Abstract
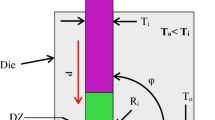
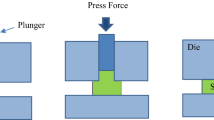
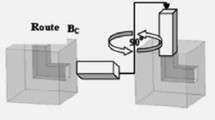
Equal-channel angular pressing (ECAP) is a prominent technique that imposes severe plastic deformation into materials to enhance their mechanical properties. In this research, experimental and numerical approaches were utilized to investigate the mechanical properties, strain behavior, and damage prediction of ECAPed 7025 aluminum alloy in various conditions, such as die channel angle, outer corner angle, and friction coefficient. Experimental results indicate that, after the first pass, the yield strength, ultimate tensile strength, and hardness magnitude are improved by approximately 95%, 28%, and 48.5%, respectively, compared with the annealed state, mainly due to grain refinement during the deformation. Finite element analysis shows that the influence of die channel angle is more important than that of outer corner angle or friction coefficient on both the strain behavior and the damage prediction. Also, surface cracks are the main cause of damage during the ECAP process for every die channel angle except for 90°; however, the cracks initiated from the neighborhood of the central regions are the possible cause of damage in the ECAPed sample with the die channel angle of 90°.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R.Z. Valiev, R.K. Islamgaliev, and I.V. Alexandrov, Bulk nanostructured materials from severe plastic deformation, Prog. Mater Sci., 45(2000), p. 103.
R.Z. Valiev and T.G. Langdon, Principles of equal-channel angular pressing as a processing tool for grain refinement, Prog. Mater. Sci., 51(2006), p. 881.
A. Azushima, R. Kopp, A. Korhonen, D.Y. Yang, F. Micari, G.D. Lahoti, P. Groche, J. Yanagimoto, N. Tsuji, A. Rosochowski, and A. Yanagida, Severe plastic deformation (SPD) processes for metals, CIRP Ann. Manuf. Technol., 57(2008), p. 716.
T.G. Langdon, Twenty-five years of ultrafine-grained materials: achieving exceptional properties through grain refinement, Acta Mater., 61(2013), p. 7035.
M. Shaarbaf and M.R. Toroghinejad, Nano-grained copper strip produced by accumulative roll bonding process, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 473(2008), p. 28.
A.P. Zhilyaev and T.G. Langdon, Using high-pressure torsion for metal processing: Fundamentals and applications, Prog. Mater. Sci., 53(2008), p. 893.
Q. Chen, D.Y. Shu, C.K. Hu, Z.D. Zhao, and B.G. Yuan, Grain refinement in an as-cast AZ61 magnesium alloy processed by multi-axial forging under the multitemperature processing procedure, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 541(2012), p. 98.
C.P. Wang, F.G. Li, Q.H. Li, and L. Wang, Numerical and experimental studies of pure copper processed by a new severe plastic deformation method, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 548(2012), p. 19.
V.M. Segal, Equal channel angular extrusion: from macromechanics to structure formation, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 271(1999), p. 322.
B.Q. Han and T.G. Langdon, Improving the high-temperature mechanical properties of a magnesium alloy by equal-channel angular pressing, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 410–411(2005), p. 435.
F. Akbaripanah, F. Fereshteh-Saniee, R. Mahmudi, and H.K. Kim, The influences of extrusion and equal channel angular pressing (ECAP) processes on the fatigue behavior of AM60 magnesium alloy, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 565(2013), p. 308.
W.J. Zhao, H. Ding, Y.P. Ren, S.M. Hao, J. Wang, and J.T. Wang, Finite element simulation of deformation behavior of pure aluminum during equal channel angular pressing, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 410–411(2005), p. 348.
A. Rebhi, T. Makhlouf, N. Njah, Y. Champion, and J.P. Couzinié, Characterization of aluminum processed by equal channel angular extrusion: effect of processing route, Mater. Charact., 60(2009), p. 1489.
C.J. Luis-Pérez, R. Luri-Irigoyen, and D. Gastón-Ochoa, Finite element modelling of an Al-Mn alloy by equal channel angular extrusion (ECAE), J. Mater. Process. Technol., 153–154(2004), p. 846.
F.Q. Yang, A. Saran, and K. Okazaki, Finite element simulation of equal channel angular extrusion, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 166(2005), p. 71.
H.S. Kim, M.H. Seo, and S.I. Hong, On the die corner gap formation in equal channel angular pressing, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 291(2000), p. 86.
S. Dumoulin, H.J. Roven, J.C. Werenskiold, and H.S. Valberg, Finite element modeling of equal channel angular pressing: Effect of material properties, friction and die geometry, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 410–411(2005), p. 248.
S.B. Xu, G.Q. Zhao, X.W. Ma, and G.C. Ren, Finite element analysis and optimization of equal channel angular pressing for producing ultra-fine grained materials, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 184(2007), p. 209.
H.S. Kim, M.H. Seo, and S.I. Hong, Plastic deformation analysis of metals during equal channel angular pressing, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 113(2001), p. 622.
S.C. Yoon, P. Quang, S.I. Hong, and H.S. Kim, Die design for homogeneous plastic deformation during equal channel angular pressing, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 187–188(2007), p. 46.
B.S. Moon, H.S. Kim, and S.I. Hong, Plastic flow and deformation homogeneity of 6061 Al during equal channel angular pressing, Scripta Mater., 46(2002), p. 131.
S.C. Yoon, H.G. Jeong, S. Lee, and H.S. Kim, Analysis of plastic deformation behavior during back pressure equal channel angular pressing by the finite element method, Comput. Mater. Sci., 77(2013), p. 202.
A.V. Nagasekhar, Y. Tick-Hon, and H.P. Seow, Deformation behavior and strain homogeneity in equal channel angular extrusion/pressing, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 192–193(2007), p. 449.
V.N. Anumalasetty, T. Yip, S. Li, and H.P. Seow, Effect of acute tool-angles on equal channel angular extrusion/pressing, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 410–411(2005), p. 269.
N.E. Mahallawy, F.A. Shehata, M.A.E. Hameed, M.I.A.E. Aal, and H.S. Kim, 3D FEM simulations for the homogeneity of plastic deformation in Al-Cu alloys during ECAP, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 527(2010), p. 1404.
S.K. Lu, H.Y. Liu, L. Yu, Y.L. Jiang, and J.H. Su, 3D FEM simulations for the homogeneity of plastic deformation in aluminum alloy HS6061-T6 during ECAP, Procedia Eng., 12(2011), p. 35.
M.S. Ghazani and B. Eghbali, Finite element simulation of cross equal channel angular pressing, Comput. Mater. Sci., 74(2013), p. 124.
X.N. Zhang, L. Hua, and Y.X. Liu, FE simulation and experimental investigation of ZK60 magnesium alloy with different radial diameters processed by equal channel angular pressing, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 535(2012), p. 153.
R.B. Figueiredo, P.R. Cetlin, and T.G. Langdon, The evolution of damage in perfect-plastic and strain hardening materials processed by equal-channel angular pressing, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 518(2009), p. 124.
F. Djavanroodi and M. Ebrahimi, Effect of die channel angle, friction and back pressure in the equal channel angular pressing using 3D finite element simulation, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 527(2010), p. 1230.
R.K. Oruganti, P.R. Subramanian, J.S. Marte, M.F. Gigliotti, and S. Amancherla, Effect of friction, backpressure and strain rate sensitivity on material flow during equal channel angular extrusion, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 406(2005), p. 102.
F. Djavanroodi and M. Ebrahimi, Effect of die parameters and material properties in ECAP with parallel channels, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 527(2010), p. 7593.
A.T. Male and M.G. Cockcroft, A method for the determination of the coefficient of friction of metals under condition of bulk plastic deformation, J. Inst. Met., 93(1964), p. 38.
H.J. Hu, D.F. Zhang, and F.S. Pan, Die structure optimization of equal channel angular extrusion for AZ31 magnesium alloy based on finite element method, Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China, 20(2010), p. 259.
P. Venkatachalam, S.R. Kumar, B. Ravisankar, V.T. Paul, and M. Vijayalakshmi, Effect of processing routes on microstructure and mechanical properties of 2014 Al alloy processed by equal channel angular pressing, Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China, 20(2010), p. 1822.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ebrahimi, M., Attarilar, S., Gode, C. et al. Damage prediction of 7025 aluminum alloy during equal-channel angular pressing. Int J Miner Metall Mater 21, 990–998 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-014-1000-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-014-1000-z