater. Res. Technol., 8(2019), No. 3, p. 2613.
R.R. Patil, C.J.K. Anurag Tilak, V. Srivastava, and A. De, Minimising electrode wear in resistance spot welding of aluminium alloys, Sci. Technol. Weld. Joining, 16(2011), No. 6, p. 509.
Z.W. Xu, Z.W. Li, S.D. Ji, and L.G. Zhang, Refill friction stir spot welding of 5083-O aluminum alloy, J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 34(2018), No. 5, p. 878.
U.F.H. Suhuddin, V. Fischer, and J.F. dos Santos, The thermal cycle during the dissimilar friction spot welding of aluminum and magnesium alloy, Scripta Mater., 68(2013), No. 1, p. 87.
Y.X. Huang, B. Han, S.X. Lv, J.C. Feng, H.J. Liu, J.S. Leng, and Y. Li, Interface behaviours and mechanical properties of filling friction stir weld joining AA 2219, Sci. Technol. Weld. Joining, 17(2012), No. 3, p. 225.
M.D. Tier, T.S. Rosendo, J.F. Dos Santos, N. Huber, J.A. Mazzaferro, C.P. Mazzaferro, and T.R. Strohaecker, The influence of refill FSSW parameters on the microstructure and shear strength of 5042 aluminium welds, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 213(2013), No. 6, p. 997.
Z.K. Shen, X.Q. Yang, Z.H. Zhang, L. Cui, and T.L. Li, Microstructure and failure mechanisms of refill friction stir spot welded 7075-T6 aluminum alloy joints, Mater. Des., 44(2013), p. 476.
T. Rosendo, B. Parra, M.A.D. Tier, A.A.M. da Silva, J.F. dos Santos, T.R. Strohaecker, and N.G. Alcântara, Mechanical and microstructural investigation of friction spot welded AA6181-T4 aluminium alloy, Mater. Des., 32(2011), No. 3, p. 1094.
J.Y. Cao, M. Wang, L. Kong, and L.J. Guo, Hook formation and mechanical properties of friction spot welding in alloy 6061-T6, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 230(2016), p. 254.
Y.Q. Zhao, H.J. Liu, S.X. Chen, Z. Lin, and J.C. Hou, Effects of sleeve plunge depth on microstructures and mechanical properties of friction spot welded alclad 7B04-T74 aluminum alloy, Mater. Des., 62(2014), p. 40.
P.B. Prangnell and C.P. Heason, Grain structure formation during friction stir welding observed by the ‘stop action technique’, Acta Mater., 53(2005), No. 11, p. 3179.
J. Shen, S.B.M. Lage, U.F.H. Suhuddin, C. Bolfarini, and J.F. dos Santos, Texture development and material flow behavior during refill friction stir spot welding of AlMgSc, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 49(2018), No. 1, p. 241.
J.Y. Cao, M. Wang, L. Kong, Y.H. Yin, and L.J. Guo, Numerical modeling and experimental investigation of material flow in friction spot welding of Al 6061-T6, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 89(2017), No. 5–8, p. 2129.
S.T. Amancio-filho, A.P.C. Camillo, L. Bergmann, J.F. dos Santos, S.E. Kury, and N.G.A. Machado, Preliminary investigation of the microstructure and mechanical behaviour of 2024 aluminium alloy friction spot welds, Mater. Trans., 52(2011), No. 5, p. 985.
Y.C. Lin, Y.C. Xia, Y.Q. Jiang, and L.T. Li, Precipitation in Al-Cu-Mg alloy during creep exposure, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 556(2012), p. 796.
S.C. Wang, M.J. Starink, and N. Gao, Precipitation hardening in Al-Cu-Mg alloys revisited, Scripta Mater., 54(2006), No. 2, p. 287.
G.R. Ebrahimi and H.R. Ezatpour, Effect of precipitation on the warm deformation behavior of AA2024 alloy, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 681(2017), p. 10.
W.C. Wu, Y.J. Wang, J.B. Wang, and S.M. Wei, Effect of electrical pulse on the precipitates and material strength of 2024 aluminum alloy, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 608(2014), p. 190.
M.J. Starink, N. Gao, L. Davin, J. Yan, and A. Cerezo, Room temperature precipitation in quenched Al-Cu-Mg alloys: a model for the reaction kinetics and yield strength development, Philos. Mag., 85(2005), No. 13, p. 1395.
C. Genevois, A. Deschamps, A. Denquin, and B. Doisneau-Cottignies, Quantitative investigation of precipitation and mechanical behaviour for AA2024 friction stir welds, Acta Mater., 53(2005), No. 8, p. 2447.
S. Cheng, Y.H. Zhao, Y.T. Zhu, and E. Ma, Optimizing the strength and ductility of fine structured 2024 Al alloy by nanoprecipitation, Acta Mater., 55(2007), No. 17, p. 5822.
G. Avramovic-Cingara, D.D. Perovic, and H.J. Mcqueen, Hot deformation mechanisms of a solution-treated Al-Li-Cu-Mg-Zr alloy, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 27(1996), No. 11, p. 3478.
A. Gerlich, P. Su, M. Yamamoto, and T.H. North, Effect of welding parameters on the strain rate and microstructure of friction stir spot welded 2024 aluminum alloy, J. Mater. Sci., 42(2007), p. 5589.
M.J. Jones, P. Heurtier, C. Desrayaud, F. Montheillet, D. Allehaux, and J.H. Driver, Correlation between microstructure and microhardness in a friction stir welded 2024 aluminium alloy, Scripta Mater., 52(2005), No. 8, p. 693.
K.V. Jata and S.L. Semiatin, Continuous dynamic recrystallization during friction stir welding of high strength aluminum alloys, Scripta Mater., 43(2000), No. 8, p. 743.
J. Han, J. Sun, T.Y. Wen, and F. Guo, Analysis of continuous recrystallization (sub) grain rotation behavior in Pb-free solder bumps under a 0.1 μm/s shear rate, J. Mater. Sci.-Mater. Electron., 29(2018), No. 13, p. 10992.
J.Q. Su, T.W. Nelson, R. Mishra, and M. Mahoney, Microstructural investigation of friction stir welded 7050-T651 aluminium, Acta Mater., 51(2003), No. 3, p. 713.
Acknowledgements
This research was financially supported by the National Science and Technology Major Project of China (No. 2017ZX04005001) and the Key Research & Development program of Shandong Province (2018GGX103053).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Gh., Zhou, L., Luo, Ly. et al. Material flow behavior and microstructural evolution during refill friction stir spot welding of alclad 2A12-T4 aluminum alloy. Int J Miner Metall Mater 28, 131–141 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-020-1998-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-020-1998-z