Abstract
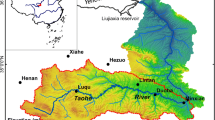
Based on the meteorological and hydrologic data in the Lijang (丽江) basin from 1979 to 2006, variational trend and characteristics of climate change and its effect on runoff in Yanggong (漾弓) River were examined in the study. The results show that the temperature have significantly increased in the drainage basin during the past 28 years. The average temperature increased markedly from 1979 to 2006, and the increase of temperature in winter was higher than those in other seasons. The annual precipitation varied with a slightly upward trend in the same period, suggesting that the increase mainly occurred in spring and summer while the decrease occurred in autumn and winter. The streamflow at Yanggong River showed a significant increasing trend. During the four seasons, spring experienced the most significant increase, and autumn experienced the smallest. On the basis of the above study, we found that the increasing trend in runoff was more significant than the increase in precipitation in the study area. That was the synactic results of variation of groundwater, ice-snow meltwater and precipitation caused by global climate change.
Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.References Cited
Ding, Y. H., Ren, G. Y., Shi, G. Y., et al., 2006. National Assessment Report of Climate Change (I): Climate Change in China and Its Future Trend. Advances in Climate Change Research, 2(1): 3–8 (in Chinese)
He, Y. Q., Li, Z. X., Yang, X. M., et al., 2008. Changes of the Hailuogou Glacier, Mt. Gongga, China, against the Background of Global Warming in the Last Several Decades. Journal of China University of Geosciences, 19(3):271–281
He, Y. Q., Zhang, D., 2004. Climatic Warming is the Major Reason for Glacier Retreat on Mt. Yulong, China. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology, 26(2): 230–231 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
He, Y. Q., Zhang, Z. L., Theakstone, W. H., et al., 2003. Changing Features of Climate and Glaciers in China’s Monsoonal Temperate Glacier Region. Journal of Geophysical Research, 108(D17): 4530–4536
IPCC Report, 2007. Climate Change 2007: Report of Working Group of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge. 16–72
Kaser, G., Juen, I., Georges, C., et al., 2003. The Impact of Glaciers on the Runoff and the Reconstruction of Mass Balance History from Hydrological Data in the Tropical Cordillera Blanca, Peru. Journal of Hydrology, 282:130–144
Kundzewicz, Z. W., Mata, L. J., Arnell, N. W., et al., 2007. Freshwater Resources and Their Management. In: Parry, M. L., Canziani, O. F., Palutikof, J. P., et al., eds., Climate Change 2007: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability. Contribution of Working Group II to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge. 73–210
Legesse, D., Vallet-Coulomb, C., Gasse, F., 2003. Hydrological Response of a Catchment to Climate and Land Use Changes in Tropical Africa: Case Study South Central Ethiopia. Journal of Hydrology, 275: 67–85
Li, Q. X., Li, W., Ju, X. H., 2006. Analysis on the Persistent Extreme Warm Period over China since 1998. Science & Technology Review, 24(4): 37–39 (in Chinese)
Li, W. H., Chen, Y. N., Hao, X. M., et al., 2006. Impacts of Climatic Changes on Runoff in the North Tianshan Mountains of China. Science in China (Series D), 36(S2): 39–44 (in Chinese)
Li, Z. X., He, Y. Q., Pu, T., et al., 2009. Changes of Climate, Glaciers and Runoff in China’s Monsoonal Temperate Glacier Region during the Last Several Decades. Quaternary International, doi:10.1016/j.quaint.2009.05.010
Li, Z. X., He, Y. Q., Yang, X. M., et al., 2008. Changes of the Hailuogou Glacier, Mt. Gongga, China, against the Background of Climate Change since the Holocene. Quaternary International, doi:10.1016/j.quaint.2008.09.005
Liu, C. Z., 2004. The Issues in the Impact Study of Climate Change on the Terrestrial Hydrological. Advances in Earth Sciences, 19(1): 115–119 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Milly, P. C. D., Dunne, K. A., Vecchia, A. V., 2005. Global Pattern of Trends in Streamflow and Water Availability in a Changing Climate. Nature, 438(7066): 347–350
Pang, H. X., He, Y. Q., Lu, A. G., et al., 2006. Comparisons of Stable Isotopic Fractionation in Winter and Summer at Baishui Glacier No. 1, Mt. Yulong. Acta Geographica Sinica, 60(5): 501–509 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Qin, D. H., Chen, Z. L., Luo, Y., et al., 2007. Updated Understanding of Climate Change Sciences. Advances in Climate Change Research, 3(2): 63–73 (in Chinese)
Rui, X. F., 2004. Principle of Hydrology. China Water Power Press, Beijing. 60–72 (in Chinese)
Shao, C., Shen, Y. P., Zhang, J., 2008. Recent Progress in Climate Change Impact on Water Cycles of Cold Regions. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology, 30(1): 1–8 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Shi, Y. F., Huang, M. H., Yao, T. D., et al., 2000. Glaciers and Their Environment in China. Science Press, Beijing. 26–27 (in Chinese)
Singh, P., Bengtsson, L., 2004. Hydrological Sensitivity of a Large Himalayan Basin to Climate Change. Hydrol. Processes, 18: 2363–2385
Wang, J., Shen, Y. P., Lu, A. X., et al., 2001. Impact of Climate Change on Snowmelt Runoff in the Mountainous Regions of Northwest China. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology, 23(1): 28–33 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Ye, B. S., Ding, Y. J., Kang, E. S., et al., 1999. Impacts of Climatic Warming on Ice-Snow Melt Runoff of Xinjiang Region in the Past 40 Years. Science in China (Series D), 29(Suppl.): 40–46
Ye, B. S., Ding, Y. J., Yang, D. Q., 2006. Regional Patterns of Climate Change in Northwest China during the Last 50 Years Viewed from Annual Discharge Change. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology, 28(3): 307–311 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Zhang, J. Y., Wang, G. Y., 2007. Study of Impact of Climate Change on Hydrology and Water Resources. Science Press, Beijing. 290–292 (in Chinese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 40971019), the West Light Foundation of Chinese Academy of Sciences (No. O828A11001), the National Basic Research Program of China (No. 2007CB411501), the Special Grant for Postgraduate Research, Innovation and Practice, the Major Directionality Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (No. KZCX-YW-317), the Fund from the State Key Laboratory of Cryospheric Sciences, and the Fund from Lijiang City Government.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, Y., Pu, T., Li, Z. et al. Climate change and its effect on annual runoff in Lijiang Basin-Mt. Yulong Region, China. J. Earth Sci. 21, 137–147 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-010-0012-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-010-0012-5