Abstract
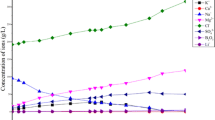
Identifying interactions among river water, groundwater and salt lake brine is important for sustainable exploitation of brine mineral resources. In this study, we investigated the water exchange rate in dry and wet seasons, and assessed the influence of seasonal water exchange on brine concentration and crystallization process in the Nalenggele (NLGL) catchment of Qaidam Basin, China. The results show that the surface water infiltration and groundwater recharge rates in the wet season were 2.81 × 10−3 and 1.15 × 10−3 m3/(s·m) in upstream, 1.63 × 10−2 and 1.53 × 10−2 m3/(s·m) in midstream, and 2.83 × 10−4 and 6.82 × 10−5 m3/(s·m) in downstream, respectively; while their counterparts in the dry season were 9.81 × 10−4 and 5.05 × 10−4 m3/(s·m) in upstream, and 8.34 × 10−3 and 7.78 × 10−3 m3/(s·m) in midstream, respectively. The water exchange strongly influenced brine concentration and crystallinzation process, with brine chemistry belonging to 3K2SO4·Na2SO4 and KCl types in wet and dry seasons, respectively. The strong water exchange in wet season destroyed the water-salt balance, while the low water exchange rate in dry season facilitated preparation of KCl products.
Similar content being viewed by others
References Cited
Batelaan, O., de Smedt, F., Triest, L., 2003. Regional Groundwater Discharge: Phreatophyte Mapping, Groundwater Modelling and Impact Analysis of Land-Use Change. Journal of Hydrology, 275(1/2):86–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0022-1694(03)00018-0
Bischoff, J. L., Israde-Alcántara, I., Garduño-Monroy, V. H., et al., 2004. The Springs of Lake Pátzcuaro: Chemistry, Salt-Balance, and Implications for the Water Balance of the Lake. Applied Geochemistry, 19(11):1827–1835. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2004.04.003
Bouchez, C., Cook, P. G., Partington, D., et al., 2021. Comparison of Surface Water-Groundwater Exchange Fluxes Derived from Hydraulic and Geochemical Methods and a Regional Groundwater Model. Water Resources Research, 57(3):e2020wr029137. https://doi.org/10.1029/2020wr029137
Chen, J. N., Fan, Z. L., Ma, Z. D., et al., 2018. Report on the Resource Reserves of Lithium, Boron, Potash Ore in Dong-Taijinaier Salt Lake, Qaidam Basin. Qinghai Institute of Geology and Mineral Exploration, Xining (in Chinese)
Cook, P. G., Favreau, G., Dighton, J. C., et al., 2003. Determining Natural Groundwater Influx to a Tropical River Using Radon, Chlorofluorocarbons and Ionic Environmental Tracers. Journal of Hydrology, 277(1/2):74–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0022-1694(03)00087-8
Cook, P. G., Lamontagne, S., Berhane, D., et al., 2006. Quantifying Groundwater Discharge to Cockburn River, Southeastern Australia, Using Dissolved Gas Tracers 222Rn and SF6. Water Resources Research, 42(10):W10411. https://doi.org/10.1029/2006wr004921
Clark, I. D., Fritz, P., 1997. Environmental Isotopes in Hydrogeology. Lewis Publishers, Boca Raton
Craig, H., 1961. Isotopic Variations in Meteoric Waters. Science, 133(3465):1702–1703. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.133.3465.1702
Dimova, N. T., Burnett, W. C., 2011. Evaluation of Groundwater Discharge into Small Lakes Based on the Temporal Distribution of Radon-222. Limnology and Oceanography, 56(2):486–494. https://doi.org/10.4319/lo.2011.56.2.0486
Dimova, N. T., Burnett, W. C., Chanton, J. P., et al., 2013. Application of Radon-222 to Investigate Groundwater Discharge into Small Shallow Lakes. Journal of Hydrology, 486:112–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2013.01.043
Ellins, K. K., Roman-Mas, A., Lee, R., 1990. Using 222Rn to Examine Groundwater/Surface Discharge Interaction in the Rio Grande de Manati, Puerto Rico. Journal of Hydrology, 115(1/2/3/4):319–341. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-1694(90)90212-g
Fu, X. C., Wang, F., Wang, H., et al., 2011. Analysis of Long-Term Changes Intemperature and Precipitation and Their Relationships with Water Resources in the Qaidam Basin in China. Resource Science, 33(3):408–415 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Gat, J., 2010. Isotopes in the Hydrological Cycle. Springer, Netherland. 127–137
Gu, W. Z., Pang, Z. H., Wang, J. Q., et al., 2011. Isotope Hydrology. Science Press, Beijing. 1113 (in Chinese)
Guo, S. Y., Li, W., Zhang, S. H., et al., 2012. Numerical Simulation of the Second Period Water Source Area of Water Supply for Salt Lake Group in Qinghai Province. South-to-North Water Diversion and Water Science & Technology, 10(4):116–120 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Han, J. B., Xu, J. X., Hussain, S. A., et al., 2021. Origin of Boron in the Gas Hure Salt Lake of Northwestern Qaidam Basin, China: Evidence from Hydrochemistry and Boron Isotopes. Acta Geologica Sinica-English Edition, 95(2):531–540. https://doi.org/10.1111/1755-6724.14377.
Han, G., Han, J. B., Liu, J. B., et al., 2020. Variation Characteristics of LiCl Deposit under Condition of Mining in East Taijnar Salt Lake, Qaidam Basin. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 25(12):17–22 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Han, J. B., Jiang, H. C., Xu, J. X., et al., 2018. Hydraulic Connection Affects Uranium Distribution in the Gas Hure Salt Lake, Qaidam Basin, China. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 25(5):4881–4895. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0722-7
Jia, S. D., Dai, Z. X., Du, X. Q., et al., 2021. Quantitative Evaluation of Groundwater and Surface Water Interaction Characteristics during a Dry Season. Water and Environment Journal, 35(4):1348–1361. https://doi.org/10.1111/wej.12734
Kendall, C., McDonnell, J. J., 1998. Isotope Tracers in Catchment Hydrology. Elsevier Science, 291–318
Kong, N., Tao, Q., Tan, H. B., et al., 2014. Distribution of Isotopes and Runoff Variation of the Rivers in the Qaidam Basin. Arid Zone Research, 31(5):948–954 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Li, T. W., 2007. The Origin Analysis by Hydrochemical Characters and Sr Isotope of Oil Field Brines in West of Qaidam Basin: [Dissertation]. Qinghai Insititute of Salt Lakes, CAS, Xining. 1–54 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Li, S. N., 2020. Evaluation of Surface-Groundwater Interactions in Golmud River Basin Using Hydrochemical and Isotopic Methods: [Dissertation]. Northwest Institute of Eco-Environment and Resources, CAS, Lanzhou. 1–64 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Liao, F., Wang, G. C., Shi, Z. M., et al., 2018. Estimation of Groundwater Discharge and Associated Chemical Fluxes into Poyang Lake, China: Approaches Using Stable Isotopes (δD and δ18O) and Radon. Hydrogeology Journal, 26(5):1625–1638. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-018-1793-3
Liu, Y. H., Li, H. M., Wen, T. T., et al., 2021. Risk Zoning of Summer Rainstorm Disaster and Its Influence in Qaidam Basin. Arid Zone Research, 38(3): 757–763 (in Chinese with English Abstract) Lu, N., 2014. Change of Lake Area in Qaidam Basin and the Influence Factors. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 28(8):83–87 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Oh, Y. H., Koh, D. C., Kwon, H. I., et al., 2021. Identifying and Quantifying Groundwater Inflow to a Stream Using 220Rn and 222Rn as Natural Tracers. Journal of Hydrology: Regional Studies, 33:100773. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrh.2021.100773
Ortega, L., Manzano, M., Custodio, E., et al., 2015. Using 222Rn to Identify and Quantify Groundwater Inflows to the Mundo River (SE Spain). Chemical Geology, 395:67–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2014.12.002
Peng, T. H., Takahashi, T., Broecker, W. S., 1974. Surface Radon Measurements in the North Pacific Ocean Station Papa. Journal of Geophysical Research, 79(12):1772–1780. https://doi.org/10.1029/jc079i012p01772
Qin, W. J., Han, D. M., Song, X. F., et al., 2021. Environmental Isotopes (δ18O, δ2H, 222Rn) and Hydrochemical Evidence for Understanding Rainfall-Surface Water-Groundwater Transformations in a Polluted Karst Area. Journal of Hydrology, 592:125748. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2020.125748.
Rong, G. Z., Tan, G. P., Zhu, C. H., 2002. Exploration Report of Lithium, Boron and Potassium Deposits in Dong-Taijinaier Salt Lake, Qaidam Basin. Qinghai Institute of Geology and Mineral Exploration, Xining (in Chinese)
Santos, I. R., Peterson, R. N., Eyre, B. D., et al., 2010. Significant Lateral Inputs of Fresh Groundwater into a Stratified Tropical Estuary: Evidence from Radon and Radium Isotopes. Marine Chemistry, 121(1/2/3/4):37–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marchem.2010.03.003
Shi, R. L., Liu, Y. F., Wang, S. J., et al., 2021. Water Demand Research and Security Analysis of Salt Lake Ecology — — A Case Study of Chaerhan Salt Lake. China Water Resources, 15:34–35 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Stellato, L., Petrella, E., Terrasi, F., et al., 2008. Some Limitations in Using 222Rn to Assess River—Groundwater Interactions: The Case of Castel Di Sangro Alluvial Plain (Central Italy). Hydrogeology Journal, 16(4):701–712. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-007-0263-0
Su, X. S., Xu, W., Yang, F. T., et al., 2015. Using New Mass Balance Methods to Estimate Gross Surface Water and Groundwater Exchange with Naturally Occurring Tracer 222Rn in Data Poor Regions: A Case Study in Northwest China. Hydrological Processes, 29(6):979–990. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.10208
Tai, Y. Y., 2015. Analysis on the Developing Schemes of Groundwater Resources of Naturel Groundwater Reservoir in Nalenggele River Alluvial-Proluvial Fan: [Dissertation]. Jilin University, Changchun (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Tan, H. B., Chen, J., Rao, W. B., et al., 2012. Geothermal Constraints on Enrichment of Boron and Lithium in Salt Lakes: an Example from a River-Salt Lake System on the Northern Slope of the Eastern Kunlun Mountains, China. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 51:21–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jseaes.2012.03.002
Wang, J. W., Huang, J. T., Fang, T., et al., 2021. Relationship of Uunderground Water Level and Climate in Northwest China’s Inland Basins under the Global Climate Change: Taking the Golmud River Catchment as an Example. China Geology, 4:402–409. 110.31035/cg2021064
Wang, W. K., Dai, Z. X., Zhao, Y. Q., et al., 2016. A Quantitative Analysis of Hydraulic Interaction Processes in Stream-Aquifer Systems. Scientific Reports, 6:19876. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep19876
Wang, Z., Wang, L. J., Shen, J. M., et al., 2021. Groundwater Characteristics and Climate and Ecological Evolution in the Badain Jaran Desert in the Southwest Mongolian Plateau. China Geology, 4:421–432. https://doi.org/10.31035/cg2021056
Wei, H. Z., Jiang, S. Y., Tan, H. B., et al., 2014. Boron Isotope Geochemistry of Salt Sediments from the Dongtai Salt Lake in Qaidam Basin: Boron Budget and Sources. Chemical Geology, 380:74–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j-chemgeo.2014.04.026
Wei, K.Q., Lin, R. F., Wang, Z. X., 1983. Hydrogen and Oxygen Stable Isotopic Composition and Tritium Content of Waters from Yangbajain Geothermal Area, Xizang, China. Geochimica, 4:338–346. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.165.9.4941
Wen, J., Deng, T. L., Wang, S. Q., et al., 2011. Caloric Evaporation Test for the Summer Salt Lake Brine in the Dongtaijinaier Salt Lake. Journal of Salt and Chemical Industry, 40(1):22–26 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Wu, X. C., Ma, T., Wang, Y. X., 2020. Surface Water and Groundwater Interactions in Wetlands. Journal of Earth Science, 31(5):1016–1028. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-020-1333-7
Wu, Y., Wen, X., Zhang, Y., 2004. Analysis of the Exchange of Groundwater and River Water by Using Radon-222 in the Middle Heihe Basin of Northwestern China. Environmental Geology, 45(5):647–653. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-003-0914-y
Xiao, Y., Shao, J. L., Cui, Y. L., et al., 2017. Groundwater Circulation and Hydrogeochemical Evolution in Nomhon of Qaidam Basin, Northwest China. Journal of Earth System Science, 126(2):1–16. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-017-0800-8
Xu, W., Su, X. S., 2019. Challenges and Impacts of Climate Change and Human Activities on Groundwater-Dependent Ecosystems in Arid Areas—A Case Study of the Nalenggele Alluvial Fan in NW China. Journal of Hydrology, 573:376–385. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2019.03.082
Xu, W., Su, X. S., Dai, Z. X., et al., 2017. Multi-Tracer Investigation of River and Groundwater Interactions: A Case Study in Nalenggele River Basin, Northwest China. Hydrogeology Journal, 25(7):2015–2029. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-017-1606-0
Xu, W., 2015. Groundwater Cycle Patterns and Its Response to Human Activities in Nalenggele Alluvial-Proluvial Plain: [Dissertation]. Jilin University, Changchun (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Yang, N., Zhou, P. P., Wang, G. C., et al., 2021. Hydrochemical and Isotopic Interpretation of Interactions between Surface Water and Groundwater in Delingha, Northwest China. Journal of Hydrology, 598:126243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2021.126243
Yin, L. H., Xu, D. D., Jia, W. H., et al., 2021. Responses of Phreatophyte Transpiration to Falling Water Table in Hyper-Arid and Arid Regions, Northwest China. China Geology, 4:410–420. https://doi.org/10.31035/cg2021052
Yu, J. Q., Gao, C. L., Cheng, A. Y., et al., 2013. Geomorphic, Hydroclimatic and Hydrothermal Controls on the Formation of Lithium Brine Deposits in the Qaidam Basin, Northern Tibetan Plateau, China. Ore Geology Reviews, 50:171–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oregeorev.2012.11.001
Yu, S. S., 1995. Study on the Water Dynamic and Chemical Characters during the Process of Brine Mining in Qarhan Salt Lake, Qinghai Province. Qinghai Insitute of Salt Lakes, CAS, Xining (in Chinese)
Zhao, D., Wang, G. C., Liao, F., et al., 2018. Groundwater-Surface Water Interactions Derived by Hydrochemical and Isotopic (222Rn, Deuterium, Oxygen-18) Tracers in the Nomhon Area, Qaidam Basin, NW China. Journal of Hydrology, 565:650–661
Zhao, Y. J., Wang, H. Y., Li, Y., et al., 2020. An Integrated Membrane Process for Preparation of Lithium Hydroxide from High Mg/Li Ratio Salt Lake Brine. Desalination, 493:114620. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2020.114620
Zhang, P. X., 1987. The Salt Lakes of the Qaidam Basin. Science Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Zhang, X. L., Li, H. L., Jiao, J. J., et al., 2021. Control Factors on Nutrient Cycling in the Lake Water and Groundwater of the Badain Jaran Desert, China. Journal of Hydrology, 598:126408. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2021.126408
Zhang, X. L., Luo, X., Jiao, J. J., et al., 2021a. Hydrogeochemistry and Fractionation of Boron Isotopes in the Inter-Dune Aquifer System of Badain Jaran Desert, China. Journal of Hydrology, 595:125984. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2021.125984
Wang, Z., Wang, L. J., Shen, J. M., et al., 2021b. Groundwater Characteristics and Climate and Ecological Evolution in the Badain Jaran Desert in the Southwest Mongolian Plateau. China Geology, 4:421–432. https://doi.org/10.31035/cg2021056
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the editors and anonymous reviewers for their helpful comments, which improved the quality of the final manuscript. This study was supported by the Key Deployment projects of the Chinese academy of sciences (No. ZDRW-ZS-2020-3), the Funds for the Qinghai Province (Nos. 2020-ZJ-932Q; 2020-ZJ-732), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 42007169), the “Western Light” of Chinese Academy of Sciences, the Fourth Batch of Qinghai Province “Thousand Talents Program for High-end Innovative Talents” (No. 2020000051) and supported by the Second Tibetan Plateau Scientific Expedition and Research Program (No. 2019QZKK0805). The final publication is available at Springer via https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-022-1731-0.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Han, J., Xu, J., Yi, L. et al. Seasonal Interaction of River Water-Groundwater-Salt Lake Brine and Its Influence on Water-Salt Balance in the Nalenggele River Catchment in Qaidam Basin, NW China. J. Earth Sci. 33, 1298–1308 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-022-1731-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-022-1731-0