Abstract
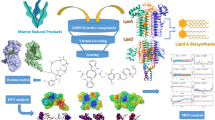
The criteria used for successful drug discovery involves high throughput screening for preclinical evaluation and its interaction with target enzymes. In silico approach resulting in the creation of drug like library and identification of essential reactions and pathways spreads across several parts of metabolism. The aim of the present study was to evaluate the preclinical property and interaction to various drug target enzymes for spiroindimicins A-D and lynamicin A and D isolated from deep marine sea derived Streptomyces sp. SCSIO 03032 with 7 selected drug target enzymes. The preclinical and molecular docking simulation was performed using In silico pharmacology and docking tool. Drug likeliness, ADME and toxicity testing findings suggested the compounds with oral drug candidate’s probability. Interaction of isolated compounds against drug target enzymes was satisfactory with Spiroindimicins C, D and Lynamicin D emerging as most potent Topoisomerase II, Cathepsin K, Cytochrome P4503A4, Aromatase P450, protein kinase and histone deacetylase inhibitors. Our results suggest that In silico approach in drug discovery procedure in later stage of development can ease up making lead molecules library.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amador, M.L., Jimeno, J., Paz-Ares, L., Cortes-Funes, H., Hidalgo, M. 2003. Progress in the development and acquisition of anticancer agents from marine sources. Annals of Oncology 14(11): 1607–1615.
Binkowski, T.A., Naghibzadeh, S., Liang, J. 2003. CASTp: Computed Atlas of Surface Topography of proteins. Nucleic Acids Research 31(13): 3352–3355.
Bowie, J., Luthy, R., Eisenberg, D. 1991. A method to identify protein sequences that fold into a known three-dimensional structure. Science 253(5016): 164–170.
Bromme, D., Lecaille, F. 2009. Cathepsin K inhibitors for osteoporosis and potential off-target effects. Expert Opinion on Investigational Drugs 18(5): 585–600.
Butler, M.S. 2008. Natural products to drugs: natural product-derived compounds in clinical trials. Nat Prod Rep 25(3): 475–516.
Chun, Y.J., Kim, S. 2003. Discovery of cytochrome P450 1B1 inhibitors as new promising anti-cancer agents. Med Res Rev 23(6): 657–668.
Ekins, S., Mestres, J., Testa, B. 2007. In silico pharmacology for drug discovery: methods for virtual ligand screening and profiling. Br J Pharmacol 152(1): 9–20.
Fortune, J.M., Osheroff, N. 2000. Topoisomerase II as a target for anticancer drugs: when enzymes stop being nice. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol 64: 221–253.
Gani. O.A., Engh, R.A. 2010. Protein kinase inhibition of clinically important staurosporine analogues. Nat Prod Rep 27(4): 489–498.
Ghose, A.K., Viswanadhan, V.N., Wendoloski, J.J. 1998. A Knowledge-Based Approach in Designing Combinatorial or Medicinal Chemistry Libraries for Drug Discovery. 1. A Qualitative and Quantitative Characterization of Known Drug Databases. Journal of Combinatorial Chemistry 1(1): 55–68.
Harvell, C.D., Kim, K., Burkholder, J.M., Colwell, R.R., Epstein, P.R., Grimes, D.J., Hofmann, E.E., Lipp, E.K., Osterhaus, A.D.M.E., Overstreet, R.M., Porter, J.W., Smith, G.W., Vasta, G.R. 1999. Emerging Marine Diseases-Climate Links and Anthropogenic Factors. Science 285(5433): 1505–1510.
Hooft, R.W., Vriend, G., Sander, C., Abola, E.E. 1996. Errors in protein structures. Nature 381(6580): 272.
Hopwood, D.A. 2007. Therapeutic treasures from the deep. Nat Chem Biol 3(8): 457–458.
Imming, P., Sinning, C., Meyer, A. 2006. Opinion-Drugs, their targets and the nature and number of drug targets. Nat Rev Drug Discov 5: 821–834.
Irvine, J.D., Takahashi, L., Lockhart, K., Cheong, J., Tolan, J.W., Selick, H.E., Grove, J.R. 1999. MDCK (Madin-Darby canine kidney) cells: A tool for membrane permeability screening. J Pharm Sci 88(1): 28–33.
Jensen, P., Fenical, W. 2000. Marine microorganisms and drug discovery: current status and future potential. Drugs from the sea, Basel; New York: Karger. 6–29.
Jirage, D.M., Keenan, S.C., Waters, N. 2010. Exploring Novel Targets for Antimalarial Drug Discovery: Plasmodial Protein Kinases. Infectious Disorders-Drug Targets (Formerly Current Drug Targets-Infectious 10(3): 134–146.
Kramer, J.A.S., John, E., Morris, Dale, L. 2007. The application of discovery toxicology and pathology towards the design of safer pharmaceutical lead candidates. Nat Rev Drug Discov 6(8): 636–649.
Kulkarni, A., Han, Y., Hopfinger, A.J. 2002. Predicting Caco-2 cell permeation coefficients of organic molecules using membrane-interaction QSAR analysis. J Chem Inf Comput Sci 42(2): 331–342.
Lane, A.A., Chabner, B.A. 2009. Histone deacetylase inhibitors in cancer therapy. J Clin Oncol 27(32): 5459–5468.
Laskowski, R.A., MacArthur, M.W., Moss, D.S., Thornton, J.M. 1993. PROCHECK: a program to check the stereochemical quality of protein structures. Journal of Applied Crystallography 26(2): 283–291.
Lipinski, C.A., Lombardo, F., Dominy, B.W., Feeney, P.J. 2001. Experimental and computational approaches to estimate solubility and permeability in drug discovery and development settings. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews 46(1–3): 3–26.
Macarulla, T., Ramos, F.J., Tabernero, J. 2008. Aurora kinase family: a new target for anticancer drug. Recent Pat Anticancer Drug Discov 3(2): 114–122.
McArthur, K.A., Mitchell, S.S., Tsueng, G., Rheingold, A., White, D.J., Grodberg, J., Lam, K.S., Potts, B.C.M. 2008. Lynamicins A-E, Chlorinated Bisindole Pyrrole Antibiotics from a Novel Marine Actinomyceteâ Journal of Natural Products 71(10): 1732–1737.
Oprea, T. 2000. Property distribution of drugrelated chemical databases*. Journal of Computer-Aided Molecular Design 14(3): 251–264.
Ouaissi, M., Ouaissi, A. 2006. Histone deacetylase enzymes as potential drug targets in cancer and parasitic diseases. J Biomed Biotechnol 2006(2): 13474.
Pandolfi, P.P. 2001. Histone deacetylases and transcriptional therapy with their inhibitors. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 48Suppl 1: S17–S19.
Ritchie, D.W., Venkatraman, V. 2010. Ultra-fast FFT protein docking on graphics processors. Bioinformatics 26(19): 2398–2405.
Sanchez, C., Mendez, C., Salas, J.A. 2006. Indolocarbazole natural products: occurrence, biosynthesis, and biological activity. Natural Product Reports 23(6): 1007–1045.
Saurav, K., Kannabiran, K. 2011. Interaction of 5-(2, 4-dimethylbenzyl) pyrrolidin-2-one with selected antifungal drug target enzymes by In silico molecular docking studies. Interdisciplinary Sciences: Computational Life Sciences 3(3): 198–203.
Teague, S.J., Davis, A.M., Leeson, P.D., Oprea, T. 1999. The Design of Leadlike Combinatorial Libraries. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 38(24): 3743–3748.
Thomas, T., Gallo, M.A., Thomas, T.J. 2004. Estrogen receptors as targets for drug development for breast cancer, osteoporosis and cardiovascular diseases. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 4(6): 483–499.
Vriend, G. 1990. WHAT IF: a molecular modeling and drug design program. J Mol Graph 8(1): 52–56, 29.
Yefi, R., Ponce, D.P., Niechi, I., Silva, E., Cabello, P., Rodriguez, D.A., Marcelain, K., Armisen, R., Quest, A.F., Tapia, J.C. 2011. Protein kinase CK2 promotes cancer cell viability via upregulation of cyclooxygenase-2 expression and enhanced prostaglandin E2 production. J Cell Biochem 112(11): 3167–3175.
Zhang, W., Liu, Z., Li, S., Yang, T., Zhang, Q., Ma, L., Tian, X., Zhang, H., Huang, C., Zhang, S., Ju, J., Shen, Y., Zhang, C. 2012. Spiroindimicins A-D: new bisindole alkaloids from a deep-sea-derived actinomycete. Org Lett 14(13): 3364–3367.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saurav, K., Zhang, W., Saha, S. et al. In silico molecular docking, preclinical evaluation of spiroindimicins A-D, lynamicin A and D isolated from deep marine sea derived Streptomyces sp. SCSIO 03032. Interdiscip Sci Comput Life Sci 6, 187–196 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12539-013-0200-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12539-013-0200-y