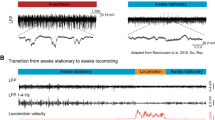
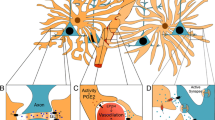
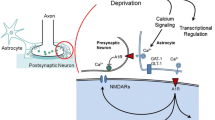
Abstract
Astrocytes have been in the limelight of active research for about 3 decades now. Over this period, ideas about their function and role in the nervous system have evolved from simple assistance in energy supply and homeostasis maintenance to a complex informational and metabolic hub that integrates data on local neuronal activity, sensory and arousal context, and orchestrates many crucial processes in the brain. Rapid progress in experimental techniques and data analysis produces a growing body of data, which can be used as a foundation for formulation of new hypotheses, building new refined mathematical models, and ultimately should lead to a new level of understanding of the contribution of astrocytes to the cognitive tasks performed by the brain. Here, we highlight recent progress in astrocyte research, which we believe expands our understanding of how low-level signaling at a cellular level builds up to processes at the level of the whole brain and animal behavior. We start our review with revisiting data on the role of noradrenaline-mediated astrocytic signaling in locomotion, arousal, sensory integration, memory, and sleep. We then briefly review astrocyte contribution to the regulation of cerebral blood flow regulation, which is followed by a discussion of biophysical mechanisms underlying astrocyte effects on different brain processes. The experimental section is closed by an overview of recent experimental techniques available for modulation and visualization of astrocyte dynamics. We then evaluate how the new data can be potentially incorporated into the new mathematical models or where and how it already has been done. Finally, we discuss an interesting prospect that astrocytes may be key players in important processes such as the switching between sleep and wakefulness and the removal of toxic metabolites from the brain milieu.




Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
Not applicable
Code availability
No code was created in preparation of the manuscript.
References
Åbjørsbråten KS, Skaaraas GHS, Cunen C et al (2022) Impaired astrocytic Ca\(^{2+}\) signaling in awake-behaving Alzheimer’s disease transgenic mice. eLife 11:e75,055. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.75055
Adamsky A, Goshen I (2018) Astrocytes in memory function: pioneering findings and future directions. Neuroscience 370:14–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2017.05.033
Adamsky A, Kol A, Kreisel T et al (2018) Astrocytic activation generates de novo neuronal potentiation and memory enhancement. Cell 174(1):59-71.e14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2018.05.002
Agarwal N, Lewis LD, Hirschler L et al. (2023) Current understanding of the anatomy, physiology, and magnetic resonance imaging of neurofluids: update from the 2022 “ISMRM imaging neurofluids study group” ’ workshop in rome. J Magn Reson Imaging
Aggarwal A, Liu R, Chen Y et al (2023) Glutamate indicators with improved activation kinetics and localization for imaging synaptic transmission. Nat Methods 20(6):925–934. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41592-023-01863-6
Aharoni D, Khakh BS, Silva AJ et al (2019) All the light that we can see: a new era in miniaturized microscopy. Nat Methods 16(1):11–13. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41592-018-0266-x
Airan RD, Thompson KR, Fenno LE et al (2009) Temporally precise in vivo control of intracellular signalling. Nature 458(7241):1025–1029. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature07926
Aleksin SG, Zheng K, Rusakov DA et al (2017) Arachne: a neural-neuroglial network builder with remotely controlled parallel computing. PLoS Comput Biol 13(3):e1005,467. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1005467
Alvestad S, Hammer J, Hoddevik EH et al (2013) Mislocalization of AQP4 precedes chronic seizures in the kainate model of temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsy Res 105(1–2):30–41
Andersen JV, Schousboe A, Wellendorph P (2023) Astrocytes regulate inhibitory neurotransmission through GABA uptake, metabolism, and recycling. Essays Biochem 67(1):77–91. https://doi.org/10.1042/EBC20220208
Araque A, Carmignoto G, Haydon PG et al (2014) Gliotransmitters travel in time and space. Neuron 81(4):728–739
Arizono M, Inavalli VVGK, Panatier A et al (2020) Structural basis of astrocytic Ca\(^{2+}\) signals at tripartite synapses. Nat Commun 11(1):1906. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-15648-4
Astiz M, Delgado-García LM, López-Mascaraque L (2022) Astrocytes as essential time-keepers of the central pacemaker. Glia 70(5):808–819. https://doi.org/10.1002/glia.24121
Attwell D, Buchan AM, Charpak S et al (2010) Glial and neuronal control of brain blood flow. Nature 468(7321):232–243. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature09613
Bai R, Springer CS Jr, Plenz D et al (2018) Fast, Na\(^+\)/K\(^+\) pump driven, steady-state transcytolemmal water exchange in neuronal tissue: a study of rat brain cortical cultures. Magn Reson Med 79(6):3207–3217
Bak LK, Schousboe A, Waagepetersen HS (2006) The glutamate/GABA-glutamine cycle: aspects of transport, neurotransmitter homeostasis and ammonia transfer. J Neurochem 98(3):641–653
Ballanyi K, Grafe P, Ten Bruggencate G (1987) Ion activities and potassium uptake mechanisms of glial cells in guinea-pig olfactory cortex slices. J Physiol 382(1):159–174
Bang J, Kim HY, Lee H (2016) Optogenetic and chemogenetic approaches for studying astrocytes and gliotransmitters. Exp Neurobiol 25(5):205–221. https://doi.org/10.5607/en.2016.25.5.205
Bankstahl M, Breuer H, Leiter I et al (2018) Blood–brain barrier leakage during early epileptogenesis is associated with rapid remodeling of the neurovascular unit. Eneuro 5(3)
Bazargani N, Attwell D (2017) Amines, astrocytes, and arousal. Neuron 94(2):228–231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2017.03.035
Bedner P, Dupper A, Hüttmann K et al (2015) Astrocyte uncoupling as a cause of human temporal lobe epilepsy. Brain 138(5):1208–1222
Bedner P, Jabs R, Steinhäuser C (2020) Properties of human astrocytes and NG2 glia. Glia 68(4):756–767
Bellot-Saez A, Stevenson R, Kékesi O et al (2021) Neuromodulation of Astrocytic K\(^+\) clearance. Int J Mol Sci 22(5):2520. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22052520
Bellot-Saez A, Cohen G, Van Schaik A et al (2018) Astrocytic modulation of cortical oscillations. Scientific Reports 8(1):11,565. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-30003-w
Berridge CW, Waterhouse BD (2003) The locus coeruleus-noradrenergic system: modulation of behavioral state and state-dependent cognitive processes. Brain Res Rev 42(1):33–84
Blutstein T, Haydon PG (2013) The importance of astrocyte-derived purines in the modulation of sleep. Glia 61(2):129–139. https://doi.org/10.1002/glia.22422
Bohmbach K, Masala N, Schönhense EM et al (2022) An astrocytic signaling loop for frequency-dependent control of dendritic integration and spatial learning. Nat Commun 13(1):7932. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-35620-8
Bohmbach K, Henneberger C, Hirrlinger J (2023) Astrocytes in memory formation and maintenance. Essays Biochem 67(1):107–117. https://doi.org/10.1042/EBC20220091
Boison D, Steinhäuser C (2018) Epilepsy and astrocyte energy metabolism. Glia 66(6):1235–1243
Bojarskaite L, Bjørnstad DM, Pettersen KH et al (2020) Astrocytic Ca\(^{2+}\) signaling is reduced during sleep and is involved in the regulation of slow wave sleep. Nat Commun 11(1):3240. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-17062-2
Borden PM, Zhang P, Shivange AV et al (2020) A fast genetically encoded fluorescent sensor for faithful in vivo acetylcholine detection in mice, fish, worms and flies. Preprint, Neurosci. https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.02.07.939504
Bordey A, Sontheimer H (1998) Electrophysiological properties of human astrocytic tumor cells in situ: enigma of spiking glial cells. J Neurophys 79(5):2782–2793
Brancaccio M, Patton AP, Chesham JE et al (2017) Astrocytes control circadian timekeeping in the suprachiasmatic nucleus via glutamatergic signaling. Neuron 93(6):1420-1435.e5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2017.02.030
Brazhe AR, Verisokin AY, Verveyko DV et al (2018) Sodium-calcium exchanger can account for regenerative Ca. Front Cell Neurosci 12:250. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2018.00250
Breithausen B, Kautzmann S, Boehlen A et al (2020) Limited contribution of astroglial gap junction coupling to buffering of extracellular K\(^+\) in CA1 stratum radiatum. Glia 68(5):918–931. https://doi.org/10.1002/glia.23751
Buskila Y, Bellot-Saez A, Morley JW (2019) Generating brain waves, the power of astrocytes. Front Neurosci 13:1125. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2019.01125
Cavus I, Kasoff WS, Cassaday MP et al (2005) Extracellular metabolites in the cortex and hippocampus of epileptic patients. Ann Neurol 57(2):226–235
Chai H, Diaz-Castro B, Shigetomi E et al (2017) Neural circuit-specialized astrocytes: transcriptomic, proteomic, morphological, and functional evidence. Neuron 95(3):531-549.e9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2017.06.029
Chander B, Chakravarthy S (2012) A computational model of neuro-glio-vascular loop interactions. PloS one 7:e48,802. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0048802
Chen H, Sun D (2005) The role of Na-K-Cl co-transporter in cerebral ischemia. Neurol Res 27(3):280–286
Chen YH, Jin SY, Yang JM et al (2023) The memory orchestra: contribution of astrocytes. Neurosci Bull 39(3):409–424. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12264-023-01024-x
Cheng YT, Woo J, Luna-Figueroa E et al (2023) Social deprivation induces astrocytic TRPA1-GABA suppression of hippocampal circuits. Neuron 111(8):1301-1315.e5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2023.01.015
Chever O, Djukic B, McCarthy KD et al (2010) Implication of Kir4.1 channel in excess potassium clearance: an in vivo study on anesthetized glial-conditional Kir4.1 knock-out mice. J Neurosci 30(47):15,769–15,777
Cho WH, Noh K, Lee BH et al (2022) Hippocampal astrocytes modulate anxiety-like behavior. Nat Commun 13(1):6536. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-34201-z
Choi IS, Kim JH, Jeong JY et al (2022) Astrocyte-derived adenosine excites sleep-promoting neurons in the ventrolateral preoptic nucleus: astrocyte-neuron interactions in the regulation of sleep. Glia 70(10):1864–1885. https://doi.org/10.1002/glia.24225
Chong PL, Garic D, Shen MD et al (2022) Sleep, cerebrospinal fluid, and the glymphatic system: a systematic review. Sleep Med Rev 61(101):572. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.smrv.2021.101572
Chuquet J, Hollender L, Nimchinsky E (2007) High-resolution in vivo imaging of the neurovascular unit during spreading depression. J Neurosci: Official J Soc Neurosci 27:4036–44. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0721-07.2007
Chvátal A, Anderová M, Hock M et al (2007) Three-dimensional confocal morphometry reveals structural changes in astrocyte morphology in situ. J Neurosci Res 85(2):260–271
Cohen Z, Molinatti G, Hamel E (1997) Astroglial and vascular interactions of noradrenaline terminals in the rat cerebral cortex. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 17(8):894–904
Covelo A, Badoual A, Denizot A (2022) Reinforcing interdisciplinary collaborations to unravel the astrocyte “calcium code”. J Mol Neurosci 72. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-022-02006-w
Curreli S, Bonato J, Romanzi S et al (2022) Complementary encoding of spatial information in hippocampal astrocytes. PLOS Biology 20(3):e3001,530. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.3001530
Delekate A, Füchtemeier M, Schumacher T et al (2014) Metabotropic P2Y1 receptor signalling mediates astrocytic hyperactivity in vivo in an Alzheimer’s disease mouse model. Nat Commun 5. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms6422
Delgado L, Navarrete M (2023) Shining the light on astrocytic ensembles. Cells 12(9):1253. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12091253
Denizot A, Arizono M, Nägerl UV et al (2019) Simulation of calcium signaling in fine astrocytic processes: effect of spatial properties on spontaneous activity. PLoS Comput Biol 15(8):e1006,795. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1006795
Descarries L, Watkins KC, Lapierre Y (1977) Noradrenergic axon terminals in the cerebral cortex of rat. III. Topometric ultrastructural analysis. Brain Res 133(2):197–222
Dibaj P, Kaiser M, Hirrlinger J et al (2007) Kir4.1 channels regulate swelling of astroglial processes in experimental spinal cord edema. J Neurochem 103(6):2620–2628
Dimkovski M, An A (2015) Computational role of astrocytes as Bayesian inference agents in shaping neural networks. Tech. Rep. EECS-2015-01, York University
Ding F, O’Donnell J, Xu Q et al (2016) Changes in the composition of brain interstitial ions control the sleep-wake cycle. Science 352(6285):550–555
Ding Z, Fan X, Zhang Y et al (2023) The glymphatic system: a new perspective on brain diseases. Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience 15(1179):988. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2023.1179988
Doron A, Rubin A, Benmelech-Chovav A et al (2022) Hippocampal astrocytes encode reward location. Nature 609(7928):772–778. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-022-05146-6
During MJ, Spencer DD (1993) Extracellular hippocampal glutamate and spontaneous seizure in the conscious human brain. The Lancet 341(8861):1607–1610
Durkee CA, Covelo A, Lines J et al (2019) G\(_{i/o}\) protein-coupled receptors inhibit neurons but activate astrocytes and stimulate gliotransmission. Glia 67(6):1076–1093. https://doi.org/10.1002/glia.23589
Eid T, Lee TSW, Thomas MJ et al (2005) Loss of perivascular aquaporin 4 may underlie deficient water and K\(^+\) homeostasis in the human epileptogenic hippocampus. Proc Natl Acad Sci 102(4):1193–1198
Eitelmann S, Stephan J, Everaerts K et al (2022) Changes in astroglial K\(^+\) upon brief periods of energy deprivation in the mouse neocortex. Int J Mol Sci 23(9):4836. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23094836
Eldar E, Cohen JD, Niv Y (2013) The effects of neural gain on attention and learning. Nat Neurosci 16(8):1146–1153
Escartin C, Galea E, Lakatos A et al (2021) Reactive astrocyte nomenclature, definitions, and future directions. Nat Neurosci 24(3):312–325. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41593-020-00783-4
Farr H, David T (2011) Models of neurovascular coupling via potassium and EET signalling. J Theor Biol 286:13–23
Fedotova A, Brazhe A, Doronin M et al (2023) Dissociation between neuronal and astrocytic calcium activity in response to locomotion in mice. Function p zqad019. https://doi.org/10.1093/function/zqad019
Felix L, Delekate A, Petzold GC et al (2020) Sodium fluctuations in astroglia and their potential impact on astrocyte function. Front Physiol 11:871. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2020.00871
Fellin T, Ellenbogen JM, De Pittà M et al (2012) Astrocyte regulation of sleep circuits: experimental and modeling perspectives. Front Comput Neurosci 6:65
Fellin T, Halassa MM, Terunuma M et al (2009) Endogenous nonneuronal modulators of synaptic transmission control cortical slow oscillations in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci 106(35):15,037–15,042. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0906419106
Feng J, Zhang C, Lischinsky JE et al (2019) A genetically encoded fluorescent sensor for rapid and specific in vivo detection of norepinephrine. Neuron 102(4):745-761.e8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2019.02.037
Fischer T, Scheffler P, Lohr C (2020) Dopamine-induced calcium signaling in olfactory bulb astrocytes. Sci Rep 10(1):631. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-57462-4
Fischer T, Prey J, Eschholz L et al (2021) Norepinephrine-induced calcium signaling and store-operated calcium entry in olfactory bulb astrocytes. Front Cell Neurosci 15(639):754. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2021.639754
Florence CM, Baillie LD, Mulligan SJ (2012) Dynamic volume changes in astrocytes are an intrinsic phenomenon mediated by bicarbonate ion flux. PloS one 7(11):e51,124
Foley J, Blutstein T, Lee S et al (2017) Astrocytic IP\(_{3}\)/Ca\(^{2+}\) signaling modulates theta rhythm and rem sleep. Front Neural Circ 11. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncir.2017.00003
Fordsmann JC, Ko RWY, Choi HB et al (2013) Increased 20-HETE synthesis explains reduced cerebral blood flow but not impaired neurovascular coupling after cortical spreading depression in rat cerebral cortex. J Neurosci 33(6):2562–2570. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2308-12.2013
Frank MG (2013) Astroglial regulation of sleep homeostasis. Curr Opin Neurobiol 23(5):812–818
Gerkau NJ, Rakers C, Petzold GC et al (2017) Differential effects of energy deprivation on intracellular sodium homeostasis in neurons and astrocytes: effects of energy deprivation on cellular sodium. J Neurosci Res 95(11):2275–2285. https://doi.org/10.1002/jnr.23995
Gerkau NJ, Lerchundi R, Nelson JSE et al (2019) Relation between activity-induced intracellular sodium transients and ATP dynamics in mouse hippocampal neurons. J Physiol 597(23):5687–5705. https://doi.org/10.1113/JP278658
Goenaga J, Araque A, Kofuji P et al (2023) Calcium signaling in astrocytes and gliotransmitter release. Front Synaptic Neurosci 15:1138,577. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnsyn.2023.1138577
Gonzalez J, Pinzón A, Angarita Rodríguez M et al (2020) Advances in astrocyte computational models: from metabolic reconstructions to multi-omic approaches. Front Neuroinform 14. https://doi.org/10.3389/fninf.2020.00035
Gordleeva S, Ermolaeva A, Kastalskiy I et al (2019) Astrocyte as spatiotemporal integrating detector of neuronal activity. Front Physiol 10sps294. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2019.00294
Gordleeva S, Tsybina Y, Krivonosov M et al (2021) Modeling working memory in a spiking neuron network accompanied by astrocytes. Front Cell Neurosci 15. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2021.631485
Gordon GR, Howarth C, Macvicar BA (2011) Bidirectional control of arteriole diameter by astrocytes. Exp Physiol. arXiv:2125.7665. https://doi.org/10.1113/expphysiol.2010.053132
Gordon GRJ, Howarth C, MacVicar BA (2016) Bidirectional control of blood flow by astrocytes: a role for tissue oxygen and other metabolic factors. In: Roach RC, Hackett PH, Wagner PD (eds) Hypoxia, vol 903. Springer US, Boston, MA, p 209–219. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4899-7678-9_15
Grabner GF, Eichmann TO, Wagner B et al (2016) Deletion of monoglyceride lipase in astrocytes attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced neuroinflammation. J Biol Chem 291(2):913–923. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M115.683615
Gray SR, Ye L, Ye JY et al (2021) Noradrenergic terminal short-term potentiation enables modality-selective integration of sensory input and vigilance state. Sci Adv 7(51):eabk1378. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.abk1378
Hadfield J, Plank M, David T (2013) Modeling secondary messenger pathways in neurovascular coupling. Bull Math Biol 75. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11538-013-9813-x
Haidey JN, Peringod G, Institoris A et al (2021) Astrocytes regulate ultra-slow arteriole oscillations via stretch-mediated TRPV4-COX-1 feedback. Cell Rep 36(5):109,405. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2021.109405
Haines TH (1994) Water transport across biological membranes. FEBS lett 346(1):115–122
Haj-Yasein NN, Jensen V, Vindedal GF et al (2011) Evidence that compromised K\(^+\) spatial buffering contributes to the epileptogenic effect of mutations in the human Kir4.1 gene (KCNJ10). Glia 59(11):1635–1642
Halassa MM, Florian C, Fellin T et al (2009) Astrocytic modulation of sleep homeostasis and cognitive consequences of sleep loss. Neuron 61(2):213–219
Hannesschlaeger C, Horner A, Pohl P (2019) Intrinsic membrane permeability to small molecules. Chem Rev 119(9):5922–5953
Haydon PG (2017) Astrocytes and the modulation of sleep. Curr Opin Neurobiol 44:28–33
Heinemann U, Gabriel S, Jauch R et al (2000) Alterations of glial cell function in temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsia 41:S185–S189
Héja L, Kardos J (2020) NCX activity generates spontaneous Ca\(^{2+}\) oscillations in the astrocytic leaflet microdomain. Cell Calcium 86(102):137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceca.2019.102137
Héja L, Szabó Z, Péter M et al (2021) Spontaneous Ca\(^{2+}\) fluctuations arise in thin astrocytic processes with real 3D geometry. Front Cell Neurosci 15:617,989. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2021.617989
Henneberger C, Bard L, Panatier A et al (2020) LTP Induction boosts glutamate spillover by driving withdrawal of perisynaptic astroglia. Neuron 108(5):919-936.e11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2020.08.030
Henning L, Unichenko P, Bedner P et al (2023) Overview article astrocytes as initiators of epilepsy. Neurochem Res 48(4):1091–1099. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-022-03773-z
Herde MK, Bohmbach K, Domingos C et al (2020) Local efficacy of glutamate uptake decreases with synapse size. Cell Reports 32(12):108,182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2020.108182
Hines D, Schmitt L, Hines R et al (2013) Antidepressant effects of sleep deprivation require astrocyte-dependent adenosine mediated signaling. Transl Psychiatry 3(1):e212–e212
Hinterkeuser S, Schröder W, Hager G et al (2000) Astrocytes in the hippocampus of patients with temporal lobe epilepsy display changes in potassium conductances. Eur J NeuroSci 12(6):2087–2096
Hladky SB, Barrand MA (2022) The glymphatic hypothesis: the theory and the evidence. Fluids and Barriers of the CNS 19(1):1–33
Howarth C, Sutherland BA, Choi HB et al (2017) A critical role for astrocytes in hypercapnic vasodilation in brain. J Neurosci 37(9):2403–2414. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0005-16.2016
Hubbard JA, Szu JI, Yonan JM et al (2016) Regulation of astrocyte glutamate transporter-1 (GLT1) and aquaporin-4 (AQP4) expression in a model of epilepsy. Exp Neurol 283:85–96
Hübel N, Hosseini M, Ziburkus J et al (2017) The role of glutamate in neuronal ion homeostasis: a case study of spreading depolarization. PLoS Comput Biol 13:e1005,804. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1005804
Hübel N, Ullah G (2016) Anions govern cell volume: a case study of relative astrocytic and neuronal swelling in spreading depolarization. PloS one 11(3):e0147,060
Iadecola C (2017) The neurovascular unit coming of age: a journey through neurovascular coupling in health and disease. Neuron 96:17–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2017.07.030
Iliff JJ, Wang M, Zeppenfeld DM et al (2013) Cerebral arterial pulsation drives paravascular CSF–interstitial fluid exchange in the murine brain. J Neurosci 33(46):18,190–18,199. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1592-13.2013
Ingiosi AM, Frank MG (2022) Noradrenergic signaling in astrocytes influences mammalian sleep homeostasis. Clocks & Sleep 4(3):332–345. https://doi.org/10.3390/clockssleep4030028
Ingiosi AM, Frank MG (2023) Goodnight, astrocyte: waking up to astroglial mechanisms in sleep. FEBS J 290(10):2553–2564. https://doi.org/10.1111/febs.16424
Ingiosi AM, Hayworth CR, Harvey DO et al (2020) A role for astroglial calcium in mammalian sleep and sleep regulation. Curr Biol 30(22):4373-4383.e7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2020.08.052
Inoue H, Si Mori, Morishima S et al (2005) Volume-sensitive chloride channels in mouse cortical neurons: characterization and role in volume regulation. Eur J NeuroSci 21(6):1648–1658
Institoris A, Vandal M, Peringod G et al (2022) Astrocytes amplify neurovascular coupling to sustained activation of neocortex in awake mice. Nat Commun 13(1):7872. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-35383-2
Ishibashi M, Egawa K, Fukuda A (2019) Diverse actions of astrocytes in gabaergic signaling. Int J Mol Sci 20(12):2964. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20122964
Iwai Y, Ozawa K, Yahagi K et al (2021) Transient astrocytic Gq signaling underlies remote memory enhancement. Front Neural Circ 15:658,343. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncir.2021.658343
Jauch R, Windmüller O, Lehmann TN et al (2002) Effects of barium, furosemide, ouabaine and 4, 4’-diisothiocyanatostilbene-2, 2’-disulfonic acid (DIDS) on ionophoretically-induced changes in extracellular potassium concentration in hippocampal slices from rats and from patients with epilepsy. Brain Res 925(1):18–27
Jefferys J, Steinhäuser C, Bedner P (2016) Chemically-induced TLE models: topical application. J Neurosci Methods 260:53–61
Jing M, Zhang Y, Wang H et al (2019) G-protein-coupled receptor-based sensors for imaging neurochemicals with high sensitivity and specificity. J Neurochem 151(3):279–288. https://doi.org/10.1111/jnc.14855
Jolivet R, Coggan J, Allaman I et al (2015) Multi-timescale modeling of activity-dependent metabolic coupling in the neuron-glia-vasculature ensemble. PLoS Comput Biol 11:e1004,036. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1004036
Kalia M, Meijer HGE, Van Gils SA et al (2021) Ion dynamics at the energy-deprived tripartite synapse. PLoS Comput Biol 17(6):e1009,019. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1009019
Kenny A, Plank MJ, David T (2018) The role of astrocytic calcium and TRPV4 channels in neurovascular coupling. J Comput Neurosci 44(1):97–114
Kettenmann H, Hanisch UK, Noda M et al (2011) Physiology of microglia. Physiol Rev 91(2):461–553
Khakh BS (2019) Astrocyte-neuron interactions in the striatum: insights on identity, form, and function. Trends Neurosci 42(9):617–630. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tins.2019.06.003
Khazipov R (2016) GABAergic synchronization in epilepsy. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 6(2):a022,764. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a022764
Kilb W, Kirischuk S (2022) GABA Release from astrocytes in health and disease. Int J Mol Sci 23(24):15,859. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232415859
Kim JH, Choi IS, Jeong JY et al (2020) Astrocytes in the ventrolateral preoptic area promote sleep. J Neurosci 40(47):8994–9011
Kim H, Baek IY, Seong J (2022) Genetically encoded fluorescent biosensors for GPCR research. Front Cell Dev Biol 10(1007):893. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2022.1007893
Kimelberg HK (2000) Review: cell volume in the CNS: regulation and implications for nervous system function and pathology. Neuroscientist 6(1):14–25
Kimelberg HK, MacVicar BA, Sontheimer H (2006) Anion channels in astrocytes: biophysics, pharmacology, and function. Glia 54(7):747–757
King CM, Bohmbach K, Minge D et al (2020) Local resting Ca\(^{2+}\) controls the scale of astroglial Ca\(^{2+}\) signals. Cell Rep 30(10):3466-3477.e4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2020.02.043
Kivi A, Lehmann TN, Kovacs R et al (2000) Effects of barium on stimulus-induced rises of [K\(^+\)]\(_o\) in human epileptic non-sclerotic and sclerotic hippocampal area CA1. Eur J NeuroSci 12(6):2039–2048
Koehler R, Gebremedhin D, Harder D (2006) Role of astrocytes in cerebrovascular regulation. J Appl Physiol (Bethesda, Md : 1985) 100:307–17. https://doi.org/10.1152/japplphysiol.00938.2005
Kofuji P, Araque A (2021) G-protein-coupled receptors in astrocyte-neuron communication. Neuroscience 456:71–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2020.03.025
Kofuji P, Ceelen P, Zahs KR et al. (2000) Genetic inactivation of an inwardly rectifying potassium channel (Kir4.1 subunit) in mice: phenotypic impact in retina. J Neurosci 20(15):5733–5740
Kol A, Adamsky A, Groysman M et al (2020) Astrocytes contribute to remote memory formation by modulating hippocampal-cortical communication during learning. Nat Neurosci 23(10):1229–1239. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41593-020-0679-6
Kostyuk AI, Demidovich AD, Kotova DA et al (2019) Circularly permuted fluorescent protein-based indicators: history, principles, and classification. Int J Mol Sci 20(17):4200. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20174200
Kroning KE, Wang W (2022) Genetically encoded tools for in vivo G-protein-coupled receptor agonist detection at cellular resolution. Clin Transl Med 12(12). https://doi.org/10.1002/ctm2.1124
Krueger JM, Rector DM, Roy S et al (2008) Sleep as a fundamental property of neuronal assemblies. Nat Rev Neurosci 9(12):910–919
Krueger JM, Nguyen JT, Dykstra-Aiello CJ et al (2019) Local sleep. Sleep Med Rev 43:14–21
Lallouette J, De Pittà M, Ben-Jacob E et al (2014) Sparse short-distance connections enhance calcium wave propagation in a 3D model of astrocyte networks. Front Comput Neurosci 8. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncom.2014.00045
Landolt HP, Holst SC (2016) Ionic control of sleep and wakefulness. Science 352(6285):517–518
Langer J, Rose CR (2009) Synaptically induced sodium signals in hippocampal astrocytes in situ: sodium signals in astrocytes. J Physiol 587(24):5859–5877. https://doi.org/10.1113/jphysiol.2009.182279
Lascola CD, Nelson DJ, Kraig RP (1998) Cytoskeletal actin gates a Cl\(^-\) channel in neocortical astrocytes. J Neurosci 18(5):1679–1692
Lebedeva A, Plata A, Nosova O et al (2018) Activity-dependent changes in transporter and potassium currents in hippocampal astrocytes. Brain Res Bull 136:37–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainresbull.2017.08.015
Lee TS, Eid T, Mane S et al (2004) Aquaporin-4 is increased in the sclerotic hippocampus in human temporal lobe epilepsy. Acta Neuropathol 108:493–502
Lee DJ, Hsu MS, Seldin MM et al (2012) Decreased expression of the glial water channel aquaporin-4 in the intrahippocampal kainic acid model of epileptogenesis. Exp Neurol 235(1):246–255
Lee SH, Mak A, Verheijen MHG (2023) Comparative assessment of the effects of DREADDs and endogenously expressed GPCRs in hippocampal astrocytes on synaptic activity and memory. Front Cell Neurosci 17:1159,756. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2023.1159756
Lenk K, Satuvuori E, Lallouette J et al (2020) A computational model of interactions between neuronal and astrocytic networks: the role of astrocytes in the stability of the neuronal firing rate. Front Comput Neurosci 13:92. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncom.2019.00092
Lerchundi R, Huang N, Rose CR (2020) Quantitative imaging of changes in astrocytic and neuronal adenosine triphosphate using two different variants of ATeam. Front Cell Neurosci 14:80. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2020.00080
Li Z, Mcconnell H, Stackhouse T et al (2021) Increased 20-HETE signaling suppresses capillary neurovascular coupling after ischemic stroke in regions beyond the infarct. Front Cell Neurosci 15:762,843. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2021.762843
Lia A, Henriques VJ, Zonta M et al (2021) Calcium signals in astrocyte microdomains, a decade of great advances. Front Cell Neurosci 15:673,433. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2021.673433
Lia A, Di Spiezio A, Speggiorin M et al (2023) Two decades of astrocytes in neurovascular coupling. Front Network Physiol 3:1162,757. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnetp.2023.1162757
Lim EY, Ye L, Paukert M (2021) Potential and realized impact of astroglia Ca\(^{2+}\) dynamics on circuit function and behavior. Front Cell Neurosci 15:682,888. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2021.682888
Lind BL, Jessen SB, Lønstrup M et al (2018) Fast Ca \(^{2+}\) responses in astrocyte end-feet and neurovascular coupling in mice. Glia 66(2):348–358. https://doi.org/10.1002/glia.23246
Lines J, Martin ED, Kofuji P et al (2020) Astrocytes modulate sensory-evoked neuronal network activity. Nat Commun 11(1):3689. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-17536-3
Linne ML, Acimovic J, Saudargiene A et al (2022) Neuron-Glia Interactions and Brain Circuits 1359:87–103. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-89439-9_4
Liu J, Feng X, Wang Y et al (2022) Astrocytes: GABAceptive and GABAergic cells in the brain. Front Cell Neurosci 16:892,497. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2022.892497
Liu L, Gao H, Li J et al (2023) Probing microdomain Ca\(^{2+}\) activity and synaptic transmission with a node-based tripartite synapse model. Front Network Physiol 3:1111,306. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnetp.2023.1111306
Loddenkemper T, Grote K, Evers S et al (2002) Neurological manifestations of the oculodentodigital dysplasia syndrome. J Neurol 249:584–595
Lohela TJ, Lilius TO, Nedergaard M (2022) The glymphatic system: implications for drugs for central nervous system diseases. Nat Rev Drug Discov 21(10):763–779
Lohr C, Beiersdorfer A, Fischer T et al (2021) Using genetically encoded calcium indicators to study astrocyte physiology: a field guide. Front Cell Neurosci 15:690,147. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2021.690147
Löscher W, Schmidt D (2011) Modern antiepileptic drug development has failed to deliver: ways out of the current dilemma. Epilepsia 52(4):657–678
Lyon KA, Allen NJ (2022) From synapses to circuits, astrocytes regulate behavior. Front Neural Circ 15:786,293. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncir.2021.786293
MacVicar BA, Newman EA (2015) Astrocyte regulation of blood flow in the brain. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 7(5):a020,388. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a020388
Magloire V, Savtchenko LP, Jensen TP et al (2023) Volume-transmitted GABA waves pace epileptiform rhythms in the hippocampal network. Curr Biol 33(7):1249-1264.e7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2023.02.051
Mann EO, Paulsen O (2007) Role of GABAergic inhibition in hippocampal network oscillations. Trends Neurosci 30(7):343–349. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tins.2007.05.003
Manninen T, Havela R, Linne ML (2018) Computational models for calcium-mediated astrocyte functions. Front Comput Neurosci 12:14. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncom.2018.00014
Manninen T, Aćimović J, Linne ML (2023) Analysis of network models with neuron-astrocyte interactions. Neuroinformatics 21(2):375–406. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12021-023-09622-w
Marina N, Christie IN, Korsak A et al (2020) Astrocytes monitor cerebral perfusion and control systemic circulation to maintain brain blood flow. Nat Commun 11(1):131. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-13956-y
Marvin JS, Borghuis BG, Tian L et al (2013) An optimized fluorescent probe for visualizing glutamate neurotransmission. Nat Methods 10(2):162–170. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.2333
Marvin JS, Shimoda Y, Magloire V et al (2019) A genetically encoded fluorescent sensor for in vivo imaging of GABA. Nat Methods 16(8):763–770. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41592-019-0471-2
Masamoto K, Unekawa M, Watanabe T et al (2015) Unveiling astrocytic control of cerebral blood flow with optogenetics. Sci Rep 5(1):11,455. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep11455
Mather M, Clewett D, Sakaki M et al (2016) Norepinephrine ignites local hotspots of neuronal excitation: how arousal amplifies selectivity in perception and memory. Behav Brain Sci 39
Matsuoka S, Philipson KD, Hilgemann DW (1996) Multiple functional states of the cardiac Na\(^+\)-Ca\(^{2+}\) exchanger. whole-cell, native-excised, and cloned-excised properties. Ann N Y Acad Sci 779:159–70
McCauley JP, Petroccione MA, D’Brant LY et al (2020) Circadian modulation of neurons and astrocytes controls synaptic plasticity in hippocampal area CA1. Cell Reports 33(2):108,255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2020.108255
Mederos S, Perea G (2019) GABAergic-astrocyte signaling: a refinement of inhibitory brain networks. Glia 67(10):1842–1851. https://doi.org/10.1002/glia.23644
Mederos S, Hernández-Vivanco A, Ramírez-Franco J et al (2019) Melanopsin for precise optogenetic activation of astrocyte-neuron networks. Glia 67(5):915–934. https://doi.org/10.1002/glia.23580
Mederos S, Sánchez-Puelles C, Esparza J et al (2021) GABAergic signaling to astrocytes in the prefrontal cortex sustains goal-directed behaviors. Nat Neurosci 24(1):82–92. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41593-020-00752-x
Mestre H, Mori Y, Nedergaard M (2020) The brain’s glymphatic system: current controversies. Trends Neurosci 43(7):458–466. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tins.2020.04.003
Meyer J, Gerkau NJ, Kafitz KW et al (2022) Rapid fluorescence lifetime imaging reveals that TRPV4 channels promote dysregulation of neuronal Na \(^{+}\) in ischemia. J Neurosci 42(4):552–566. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0819-21.2021
Morita M (2023) Modern microscopic approaches to astrocytes. Int J Mol Sci 24(6):5883. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24065883
Mouton PR, Pakkenberg B, Gundersen HJG et al (1994) Absolute number and size of pigmented locus coeruleus neurons in young and aged individuals. J Chem Neuroanat 7(3):185–190
Mu Y, Bennett DV, Rubinov M et al (2019) Glia accumulate evidence that actions are futile and suppress unsuccessful behavior. Cell 178(1):27-43.e19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2019.05.050
Murphy TR, Davila D, Cuvelier N et al (2017) Hippocampal and cortical pyramidal neurons swell in parallel with astrocytes during acute hypoosmolar stress. Front Cell Neurosci 11:275
Nadjar A, Blutstein T, Aubert A et al (2013) Astrocyte-derived adenosine modulates increased sleep pressure during inflammatory response: astrocytes mediate somnogenic effects of LPS. Glia 61(5):724–731. https://doi.org/10.1002/glia.22465
Nadkarni S, Jung P (2007) Modeling synaptic transmission of the tripartite synapse. Phys Biol 4:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1088/1478-3975/4/1/001
Nagai J, Rajbhandari AK, Gangwani MR et al (2019) Hyperactivity with disrupted attention by activation of an astrocyte synaptogenic cue. Cell 177(5):1280-1292.e20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2019.03.019
Nagai J, Bellafard A, Qu Z et al (2021) Specific and behaviorally consequential astrocyte Gq GPCR signaling attenuation in vivo with i\(\beta \)ARK. Neuron 109(14):2256-2274.e9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2021.05.023
Newman EA (1986) Regional specialization of the membrane of retinal glial cells and its importance to K\(^+\) spatial buffering a. Ann N Y Acad Sci 481(1):273–286
Nicholson C, Hrabětová S (2017) Brain extracellular space: the final frontier of neuroscience. Biophys J 113(10):2133–2142
Nimmerjahn A, Mukamel EA, Schnitzer MJ (2009) Motor behavior activates Bergmann glial networks. Neuron 62(3):400–412. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2009.03.019
Nobili L, De Gennaro L, Proserpio P et al (2012) Local aspects of sleep: observations from intracerebral recordings in humans. Prog Brain Res 199:219–232
Oberheim NA, Takano T, Han X et al (2009) Uniquely hominid features of adult human astrocytes. J Neurosci 29(10):3276–3287
Oe Y, Wang X, Patriarchi T et al (2020) Distinct temporal integration of noradrenaline signaling by astrocytic second messengers during vigilance. Nat Commun 11(1):471. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-14378-x
Oschmann F, Berry H, Obermayer K et al (2018) From in silico astrocyte cell models to neuron-astrocyte network models: a review. Brain Res Bull 136:76–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainresbull.2017.01.027
Østby I, Øyehaug L, Einevoll GT et al (2009) Astrocytic mechanisms explaining neural-activity-induced shrinkage of extraneuronal space. PLoS Comput Biol 5(1):e1000,272
Ozawa K, Nagao M, Konno A et al (2023) Astrocytic GPCR-Induced Ca\(^{2+}\) Signaling is not causally related to local cerebral blood flow changes. Int J Mol Sci 24(17):13,590. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241713590
Pannasch U, Freche D, Dallérac G et al (2014) Connexin 30 sets synaptic strength by controlling astroglial synapse invasion. Nat Neurosci 17(4):549–558. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.3662
Paukert M, Agarwal A, Cha J et al (2014) Norepinephrine controls astroglial responsiveness to local circuit activity. Neuron 82(6):1263–1270. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2014.04.038
Pelluru D, Konadhode RR, Bhat NR et al (2016) Optogenetic stimulation of astrocytes in the posterior hypothalamus increases sleep at night in C57 BL/6J mice. Eur J NeuroSci 43(10):1298–1306. https://doi.org/10.1111/ejn.13074
Peng W, Liu X, Ma G et al (2023) Adenosine-independent regulation of the sleep-wake cycle by astrocyte activity. Cell Discov 9(1):16. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41421-022-00498-9
Perea G, Yang A, Boyden ES et al (2014) Optogenetic astrocyte activation modulates response selectivity of visual cortex neurons in vivo. Nat Commun 5(1):3262. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms4262
Pfitzner J (1976) Poiseuille and his law. Anaesthesia 31(2):273–275
Pigarev IN, Nothdurft HC, Kastner S (1997) Evidence for asynchronous development of sleep in cortical areas. Neuroreport 8(11):2557–2560
Pittolo S, Yokoyama S, Willoughby DD et al (2022) Dopamine activates astrocytes in prefrontal cortex via \(A\)1-adrenergic receptors. Cell Rep 40(13):111,426. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2022.111426
Polack PO, Friedman J, Golshani P (2013) Cellular mechanisms of brain state-dependent gain modulation in visual cortex. Nat Neurosci 16(9):1331–1339
Porter-Stransky KA, Centanni SW, Karne SL et al (2019) Noradrenergic transmission at alpha1-adrenergic receptors in the ventral periaqueductal gray modulates arousal. Biol Psychiatry 85(3):237–247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2018.07.027
Poskanzer KE, Yuste R (2016) Astrocytes regulate cortical state switching in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci 113(19). https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1520759113
Przybyło M, Drabik D, Doskocz J et al (2021) The effect of the osmotically active compound concentration difference on the passive water and proton fluxes across a lipid bilayer. Int J Mol Sci 22(20):11,099
Purnell BS, Alves M, Boison D (2023) Astrocyte-neuron circuits in epilepsy. Neurobiol Dis 179:106,058. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2023.106058
Qin H, He W, Yang C et al (2020) Monitoring astrocytic Ca\(^{2+}\) activity in freely behaving mice. Front Cell Neurosci 14:603,095. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2020.603095
Rasmussen RN, Asiminas A, Carlsen EMM et al (2023) Astrocytes: integrators of arousal state and sensory context. Trends Neurosci 46(6):418–425. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tins.2023.03.003
Rector DM, Schei JL, Van Dongen HPA et al (2009) Physiological markers of local sleep. Eur J NeuroSci 29(9):1771–1778. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1460-9568.2009.06717.x
Reitman ME, Tse V, Mi X et al (2023) Norepinephrine links astrocytic activity to regulation of cortical state. Nat Neurosci 26(4):579–593. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41593-023-01284-w
Risher WC, Andrew RD, Kirov SA (2009) Real-time passive volume responses of astrocytes to acute osmotic and ischemic stress in cortical slices and in vivo revealed by two-photon microscopy. Glia 57(2):207–221
Risher WC, Croom D, Kirov SA (2012) Persistent astroglial swelling accompanies rapid reversible dendritic injury during stroke-induced spreading depolarizations. Glia 60(11):1709–1720
Rojas H, Colina C, Ramos M et al (2007) Na\(^+\) entry via glutamate transporter activates the reverse Na\(^+\)/Ca\(^{2+}\) exchange and triggers Ca(i)\(^{2+}\)-induced Ca\(^{2+}\) release in rat cerebellar type-1 astrocytes. J Neurochem 100(5):1188–202. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-4159.2006.04303.x
Rose CR, Felix L, Zeug A et al (2018) Astroglial glutamate signaling and uptake in the hippocampus. Frontiers in Molecular Neuroscience 10:451
Rose CR, Ziemens D, Verkhratsky A (2020) On the special role of NCX in astrocytes: translating Na+-transients into intracellular Ca\(^{2+}\) signals. Cell Calcium 86:102,154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceca.2019.102154
Roth BL (2016) DREADDs for neuroscientists. Neuron 89(4):683–694. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2016.01.040
Roux L, Buzsáki G (2015) Tasks for inhibitory interneurons in intact brain circuits. Neuropharmacology 88:10–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2014.09.011
Rusakov DA (2015) Disentangling calcium-driven astrocyte physiology. Nat Rev Neurosci 16(4):226–233
Rusakov DA, Bard L, Stewart MG et al (2014) Diversity of astroglial functions alludes to subcellular specialisation. Trends Neurosci 37(4):228–242
Rusina E, Bernard C, Williamson A (2021) The kainic acid models of temporal lobe epilepsy. Eneuro 8(2)
Samuels ER, Szabadi E (2008) Functional neuroanatomy of the noradrenergic locus coeruleus: its roles in the regulation of arousal and autonomic function part i: principles of functional organisation. Curr Neuropharmacol 6(3):235–253
Saper CB, Chou TC, Scammell TE (2001) The sleep switch: hypothalamic control of sleep and wakefulness. Trends Neurosci 24(12):726–731
Savtchenko LP, Bard L, Jensen TP et al (2018) Disentangling astroglial physiology with a realistic cell model in silico. Nat Commun 9(1):3554. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-05896-w
Schröder W, Hinterkeuser S, Seifert G et al (2000) Functional and molecular properties of human astrocytes in acute hippocampal slices obtained from patients with temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsia 41:S181–S184
Schummers J, Yu H, Sur M (2008) Tuned responses of astrocytes and their influence on hemodynamic signals in the visual cortex. Science 320(5883):1638–1643. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1156120
Schwarz LA, Luo L (2015) Organization of the locus coeruleus-norepinephrine system. Curr Bio 25(21):R1051–R1056
Seifert G, Schilling K, Steinhäuser C (2006) Astrocyte dysfunction in neurological disorders: a molecular perspective. Nat Rev Neurosci 7(3):194–206
Semyanov A, Verkhratsky A (2021) Astrocytic processes: from tripartite synapses to the active milieu. Trends Neurosci 44(10):781–792. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tins.2021.07.006
Semyanov A, Henneberger C, Agarwal A (2020) Making sense of astrocytic calcium signals – from acquisition to interpretation. Nat Rev Neurosci 21(10):551–564. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41583-020-0361-8
Senarathna J, Yu H, Deng C et al (2019) A miniature multi-contrast microscope for functional imaging in freely behaving animals. Nat Commun 10(1):99. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-07926-z
Siclari F, Tononi G (2017) Local aspects of sleep and wakefulness. Curr Opin Neurobiol 44:222–227
Siuda ER, McCall JG, Al-Hasani R et al (2015) Optodynamic simulation of \(\beta \)-adrenergic receptor signalling. Nat Commun 6(1):8480. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms9480
Slezak M, Kandler S, Van Veldhoven PP et al (2019) Distinct mechanisms for visual and motor-related astrocyte responses in mouse visual cortex. Curr Biol 29(18):3120-3127.e5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2019.07.078
Sonoda K, Matsui T, Bito H et al (2018) Astrocytes in the mouse visual cortex reliably respond to visual stimulation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 505(4):1216–1222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.10.027
Springer CS Jr (2018) Using 1H2O MR to measure and map sodium pump activity in vivo. J Magn Reson 291:110–126
Stimberg M, Goodman D, Brette R et al (2019) Modeling neuron-glia interactions with the brian 2 simulator 471–505. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-00817-8_18
Strecker RE, Morairty S, Thakkar MM et al (2000) Adenosinergic modulation of basal forebrain and preoptic/anterior hypothalamic neuronal activity in the control of behavioral state. Behav Brain Res 115(2):183–204
Sutera SP, Skalak R (1993) The history of Poiseuille’s law. Ann Rev Fluid Mech 25(1):1–20
Sword J, Masuda T, Croom D et al (2013) Evolution of neuronal and astroglial disruption in the peri-contusional cortex of mice revealed by in vivo two-photon imaging. Brain 136(5):1446–1461
Syková E, Nicholson C (2008) Diffusion in brain extracellular space. Physiol Rev 88(4):1277–1340
Szymusiak R, Gvilia I, McGinty D (2007) Hypothalamic control of sleep. Sleep Med 8(4):291–301
Tesler F, Linne ML, Destexhe A (2021) A key role of astrocytic calcium dynamics to link neuronal activity with the bold signal. bioRxiv
Thapaliya P, Pape N, Rose CR et al (2023) Modeling the heterogeneity of sodium and calcium homeostasis between cortical and hippocampal astrocytes and its impact on bioenergetics. Front Cell Neurosci 17(1035):553. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2023.1035553
Thrane AS, Rangroo Thrane V, Zeppenfeld D et al (2012) General anesthesia selectively disrupts astrocyte calcium signaling in the awake mouse cortex. Proc Natl Acad Sci 109(46):18,974–18,979
Tichy AM, Gerrard EJ, Sexton PM et al (2019) Light-activated chimeric GPCRs: limitations and opportunities. Current Opinion in Structural Biology 57:196–203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbi.2019.05.006
Toman M, Wade JJ, Verkhratsky A et al (2023) The influence of astrocytic leaflet motility on ionic signalling and homeostasis at active synapses. Sci Rep 13(1):3050. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-023-30189-8
Tsunematsu T, Sakata S, Sanagi T et al (2021) Region-specific and state-dependent astrocyte Ca\(^{2+}\) dynamics during the sleep-wake cycle in mice. J Neurosci 41(25):5440–5452. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2912-20.2021
Turovsky EA, Braga A, Yu Y et al (2020) Mechanosensory signaling in astrocytes. J Neurosci 40(49):9364–9371. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1249-20.2020
Tyurikova O, Shih PY, Dembitskaya Y et al (2022) K \(^{+}\) efflux through postsynaptic NMDA receptors suppresses local astrocytic glutamate uptake. Glia 70(5):961–974. https://doi.org/10.1002/glia.24150
Unger EK, Keller JP, Altermatt M et al (2020) Directed evolution of a selective and sensitive serotonin sensor via machine learning. Cell 183(7):1986-2002.e26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2020.11.040
Untiet V, Beinlich FRM, Kusk P et al (2023) Astrocytic chloride is brain state dependent and modulates inhibitory neurotransmission in mice. Nat Commun 14(1):1871. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-37433-9
Urban DJ, Roth BL (2015) DREADDs (designer receptors exclusively activated by designer drugs): chemogenetic tools with therapeutic utility. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 55(1):399–417. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-pharmtox-010814-124803
Vaidyanathan TV, Collard M, Yokoyama S et al (2021) Cortical astrocytes independently regulate sleep depth and duration via separate GPCR pathways. eLife 10:e63,329. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.63329
Van Den Herrewegen Y, Sanderson TM, Sahu S et al (2021) Side-by-side comparison of the effects of Gq- and Gi-DREADD-mediated astrocyte modulation on intracellular calcium dynamics and synaptic plasticity in the hippocampal CA1. Mol Brain 14(1):144. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13041-021-00856-w
Verhoog QP, Holtman L, Aronica E et al (2020) Astrocytes as guardians of neuronal excitability: mechanisms underlying epileptogenesis. Front Neurol 11:591,690. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2020.591690
Verisokin AY, Verveyko DV, Kucherenko VV et al (2021b) Translating from Na\(^+\) to Ca\(^{2+}\): Na/Ca-exchanger exerts Na\(^+\)-dependent control over astrocytic Ca\(^{2+}\) oscillations. Eur Phys J Plus 136(7):718. https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-021-01687-3
Verisokin A, Verveyko D, Kuryshovav E et al (2018) Noise-sustained patterns in a model of volume-coupled neural tissue. Chaos Interdiscip J Nonlinear Sci 28:106,326. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5039854
Verisokin A, Verveyko D, Kirsanov A et al (2023) Computational model of noradrenaline modulation of astrocyte responses to synaptic activity. Mathematics 11(3):628
Verisokin A, Verveyko D, Postnov D (2017) Turing-like structures in a functional model of cortical spreading depression. Phys Rev E 96. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevE.96.062409
Verisokin A, Verveyko D, Postnov D et al (2021a) Modeling of astrocyte networks: toward realistic topology and dynamics. Front Cell Neurosci 15:50. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2021.645068. https://www.frontiersin.org/article/10.3389/fncel.2021.645068
Verkhratsky A, Rose CR (2020) Na\(^+\)-dependent transporters: the backbone of astroglial homeostatic function. Cell Calcium 85:102,136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceca.2019.102136
Verkhratsky A, Untiet V, Rose CR (2020) Ionic signalling in astroglia beyond calcium. J Phys 598(9):1655–1670
Verveyko D, Verisokin A, Postnov D et al (2021) Connectivity promotes repeatable activation patterns in the model of astrocytic networks. Eur Phys J Plus 136. https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-021-01708-1
Vezzani A, Ravizza T, Bedner P et al (2022) Astrocytes in the initiation and progression of epilepsy. Nat Rev Neurol 18(12):707–722. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41582-022-00727-5
Volgraf M, Gorostiza P, Numano R et al (2006) Allosteric control of an ionotropic glutamate receptor with an optical switch. Nat Chem Biol 2(1):47–52. https://doi.org/10.1038/nchembio756
Wahis J, Holt MG (2021) Astrocytes, noradrenaline, \(A\)1-adrenoreceptors, and neuromodulation: evidence and unanswered questions. Front Cell Neurosci 15:645,691. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2021.645691
Walch E, Fiacco TA (2022) Honey, I shrunk the extracellular space: measurements and mechanisms of astrocyte swelling. Glia 70(11):2013–2031. https://doi.org/10.1002/glia.24224
Walch E, Murphy TR, Cuvelier N et al (2020) Astrocyte-selective volume increase in elevated extracellular potassium conditions is mediated by the Na\(^+\)/K\(^+\) ATPase and occurs independently of aquaporin 4. ASN neuro 12(1759091420967):152
Walrave L, Vinken M, Leybaert L et al (2020) Astrocytic connexin43 channels as candidate targets in epilepsy treatment. Biomolecules 10(11):1578
Walz W (1991) Accumulation of intracellular bicarbonate accounts for the missing anion during potassium-evoked swelling of cortical type-1-like astrocytes a. Ann N Y Acad Sci 633(1):589–591
Walz W (2000) Role of astrocytes in the clearance of excess extracellular potassium. Neurochem Int 36(4–5):291–300. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0197-0186(99)00137-0
Walz W (2002) Chloride/anion channels in glial cell membranes. Glia 40(1):1–10
Walz W, Hinks EC (1985) Carrier-mediated KCl accumulation accompanied by water movements is involved in the control of physiological K\(^+\) levels by astrocytes. Brain Res 343(1):44–51
Walz W, Shargool M, Hertz L (1984) Barium-induced inhibition of K\(^+\) transport mechanisms in cortical astrocytes-its possible contribution to the large Ba\(^{2+}\)-evoked extracellular K\(^+\) signal in brain. Neuroscience 13(3):945–949
Wang W, Kim CK, Ting AY (2019) Molecular tools for imaging and recording neuronal activity. Nat Chem Biol 15(2):101–110. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41589-018-0207-0
Wang F, Wang W, Gu S et al (2023) Distinct astrocytic modulatory roles in sensory transmission during sleep, wakefulness, and arousal states in freely moving mice. Nat Commun 14(1):2186. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-37974-z
Webb WB (1982) Biological rhythms, sleep, and performance. John Wiley & Sons
Wei Y, Ullah G, Ingram J et al (2014) Oxygen and seizure dynamics: Ii. computational modeling. J Neurophys 112. https://doi.org/10.1152/jn.00541.2013
Wieronska J, Cieślik P, Kalinowski L (2021) Nitric oxide-dependent pathways as critical factors in the consequences and recovery after brain ischemic hypoxia. Biomolecules 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11081097
Wilson CS, Mongin AA (2019) The signaling role for chloride in the bidirectional communication between neurons and astrocytes. Neuroscience letters 689:33–44
Wotton CA, Cross CD, Bekar LK (2020) Serotonin, norepinephrine, and acetylcholine differentially affect astrocytic potassium clearance to modulate somatosensory signaling in male mice. J Neurosci Res 98(5):964–977. https://doi.org/10.1002/jnr.24597
Wu YW, Gordleeva S, Tang X et al (2019) Morphological profile determines the frequency of spontaneous calcium events in astrocytic processes. Glia 67(2):246–262. https://doi.org/10.1002/glia.23537
Wu Z, He K, Chen Y et al (2022) A sensitive GRAB sensor for detecting extracellular ATP in vitro and in vivo. Neuron 110(5):770-782.e5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2021.11.027
Wu Z, Cui Y, Wang H et al (2023) Neuronal activity-induced, equilibrative nucleoside transporter-dependent, somatodendritic adenosine release revealed by a GRAB sensor. Proc Natl Acad Sci 120(14):e2212387,120. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2212387120
Xie L, Kang H, Xu Q et al (2013) Sleep drives metabolite clearance from the adult brain. science 342(6156):373–377
XVI European Glia Meeting (2023) XVI European meeting on glial cells in health and disease. https://glia2023.eu/symposia-and-workshop/
Yu H, Senarathna J, Tyler BM et al (2015) Miniaturized optical neuroimaging in unrestrained animals. NeuroImage 113:397–406. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2015.02.070
Yu X, Taylor AM, Nagai J et al (2018) Reducing astrocyte calcium signaling in vivo alters striatal microcircuits and causes repetitive behavior. Neuron 99(6):1170-1187.e9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2018.08.015
Yu X, Nagai J, Khakh BS (2020) Improved tools to study astrocytes. Nat Rev Neurosci 21(3):121–138. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41583-020-0264-8
Yu X, Nagai J, Marti-Solano M et al (2020) Context-specific striatal astrocyte molecular responses are phenotypically exploitable. Neuron 108(6):1146-1162.e10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2020.09.021
Yu X, Moye SL, Khakh BS (2021) Local and CNS-wide astrocyte intracellular calcium signaling attenuation in vivo with CalEx \(^{\text{ flox }}\) Mice. J Neurosci 41(21):4556–4574. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0085-21.2021
Yu G, Onodera H, Aono Y et al (2016) Optical manipulation of the alpha subunits of heterotrimeric G proteins using photoswitchable dimerization systems. Sci Rep 6(1):35,777. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep35777
Zhang Y, Looger LL (2023) Fast and sensitive GCaMP calcium indicators for neuronal imaging. J Physiol p JP283832. https://doi.org/10.1113/JP283832
Zheng K, Bard L, Reynolds JP et al (2015) Time-resolved imaging reveals heterogeneous landscapes of nanomolar Ca\(^2\) in neurons and astroglia. Neuron 88(2):277–288. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2015.09.043
Zhong S, Navaratnam D, Santos-Sacchi J (2014) A genetically-encoded YFP sensor with enhanced chloride sensitivity, photostability and reduced pH interference demonstrates augmented transmembrane chloride movement by Gerbil Prestin (SLC26a5). PLoS ONE 9(6):e99,095. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0099095
Zhou N, Gordon GR, Feighan D et al (2010) Transient swelling, acidification, and mitochondrial depolarization occurs in neurons but not astrocytes during spreading depression. Cerebral cortex 20(11):2614–2624
Zielinski MR, McKenna JT, McCarley RW (2016) Functions and mechanisms of sleep. AIMS neurosci 3(1):67
Ziemens D, Oschmann F, Gerkau NJ et al (2019) Heterogeneity of activity-induced sodium transients between astrocytes of the mouse hippocampus and neocortex: mechanisms and consequences. J Neurosci 39(14):2620–2634. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2029-18.2019
Zisis E, Keller D, Kanari L et al (2021) Digital reconstruction of the neuro-glia-vascular architecture. Cereb Cortex 31(12):5686–5703. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhab254
Funding
This research was funded by the Russian Science Foundation, project #22-14-00033 (“Introduction”); project #22-74-00146 (“New evidence”); project #22-15-00143 (“New models”).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: AB, AV, DV, and DP; writing—original draft preparation: AB, AV, DV, and DP; writing—review and editing: AB and DP; visualization: AB, DV, and DP.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Consent to participate
Not applicable
Consent for publication
Manuscript does not contain any individual person’s data.
Ethis approval
Not applicable
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Alexey Brazhe, Andrey Verisokin, Darya Verveyko, and Dmitry Postnov contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Brazhe, A., Verisokin, A., Verveyko, D. et al. Astrocytes: new evidence, new models, new roles. Biophys Rev 15, 1303–1333 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12551-023-01145-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12551-023-01145-7