Abstract
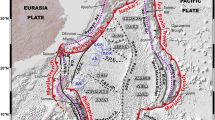
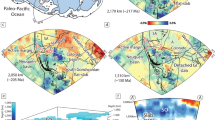
The past size and location of the hypothesized proto-South China Sea vanished ocean basin has important plate-tectonic implications for Southeast Asia since the Mesozoic. Here we present new details on proto-South China Sea paleogeography using mapped and unfolded slabs from tomography. Mapped slabs included: the Eurasia-South China Sea slab subducting at the Manila trench; the northern Philippine Sea Plate slab subducting at the Ryukyu trench; and, a swath of detached, subhorizontal, slab-like tomographic anomalies directly under the South China Sea at 450 to 700 km depths that we show is subducted ‘northern proto-South China Sea’ lithosphere. Slab unfolding revealed that the South China Sea lay directly above the ‘northern Proto-South China Sea’ with both extending 400 to 500 km to the east of the present Manila trench prior to subduction. Our slab-based plate reconstruction indicated the proto-South China Sea was consumed by double-sided subduction, as follows: (1) The ‘northern proto-South China Sea’ subducted in the Oligo–Miocene under the Dangerous Grounds and southward expanding South China Sea by in-place ‘self subduction’ similar to the western Mediterranean basins; (2) limited southward subduction of the proto-South China Sea under Borneo occurred pre-Oligocene, represented by the 800–900 km deep ‘southern proto-South China Sea’ slab.
Article PDF
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
References Cited
Bai Y. L., Wu, S. G., Liu, Z., et al., 2015. Full-Fit Reconstruction of the South China Sea Conjugate Margins. Tectonophysics, 661: 121–135. https://doi.org/10.13039/501100002858
Barckhausen U., Engels, M., Franke, D., et al., 2014. Evolution of the South China Sea: Revised Ages for Breakup and Seafloor Spreading. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 58: 599–611. https://doi.org/10.13039/501100002347
Bezada M. J., Humphreys, E. D., Toomey, D. R., et al., 2013. Evidence for Slab Rollback in Westernmost Mediterranean from Improved Upper Mantle Imaging. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 368: 51–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2013.02.024
Boyden J. A., Müller, R. D., Gurnis, M., et al., 2011. Next-Generation Plate-Tectonic Reconstructions Using GPlates. In: Keller, G. R., Baru, C., eds. Geoinformatics: Cyber Infrastructure for the Solid Earth Sciences. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge. 95–113
Briais, A., Patriat, P., Tapponnier, P., 1993. Updated Interpretation of Magnetic Anomalies and Seafloor Spreading Stages in the South China Sea: Implications for the Tertiary Tectonics of Southeast Asia. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 98(B4): 6299–6328. https://doi.org/10.1029/92jb02280
Cullen A. B., 2010. Transverse Segmentation of the Baram-Balabac Basin, NW Borneo: Refining the Model of Borneo’s Tectonic Evolution. Petroleum Geoscience, 16(1): 3–29. https://doi.org/10.1144/1354-079309-828
Cullen A. B., Zechmeister, M. S., Elmore, R. D., et al., 2012. Paleomagnetism of the Crocker Formation, Northwest Borneo: Implications for Late Cenozoic Tectonics. Geosphere, 8(5): 1146–1169. https://doi.org/10.1130/ges00750.1
Domeier M., Doubrovine, P. V., Torsvik, T. H., et al., 2016. Global Correlation of Lower Mantle Structure and Past Subduction. Geophysical Research Letters, 43(10): 4945–4953. https://doi.org/10.13039/501100000781
Dziewonski A. M., Anderson, D. L., 1981. Preliminary Reference Earth Model. Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors, 25(4): 297–356. https://doi.org/10.1016/0031-9201(81)90046-7
Engdahl E. R., van der Hilst, R., Buland, R., 1998. Global Teleseismic Earthquake Relocation with Improved Travel Times and Procedures for Depth Determination. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 88(3): 722–743
Engdahl, E. R., Villaseñor, A., 2002. Global Seismicity: 1900–1999. In: Lee, W. H. K., Kanamori, H., Jennings, P. C., et al., eds., International Handbook of Earthquake and Engineering Seismology, Part A. Academic Press, Cambridge. 665–690
Faccenna, C., Becker, T. W., Auer, L., et al., 2014. Mantle Dynamics in the Mediterranean. Reviews of Geophysics, 52(3): 283–332. https://doi.org/10.1002/2013rg000444
Fan J. K., Zhao, D. P., Dong, D. D., et al., 2017. P-Wave Tomography of Subduction Zones around the Central Philippines and Its Geodynamic Implications. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 146: 76–89. https://doi.org/10.13039/501100001809
Franke D., Barckhausen, U., Heyde, I., et al., 2008. Seismic Images of a Collision Zone Offshore NW Sabah/Borneo. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 25(7): 606–624. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2007.11.004
Fukao Y., Obayashi, M., Inoue, H., et al., 1992. Subducting Slabs Stagnant in the Mantle Transition Zone. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 97(B4): 4809–4822. https://doi.org/10.1029/91jb02749
Fuller M., Ali, J. R., Moss, S. J., et al., 1999. Paleomagnetism of Borneo. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 17(1/2): 3–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0743-9547(98)00057-9
Goes S., Agrusta, R., van Hunen, J., et al., 2017. Subduction-Transition Zone Interaction: A Review. Geosphere, 13(3): 644–664. https://doi.org/10.1130/ges01476.1
Hafkenscheid E., Wortel, M. J. R., Spakman, W., 2006. Subduction History of the Tethyan Region Derived from Seismic Tomography and Tectonic Reconstructions. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 111(B8): B08401. https://doi.org/10.1029/2005jb003791
Hall R., 2002. Cenozoic Geological and Plate Tectonic Evolution of SE Asia and the SW Pacific: Computer-Based Reconstructions, Model and Animations. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 20(4): 353–431. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1367-9120(01)00069-4
Hall R., 2012. Late Jurassic–Cenozoic Reconstructions of the Indonesian Region and the Indian Ocean. Tectonophysics, 570/571: 1–41. https://doi.org/10.13039/501100000288
Hall R., Spakman, W., 2015. Mantle Structure and Tectonic History of SE Asia. Tectonophysics, 658: 14–45. https://doi.org/10.13039/501100005416
Hinz K., Fritsch, J., Kempter, E. H. K., et al., 1989. Thrust Tectonics along the North-Western Continental Margin of Sabah/Borneo. Geologische Rundschau, 78(3): 705–730. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf01829317
Holloway N. H., 1982. North Palawan Block, Philippines—Its Relation to Asian Mainland and Role in Evolution of South China Sea. AAPG Bulletin, 66(9): 1355. https://doi.org/10.1306/03b5a7a5-16d1-11d7-8645000102c1865d
Huang Z. C., Zhao, D. P., Wang, L., 2015. P Wave Tomography and Anisotropy beneath Southeast Asia: Insight into Mantle Dynamics. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 120(7): 5154–5174. https://doi.org/10.13039/501100001809
Hutchison C. S., Bergman, S. C., Swauger, D. A., et al., 2000. A Miocene Collisional Belt in North Borneo: Uplift Mechanism and Isostatic Adjustment Quantified by Thermochronology. Journal of the Geological Society, 157(4): 783–793. https://doi.org/10.1144/jgs.157.4.783
Hutchison C. S., 2010. Oroclines and Paleomagnetism in Borneo and South-East Asia. Tectonophysics, 496(1/2/3/4): 53–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tecto.2010.10.008
Hutchison C. S., 1996. The ‘Rajang Accretionary Prism’ and ‘Lupar Line’ Problem of Borneo. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 106(1): 247–261. https://doi.org/10.1144/gsl.sp.1996.106.01.16
Koulakov I., 2011. High-Frequency P and S Velocity Anomalies in the Upper Mantle beneath Asia from Inversion of Worldwide Traveltime Data. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 116(B4): B04301. https://doi.org/10.1029/2010jb007938
Legendre C. P., Zhao, L., Chen, Q. F., 2015. Upper-Mantle Shear-Wave Structure under East and Southeast Asia from Automated Multimode Inversion of Waveforms. Geophysical Journal International, 203(1): 707–719. https://doi.org/10.1093/gji/ggv322
Li C., van der Hilst, R. D., Engdahl, E. R., et al., 2008. A New Global Model for P Wave Speed Variations in Earth’s Mantle. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 9(5): Q05018. https://doi.org/10.1029/2007gc001806
Li C., van der Hilst, R. D., 2010. Structure of the Upper Mantle and Transition Zone beneath Southeast Asia from Traveltime Tomography. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 115(B7): B07308. https://doi.org/10.1029/2009jb006882
Li C.-F., Xu, X., Lin, J., et al., 2014. Ages and Magnetic Structures of the South China Sea Constrained by Deep Tow Magnetic Surveys and IODP Expedition 349. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 15(12): 4958–4983. https://doi.org/10.13039/501100001809
Lister G. S., White, L. T., Hart, S., et al., 2012. Ripping and Tearing the Rolling-Back New Hebrides Slab. Australian Journal of Earth Sciences, 59(6): 899–911. https://doi.org/10.1080/08120099.2012.686454
Lu R.-Q., Suppe, J., He, D.-F., et al., 2013. Deep Subducting Slab Reconstruction and Its Geometry, Kinematics: A Case Study for the Tonga-Kermadec Slab from Tomography. Chinese Journal Geophysics, 56(11): 3837–3845
Obayashi, M., Yoshimitsu, J., Nolet, G., et al., 2013. Finite Frequency Whole Mantle P Wave Tomography: Improvement of Subducted Slab Images. Geophysical Research Letters, 40(21): 5652–5657. https://doi.org/10.1002/2013gl057401
Pubellier M., Morley, C. K., 2014. The Basins of Sundaland (SE Asia): Evolution and Boundary Conditions. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 58: 555–578. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2013.11.019
Rangin C., Spakman, W., Pubellier, M., et al., 1999. Tomographic and Geological Constraints on Subduction along the Eastern Sundaland Continental Margin (South-East Asia). Bulletin de la Societe Geologique de France, 170(6): 775–788
Rawlinson, N., Fichtner, A., Sambridge, M., et al., 2014. Chapter One—Seismic Tomography and the Assessment of Uncertainty. In: Renata, D., ed., Advances in Geophysics. Elsevier, 55: 1–76. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0065268714000028
Replumaz, A., Tapponnier, P., 2003. Reconstruction of the Deformed Collision Zone between India and Asia by Backward Motion of Lithospheric Blocks. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 108(B6): 2285. https://doi.org/10.1029/2001jb000661
Schlüter H. U., Hinz, K., Block, M., 1996. Tectono-Stratigraphic Terranes and Detachment Faulting of the South China Sea and Sulu Sea. Marine Geology, 130(1/2): 39–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/0025-3227(95)00137-9
Seton M., Müller, R. D., Zahirovic, S., et al., 2012. Global Continental and Ocean Basin Reconstructions since 200 Ma. Earth-Science Reviews, 113(3/4): 212–270. https://doi.org/10.13039/501100000923
Sibuet J.-C., Yeh, Y.-C., Lee, C.-S., 2016. Geodynamics of the South China Sea. Tectonophysics, 692: 98–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tecto.2016.02.022
Sigloch K., Mihalynuk, M. G., 2013. Intra-Oceanic Subduction Shaped the Assembly of Cordilleran North America. Nature, 496(7443): 50–56. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature12019
Spakman W., Wortel, M. J. R., 2004. Tomographic View on Western Mediterranean Geodynamics. In: Cavazza, W., Roure, F. M., Spakman, W., et al., eds., The TRANSMED Atlas, The Mediterranean Region from Crust to Mantle. Springer-Verlag, Heidelberg. 31–52
Sun, W., Lin, C.-T., Zhang, C.-C., et al., 2016. Initiation and Evolution of the South China Sea: An Overview. Acta Geochimica, 35(3): 215–225
Tan, E., Gurnis, M., Han, L. J., 2002. Slabs in the Lower Mantle and Their Modulation of Plume Formation. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 3(11): 1–24. https://doi.org/10.1029/2001gc000238
Taylor B., Hayes, D. E., 1983. Origin and History of the South China Sea Basin. In: Hayes, D. E., ed., The Tectonic and Geologic Evolution of Southeast Asian Seas and Islands: Part 2. American Geophysical Union, Washington D.C. Geophysical Monographs Series, 27: 23–56
Torsvik, T. H., Müller, R. D., Van der Voo, R., et al., 2008. Global Plate Motion Frames: Toward a Unified Model. Reviews of Geophysics, 46(3): 44. https://doi.org/10.1029/2007rg000227
van der Meer D. G., Spakman, W., van Hinsbergen, D. J. J., et al., 2009. Towards Absolute Plate Motions Constrained by Lower-Mantle Slab Remnants. Nature Geoscience, 3(1): 36–40. https://doi.org/10.1038/ngeo708
van der Meer D. G., van Hinsbergen, D. J. J., Spakman, W., 2017. Atlas of the Underworld: Slab Remnants in the Mantle, Their Sinking History, and a New Outlook on Lower Mantle Viscosity. Tectonophysics. https://doi.org/10.13039/https://doi.org/10.13039/100010663
von Hagke C., Philippon, M., Avouac, J.-P., et al., 2016. Origin and Time Evolution of Subduction Polarity Reversal from Plate Kinematics of Southeast Asia. Geology, 44(8): 659–662. https://doi.org/10.1130/g37821.1
Wu J., Suppe, J., Lu, R. Q., et al., 2016. Philippine Sea and East Asian Plate Tectonics since 52 Ma Constrained by New Subducted Slab Reconstruction Methods. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 121(6): 4670–4741. https://doi.org/10.13039/501100006477
Yan P., Liu, H. L., 2004. Tectonic-Stratigraphic Division and Blind Fold Structures in Nansha Waters, South China Sea. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 24(3): 337–348. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jseaes.2003.12.005
Zahirovic S., Seton, M., Müller, R. D., 2014. The Cretaceous and Cenozoic Tectonic Evolution of Southeast Asia. Solid Earth, 5(1): 227–273. https://doi.org/10.5194/se-5-227-2014
Zahirovic S., Müller, R. D., Seton, M., et al., 2015. Tectonic Speed Limits from Plate Kinematic Reconstructions. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 418: 40–52. https://doi.org/10.13039/501100001774
Zahirovic S., Matthews, K. J., Flament, N., et al., 2016. Tectonic Evolution and Deep Mantle Structure of the Eastern Tethys since the Latest Jurassic. Earth-Science Reviews, 162: 293–337. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2016.09.005
Zhao D. P., 2015. The 2011 Tohoku Earthquake (M w 9.0) Sequence and Subduction Dynamics in Western Pacific and East Asia. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 98: 26–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jseaes.2014.10.022
Zhou D., Ru, K., Chen, H.-Z., 1995. Kinematics of Cenozoic Extension on the South China Sea Continental Margin and Its Implications for the Tectonic Evolution of the Region. Tectonophysics, 251(1/2/3/4): 161–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/0040-1951(95)00018-6
Acknowledgments
We thank JES special issue guest editor Prof. Hua-Wei Zhou for inviting this paper. We also thank Prof. Zhou for his role in organizing an informative 2016 workshop on geophysical imaging in Qingdao, China, where portions of this paper were presented. We are grateful to JES staffs for support and help with this JES special issue. Jean-Claude Sibuet is thanked for sharing South China Sea expertise and insightful feedback on the proto-South China Sea reconstructions. Yiduo Liu and Yi-Wei Chen provided helpful comments on the draft manuscript. Two anonymous reviewers contributed thoughtful and constructive comments that improved the final paper. Please see the supplementary data section for a proto-South China Sea plate reconstruction movie file and digital GPlates plate reconstruction files. The final publication is available at Springer via https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-017-0813-x.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
Open Access: This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (https://doi.org/creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, J., Suppe, J. Proto-South China Sea Plate Tectonics Using Subducted Slab Constraints from Tomography. J. Earth Sci. 29, 1304–1318 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-017-0813-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-017-0813-x