Abstract
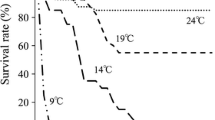
The effects of water temperature (15, 20, 25, 30, and 35 °C) on survival, growth performance, digestive enzyme activities, and body composition of Plectropomus leopardus were studied for a period of 6 weeks. One hundred eighty fish with initial body weights of 26.5 ± 1.5 g were randomly arranged into 15 glass aquaria in equal numbers in five recirculating systems to form five groups in triplicate. The results showed that survival of P. leopardus at 35 °C was significantly greater (P < 0.05) than survival at 15 °C. No death was recorded at 20, 25, and 30 °C. Among all treatment groups, the significantly highest average individual harvesting weight, weight gain, feed ingestion rate and protease enzyme activity of P. leopardus were observed in 30 °C group. Similar results were also observed in protein and fat content in this species. Based on the present findings, a culture temperature of 30 °C can be considered to be the optimum temperature for the aquaculture of juvenile P. leopardus. However, more research is still needed to optimize the nutrition and photoperiod of P. leopardus culture.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Qu M, Ding S, Xu X, Shen M, You Y, Su Y (2012) Ontogenetic development of the digestive system and growth in coral trout (Plectropomus leopardus). Aquaculture 334–337:132–141
Masuma S, Tezuka N, Teruya K (1993) Embryonic and morphological development of larval and juvenile coral trout, Plectropomus leopardus. Jpn J Ichthyol 40:333–342
Martinez-Palacios CA, Tovar EB, Taylor JF, Duran GR, Ross LG (2002) Effect of temperature on growth and survival of Chirostoma estor estor, Jordan 1879, monitored using a simple video technique for remote measurement of length and mass of larval and juvenile fishes. Aquaculture 209:369–377
Ye L, Yang S, Zhu X, Liu M, Lin J, Wu K (2011) Effects of temperature on survival, development, growth and feeding of larvae of yellowtail clownfish Amphiprion clarkii (Pisces: Perciformes). Acta Ecol Sin 31:241–245 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Handeland SO, Imsland AK, Stefansson SO (2008) The effect of temperature and fish size on growth, feed intake, food conversion efficiency and stomach evacuation rate of Atlantic salmon post-smolts. Aquaculture 283:36–42
Choa BY, Carter CG, Battaglene SC (2010) Effects of temperature regime on growth and development of post-larval striped trumpeter (Latris lineata). Aquaculture 305:95–101
Rahman MM, Verdegem MJ (2010) Effects of intra- and interspecific competition on diet, growth and behaviour of Labeo calbasu (Hamilton) and Cirrhinus cirrhosus (Bloch). Appl Anim Behav Sci 128:103–108
Tsuji M, Abe H, Hanyuu K, Kuriyama I, Tsuchihashi Y, Tsumoto K, Nigou T, Kasuya T, Katou T, Kawamura T, Okada K, Uji S, Sawada Y (2014) Effect of temperature on survival, growth and malformation of cultured larvae and juveniles of the seven-band grouper Epinephelus septemfasciatus. Fish Sci 80:69–81
Ayling RD, Baker SE, Peek ML, Simon AJ, Nicholas RJ (2000) Comparison of in vitro activity of danofloxacin, florfenicol, oxytetracycline, spectinomycin and tilmicosin against recent field isolates of Mycoplasma bovis. Vet Rec 146:745–747
Yang M, Wang Y, Fu S, Shen M, Zheng F, Wang G, Yin S, Li X (2012) Effects of different temperatures and salinities and pH values on the early development of Plectropomus leopardus Lacépède. J Trop Org 3:104–108 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhu ZY, Yue GH (2008) The complete mitochondrial genome of red grouper Plectropomus leopardus and its applications in identification of grouper species. Aquaculture 276:44–49
Kenzo Y, Kazuhisa Y, Kimio A, Masayuki C, Koji H, Shinichi K (2008) Influence of light intensity on feeding, growth, and early survival of leopard coral grouper (Plectropomus leopardus) larvae under mass-scale rearing conditions. Aquaculture 279:55–62
Burka JF, Hammell KL, Horsberg TE, Johnson GR, Rainnie DJ, Speare DJ (1997) Drugs in salmonid aquaculture—a review. J Vet Pharmacol Ther 20(5):333–349
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Kunitz M (1947) Crystalline soybean trypsin inhibitor: II. General properties. J Gen Physiol 30:291–310
Rick W, Stegbauer HP (1984) Alfa-amylase: measurement of reducing groups. In: Bergermeyer HU, Grab M (eds) Methods of enzymatic analysis. Enzymes, vol 5, 3rd edn. Chemie Verlag, Weinheim, pp 885–889
Ebling ME (1968) The Dumas method for nitrogen in feeds. J AOAC Int 51:766–770
Rahman MM, Jo Q, Gong YG, Miller SA, Hossain MY (2008) A comparative study of common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.) and calbasu (Labeo calbasu Hamilton) on bottom soil resuspension, water quality, nutrient accumulations, food intake and growth of fish in simulated rohu (Labeo rohita Hamilton) ponds. Aquaculture 285:78–83
Rahman MM, Meyer CG (2009) Effects of food type on diel behaviours of common carp Cyprinus carpio L. in simulated aquaculture pond conditions. J Fish Biol 74:2269–2278
Khatune-Jannat M, Rahman MM, Bashar MA, Hasan MD, Ahamed F, Hossain MY (2012) Effects of stocking density on survival, growth and production of Thai climbing perch (Anabas testudineus) under fed ponds. Sains Malays 41:1205–1210
Zhang Y, Yu D, Huang G (2011) Impacts of ecological factors on hatching of fertilized eggs and survival of larvae of coral grouper Plectropomus leopardus. Guangdong Agric Sci 10:102–105 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhang H, Liu X, Wang Y, Liufu Y, Huang G, Luo G, Wang H, Lin H (2006) Effects of temperature, salinity and pH on hatch and larval activity of Epinephelus coioides. J Trop Oceanogr 25:31–36 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Qu H, Li X, He Q, Li Z (2009) Effects of temperature and salinity on hatching rates and larval survival of Epinephelus lanceol. Hebei Fish 8:6–9 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Rungruangsak-Torrissen K, Moss R, Andresen LH, Berg A, Waagbø R (2006) Different expressions of trypsin and chymotrypsin in relation to growth in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.). Fish Physiol Biochem 32:7–23
Sunde J (2006) Digestive protease activities, growth and feed utilisation in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.). PhD thesis, University of Bergen, Norway
Rungruangsak-Torrissen K, Sundby A (2000) Protease activities, plasma free amino acids and insulin at different ages of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) with genetically different trypsin isozymes. Fish Physiol Biochem 22:337–347
Sunde J, Taranger GL, Rungruangsak-Torrissen K (2001) Digestive protease activities and free amino acids in white muscle as indicators for feed conversion efficiency and growth rate in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.). Fish Physiol Biochem 25:335–345
Li Y, Sun G, Liu Y, Gao T, Yu K, Liu J (2011) Effects of temperature on feed intake, growth and digestive enzyme activity of turbot Scophthalmus maximus L. in high stocking density of closed recirculation aquaculture system. Prog Fish Sci 32:17–24 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Cui Y, Wootton RJ (1988) Effects of ration, temperature and body size on the body composition, energy content and condition of the minnow, Phoxinus phoxinus (L.). J Fish Biol 32:749–764
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Yanguang Yu, Hongzhen You, and Xueliang Yao for their help in the experiment. In particular, we would also like to thank two anonymous reviewers for professional revision of the manuscript. This research was supported by Tianjin Agricultural Science and Technology Achievement Transformation and Promotion project (No. 201103040), Natural Science Fund of Tianjin (Nos. 14JCQNJC15200, 14ZXNZNC00045, and 11JCYBJC08800), Tianjin Science and Technology Key Program (No. 12ZCZDNC01100), China Spark Program (No. 2011GA610002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, Z., Xia, S., Feng, S. et al. Effects of water temperature on survival, growth, digestive enzyme activities, and body composition of the leopard coral grouper Plectropomus leopardus . Fish Sci 81, 107–112 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12562-014-0832-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12562-014-0832-9