Abstract
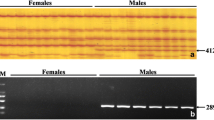
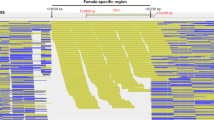
White trevally Pseudocaranx dentex is a high-value carangid fish species that is only cultured in Japan under full lifecycle aquaculture conditions. To make the reproductive process successful and efficient, sexual phenotyping of broodstock is essential, and this has conventionally been practiced via examination upon abdominal compression. However, in certain cases, sexual phenotyping is not successful due to unsuccessful sperm or semen collection, which leads to misclassification of the phenotype. This study identified the male characteristic DNA sequence of P. dentex. The pectoral fins of eight male and eight female 6-year-old F3 generation broodstock fish were utilized for male sex hormone quantification to determine each sex phenotype. The same fish DNA samples were subjected to bulked-amplified fragment length polymorphism (AFLP) screening, and a male characteristic AFLP DNA fragment of 227 bp in size was identified. A male characteristic fragment was also confirmed by second amplification when it was performed individually. All eight males used for screening carried the AFLP fragment, while none of the eight females did. AFLP was conducted for all 40 broodstock, and it was determined that all 24 putative males were AFLP positive, and 4 of the 16 putative females were AFLP positive. These results indicate that P. dentex may have a male characteristic DNA polymorphism. The nucleotide sequence of the male characteristic fragment showed high homology to Atlantic horse mackerel Trachurus trachurus chromosome 5, and the sequence did not have clear homology to known coding genes. Further studies are required to identify the sex-determining gene of P. dentex in the vicinity of the DNA sequence identified in this study.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agawa Y, Komiya T, Honryo T, Kurata M, Okada T, Murata O, Kumai H, Sawada Y (2011) Screening of the male characteristic DNA fragment using AFLP analysis in Pacific bluefintuna, Thunnus orientalis. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 77:639–646 (in Japanese, with English abstract)
Agawa Y, Iwaki M, Komiya T, Honryo T, Tamura K, Okada T, Yagishita N, Kobayashi T, Sawada Y (2015) Identification of male sex-linked DNA sequence of the cultured Pacific bluefin tuna Thunnus orientalis. Fish Sci 81:113–121
Aoki R, Chuda H, Washio Y, Masuma S, Kato K (2020) Sex discrimination of cultured greater amberjack Seriola dumerili using steroid hormones. Fish Sci 86:57–64
Aquaculture Network (2020) ACN Report no. 53 September 2020 (in Japanese)
Baird NA, Etter PD, Atwood TS, Currey MC, Shiver AL, Lewis ZA, Selker EU, Cresko WA, Johnson EA (2008) Rapid SNP discovery and genetic mapping using sequenced RAD markers. PLOS One 3:e3376
Caputo V, Marchegiani F, Olmo E (1996) Karyotype differentiation between two species of carangid fishes, genus Trachurus (Perciformes: Carangidae). Mar Biol 127:193–199
Catanach A, Ruigrok M, Bowatte D, Davy M, Storey R, Valenza-Troubat N, López-Girona E, Hilario E, Wylie MJ, Chagné D, Wellenreuther M (2021) The genome of New Zealand trevally (Carangidae: Pseudocaranx georgianus) uncovers a XY sex determination locus. BMC Genom 22:785
Chen SL, Li J, Deng SP, Tian YS, Wang QY, Zhuang ZM, Sha ZX, Xu JY (2007) Isolation of female-specific AFLP markers and molecular identification of genetic sex in half-smooth tongue sole (Cynoglossus semilaevis). Mar Biotechnol (NY) 9:273–280
Coimbra MRM, Kobayashi K, Koretsugu S, Hasegawa O, Ohara E, Ozaki A, Sakamoto T, Naruse K, Okamoto N (2003) A genetic linkage map of the Japanese flounder, Paralichthys olivaceus. Aquaculture 220:203–218
Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) (1999) The living marine resources of the western central Pacific. In: Carpenter KE, Niem VH (Eds) Bony Fishes, part 2 (Mugilidae to Carangidae), vol 4, p 2730.
Fuji K, Yoshida K, Hattori K, Ozaki A, Araki K, Okauchi M, Kubota S, Okamoto N, Sakamoto T (2010) Identifications of the sex-linked locus in yellowtail, Seriola quinqueradiata. Aquaculture 308:S51–S55
Harada T, Murata O, Miyasita S (1984) Maturation and egg yield of striped jack, Caranx delicatissimus. Bull FLKU 2:143–149
Honryo T, Kurata M, Katayama S, Takaoka O, Agawa Y, Sawada Y (2020) Swim bladder inflation of white trevally, Pseudocaranx dentex (Bloch and Schneider, 1801), larvae without air gulping. Aquacult Res 51:432–435. https://doi.org/10.1111/are.14321
Kölliker R, Jones ES, Jahufer MZZ, Forster JW (2001) Bulked AFLP analysis for the assessment of genetic diversity in white clover (Trifolium repens L.). Euphytica 121:305–315
Koyama T, Nakamoto M, Morishima K, Yamashita R, Yamashita T, Sasaki K, Kuruma Y, Mizuno N, Suzuki M, Okada Y, Ieda R, Uchino T, Tasumi S, Hosoya S, Uno S, Koyama J, Toyoda A, Kikuchi K, Sakamoto T (2019) A SNP in a steroidogenic enzyme is associated with phenotypic sex in Seriola fishes. Curr Biol 29:1901-1909.e8
Ma H, Chen S, Yang J, Ji X, Chen S, Tian Y, Bi J (2010) Isolation of sex-specific AFLP markers in spotted halibut (Verasper variegatus). Environ Biol Fish 88:9–14
Mushiake K (2005) White trevally Peudocaranx dentex. In: Kumai TH (ed) Aquaculture system Koseisha-Koseikaku. Koseisha-Koseikaku, Tokyo, pp 149–171 (in Japanese)
Nakabo T (eds) (1993) Fishes of Japan with pictorial keys to the species. Chapter Carangidae, p 701 (in Japanese)
Ouchi K, Adachi S, Nagahama Y (1987) Changes in plasma levels of steroid hormones during sexual maturation of male red sea bream Pagrus major. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 54:593–597 (in Japanese with English abstract)
Peterson BK, Weber JN, Kay EH, Fisher HS, Hoekstra HE (2012) Double digest RADseq: an inexpensive method for de novo SNP discovery and genotyping in model and non-model species. PLOS One 7:e37135
Santini F, Carnevale G (2015) First multilocus and densely sampled time tree of trevallies, pompanos and allies (Carangoidei, Percomorpha) suggests a Cretaceous origin and Eocene radiation of a major clade of piscivores. Mol Phylogenet Evol 83:33–39
Sawayama E, Noguchi D, Nakayama K, Takagi M (2018) Identification, characterization, and mapping of a novel SNP associated with body color transparency in juvenile red sea bream (Pagrus major). Mar Biotechnol (NY) 20:481–489
Slembrouck J, Arifin OZ, Pouil S, Subagja J, Yani A, Kristanto AH, Legendre M (2019) Gender identification in farmed giant gourami (Osphronemus goramy): a methodology for better broodstock management. Aquaculture 498:388–395
Takaoka O, Ji SC, Ishimaru K, Lee SW, Jeong GS, Biswas A, Takii K (2012) Medicinal herbs promote resistances of larval and juvenile striped jack Pseudocaranx dentex for various stresses. Aquacult Sci 6:199–205
Vos P, Hogers R, Bleeker M, Reijans M, van de Lee T, Hornes M, Frijters A, Pot J, Peleman J, Kuiper M, Zabeau M (1995) AFLP: a new technique for DNA fingerprinting. Nucleic Acids Res 23:4407–4414
Yamamoto E (1999) Studies on sex-manipulation and production of cloned populations in hirame, Paralichthys olivaceus (Temminck et Schlegel). Aquaculture 173:235–246
Yamaoka K, Han H-S, Taniguchi N (1992) Genetic dimorphism in Pseudocaranx dentex from Tosa Bay, Japan. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 58:39–44
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the staff members of the Aquaculture Research Institute, Kindai University, Oshima Station for their daily assistance in fish maintenance, husbandry, and specimen collection. Mr. Y. Inoue and Mr. N. Taniyama assisted with experiments. We thank our former student Mr. J. Miller for English correction. This study was supported by a grant from FLKU and METI, Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Agawa, Y., Saiki, T., Miyamoto, T. et al. Identification of the male sex-linked DNA sequence of cultured white trevally Pseudocaranx dentex. Fish Sci 88, 319–327 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12562-022-01589-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12562-022-01589-y