Abstract
Accurate knowledge of the spatio-temporal variation in soil moisture provides insight into larger-scale hydrological processes and can, therefore, help in improving hydrological predictions. The strength of remote sensing for mapping surface soil moisture is well proven. In addition, data assimilation offers the opportunity to combine the advantages of modelling with those of remote sensing data to achieve higher accuracy and continuous improvement in hydrological forecasts. In this study, Advanced Microwave Scanning Radiometer for Earth observation science soil moisture product was assimilated into Variable Infiltration Capacity (VIC) hydrological model using Kalman filter data assimilation technique. Further, the updated multilayer spatio-temporal soil moisture distributions across the Mahanadi Basin, India, were simulated using the hydrological model. The VIC model was set up and parameterized using field-observed and remote sensing-derived data. Based on the sensitivity analysis of the model, the ‘four-parameter’ (Tmax, Tmin, Prec, and WS) meteorological forcing scenario was selected as the operational scenario. The output fluxes obtained from VIC were routed to simulate discharge at five stations for the calibration and validation of the model. With R2 and model efficiency values close to 0.95 and 0.99, respectively, the model was proven to be suitable for simulating the hydrological responses of the basin. Soil moisture was assimilated in the top soil layer of the model using the Kalman filter approach, and the multilayer soil moisture regime was generated using the modelling approach. The validation of soil moisture (assimilated) products proves that these products are better than remote sensing and traditionally modelled soil moisture products, in both spatial and temporal domains in terms of availability and accuracy.


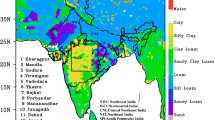
Source: NBSSLUP

Source: ISRO-GBP







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aggarwal, S. P., Garg, V., Gupta, P. K., Nikam, B. R., & Thakur, P. K. (2012). Climate and LULC change scenarios to study its impact on hydrological regime. International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences (ISPRS), 39-B8, 147–152. https://doi.org/10.5194/isprsarchives-xxxix-b8-147-2012.
Aggarwal, S. P., Garg, V., Gupta, P. K., Nikam, B. R., Thakur, P. K., & Roy, P. S. (2013). Runoff potential assessment over Indian landmass: A macro-scale hydrological modeling approach. Current Science, 104(7), 950–959.
Al Bitar, A., Leroux, D., Kerr, Y. H., Merlin, O., Richaume, P., Sahoo, A., et al. (2012). Evaluation of SMOS soil moisture products over continental US using the SCAN/SNOTEL network. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 50(5), 1572–1586.
Behera, S. S., Nikam, B. R. & Babel, M. S. (2017). Assimilation of remotely sensed soil moisture into hydrological model: A case study of Mahanadi Basin, India. In: Proceedings of ACRS 2017: 38th Asian Conference on Remote Sensing organized at New Delhi, India, October 23–27, 2017.
Best, M. J., Pryor, M., Clark, D. B., Rooney, G. G., Essery, R., Ménard, C. B., et al. (2011). The joint UK land environment simulator (JULES), model description—Part 1: Energy and water fluxes. Geoscientific Model Development, 4(3), 677–699.
Brocca, L., Melone, F., Moramarco, T., Wagner, W., Naeimi, V., Bartalis, Z., et al. (2010). Improving runoff prediction through the assimilation of the ASCAT soil moisture product. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences, 14(10), 1881.
Brocca, L., Moramarco, T., Melone, F., Wagner, W., Hasenauer, S., & Hahn, S. (2012). Assimilation of surface-and root-zone ASCAT soil moisture products into rainfall–runoff modeling. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 50(7), 2542–2555.
Brooks, R. H., & Corey, A. T. (1964). Hydraulic properties of porous media and their relation to drainage design. Transactions of the ASAE, 7(1), 26–0028.
Chen, F., Mitchell, K., Schaake, J., Xue, Y., Pan, H. L., Koren, V., et al. (1996). Modeling of land surface evaporation by four schemes and comparison with FIFE observations. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 101(D3), 7251–7268.
Choudhury, B. J., Schmugge, T. J., Chang, A., & Newton, R. W. (1979). Effect of surface roughness on the microwave emission from soils. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 84(C9), 5699–5706.
Clark, D. B., Mercado, L. M., Sitch, S., Jones, C. D., Gedney, N., Best, M. J., et al. (2011). The joint UK land environment simulator (JULES), model description—Part 2: Carbon fluxes and vegetation dynamics. Geoscientific Model Development, 4(3), 701–722.
Crosson, W. L., Laymon, C. A., Inguva, R., & Schamschula, M. P. (2002). Assimilating remote sensing data in a surface flux–soil moisture model. Hydrological Processes, 16(8), 1645–1662.
Dai, Y., Zeng, X., Dickinson, R. E., Baker, I., Bonan, G. B., Bosilovich, M. G., et al. (2003). The common land model (CLM). Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 84, 1013–1023.
De Lannoy, G. J., Houser, P. R., Pauwels, V., & Verhoest, N. E. (2007). State and bias estimation for soil moisture profiles by an ensemble Kalman filter: Effect of assimilation depth and frequency. Water Resources Research. https://doi.org/10.1029/2006wr005100.
Draper, C., Mahfouf, J. F., Calvet, J. C., Martin, E., & Wagner, W. (2011). Assimilation of ASCAT near-surface soil moisture into the SIM hydrological model over France. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences, 15(12), 3829.
Entekhabi, D., Nakamura, H., & Njoku, E. G. (1994). Solving the inverse problem for soil moisture and temperature profiles by sequential assimilation of multifrequency remotely sensed observations. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 32(2), 438–448.
Entekhabi, D., Njoku, E. G., O’Neill, P. E., Kellogg, K. H., Crow, W. T., Edelstein, W. N., et al. (2010). The soil moisture active passive (SMAP) mission. Proceedings of the IEEE, 98(5), 704–716.
Gao, Z., Xhang, Z., & Zhang, X. (2009). Responses of water yield to changes in vegetation at a temporal scale. Frontiers of Forestry in China, 4(1), 53–59.
Garg, V., Aggarwal, S. P., Gupta, P. K., Nikam, B. R., & Thakur, P. K. (2017). Assessment of land use land cover change impact on hydrological regime of a basin. Environmental Earth Sciences, 76, 635. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-017-6976-z.
Garg, V., Aggarwal, S. P., Nikam, B. R., & Thakur, P. K. (2013). Hypothetical scenario based impact assessment of climate change on runoff potential of a basin. ISH Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 19(3), 244–249.
Garg, V., Dhumal, I. R., Nikam, B. R., Thakur, P. K., Aggarwal, S. P., Srivastav, S. K. & Senthil Kumar, A. (2016). Water resources assessment of Godavari river basin, India. In: Proceedings of ACRS 2016: 37th Asian conference on remote sensing organized at Colombo, Sri Lanka, October 17–21, 2016.
Garg, V., Khwanchanok, A., Gupta, P. K., Aggarwal, S. P., Kiriwongwattana, K., Thakur, P. K., et al. (2012). Urbanisation effect on hydrological response: A case study of Asian River Watershed, India. Journal of Environment and Earth Science, 2(9), 39–50.
Georgakakos, K. P. (1996). Soil moisture theories and observations (special issue). Journal of Hydrology, 184, 131–152.
Gupta, P. K. (2012). User friendly open GIS tool for large scale data assimilation-A case study of hydrological modelling. ISPRS-International archives of the photogrammetry, remote sensing and spatial information sciences (pp. 427–430).
Hanson, J. D., Rojas, K. W., & Schaffer, M. J. (1999). Calibrating the root zone water quality model. Agronomy Journal, 91, 171–177.
Heathman, G. C., Starks, P. J., Ahuja, L. R., & Jackson, T. J. (2003). Assimilation of surface soil moisture to estimate profile soil water content. Journal of Hydrology, 279(1), 1–17.
Houser, P. R., Shuttleworth, W. J., Famiglietti, J. S., Gupta, H. V., Syed, K. H., & Goodrich, D. C. (1998). Integration of soil moisture remote sensing and hydrologic modeling using data assimilation. Water Resources Research, 34(12), 3405–3420.
Hurkmans, R. T. W. L., Terink, W., Uijlenhoet, R., Moors, E. J., Troch, P. A., & Verburg, P. H. (2009). Effects of land use changes on streamflow generation in the Rhine basin. Water Resources Research, 45, W06405. https://doi.org/10.1029/2008WR007574.
Imaoka, K., Kachi, M., Fujii, H., Murakami, H., Hori, M., Ono, A., et al. (2010). Global change observation mission (GCOM) for monitoring carbon, water cycles, and climate change. Proceedings of the IEEE, 98(5), 717–734.
Kalman, R. E. (1960). A new approach to linear filtering and prediction problems. Journal of Basic Engineering, 82(1), 35–45.
Kerr, Y. H., Waldteufel, P., Wigneron, J. P., Martinuzzi, J. A. M. J., Font, J., & Berger, M. (2001). Soil moisture retrieval from space: The soil moisture and ocean salinity (SMOS) mission. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 39(8), 1729–1735.
Koster, R. D., & Milly, P. C. D. (1997). The interplay between transpiration and runoff formulations in land surface schemes used with atmospheric models. Journal of Climate, 10(7), 1578–1591.
Koster, R. D., & Suarez, M. J. (1996). Energy and water balance calculations in the Mosaic LSM. Technical Report Series on Global Modeling and Data Assimilation. NASA Technical Memorandum 104606, 9.
Kostov, K. G., & Jackson, T. J. (1993). Estimating profile soil moisture from surface layer measurements–A review. SPIE, 1941, 125–136.
Kumar, S. V., Reichle, R. H., Harrison, K. W., Peters-Lidard, C. D., Yatheendradas, S., & Santanello, J. A. (2012). A comparison of methods for a priori bias correction in soil moisture data assimilation. Water Resources Research. https://doi.org/10.1029/2010wr010261.
Lahoz, W. A., & De Lannoy, G. J. (2014). Closing the gaps in our knowledge of the hydrological cycle over land: conceptual problems. Surveys In Geophysics, 35(3), 623–660.
Lawrence, D. M., Oleson, K. W., Flanner, M. G., Thornton, P. E., Swenson, S. C., Lawrence, P. J., et al. (2011). Parameterization improvements and functional and structural advances in version 4 of the Community Land Model. Journal of Advances in Modeling Earth Systems. https://doi.org/10.1029/2011ms00045.
Leroux, D. J., Kerr, Y. H., Richaume, P., & Fieuzal, R. (2013). Spatial distribution and possible sources of SMOS errors at the global scale. Remote Sensing of Environment, 133, 240–250.
Liang, X., Lettenmaier, D. P., Wood, E. F., & Burges, S. J. (1994). A simple hydrologically based model of land surface water and energy fluxes for general circulation models. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 99(D7), 14415–14428.
Liang, X., Wood, E. F., & Lettenmaier, D. P. (1996). Surface soil moisture parameterization of the VIC-2L model: Evaluation and modification. Global and Planetary Change, 13(1–4), 195–206.
Liang, X., Wood, E. F., & Lettenmaier, D. P. (1999). Modeling ground heat flux in land surface parameterization schemes. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 104(D8), 9581–9600.
Liang, X., & Xie, Z. (2001). A new surface runoff parameterization with subgrid-scale soil heterogeneity for land surface models. Advances in Water Resources, 24(9), 1173–1193.
Lohmann, D., Nolte-Holube, R. A. L. P. H., & Raschke, E. (1996). A large-scale horizontal routing model to be coupled to land surface parametrization schemes. Tellus A, 48(5), 708–721.
Lohmann, D., Raschke, E., Nijssen, B., & Lettenmaier, D. P. (1998a). Regional scale hydrology: I. Formulation of the VIC-2L model coupled to a routing model. Hydrological Sciences Journal, 43(1), 131–141.
Lohmann, D., Raschke, E., Nijssen, B., & Lettenmaier, D. P. (1998b). Regional scale hydrology: II. Application of the VIC-2L model to the Weser River. Germany. Hydrological Sciences Journal, 43(1), 143–158.
Martens, B., Lievens, H., Colliander, A., Jackson, T. J., & Verhoest, N. E. (2015). Estimating effective roughness parameters of the L-MEB model for soil moisture retrieval using passive microwave observations from SMAPVEX12. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 53(7), 4091–4103.
Masson, V., Le Moigne, P., Martin, E., Faroux, S., Alias, A., Alkama, R., et al. (2013). The SURFEXv7. 2 land and ocean surface platform for coupled or offline simulation of earth surface variables and fluxes. Geoscientific Model Development, 6, 929–960.
Matgen, P., Fenicia, F., Heitz, S., Plaza, D., de Keyser, R., Pauwels, V. R. N., et al. (2012). Can ASCAT-derived soil wetness indices reduce predictive uncertainty in well-gauged areas? A comparison with in situ observed soil moisture in an assimilation application. Advances in Water Resources, 44, 49–65.
Maurer, E. P., O’Donnell, G. M., Lettenmaier, D. P., & Roads, J. O. (2001). Evaluation of the land surface water budget in NCEP/NCAR and NCEP/DOE reanalyses using an off-line hydrologic model. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 106(D16), 17841–17862.
Merlin, O., Al Bitar, A., Walker, J. P., & Kerr, Y. (2010). An improved algorithm for disaggregating microwave-derived soil moisture based on red, near-infrared and thermal-infrared data. Remote Sensing of Environment, 114(10), 2305–2316.
Nash, J. E., & Sutcliffe, J. V. (1970). River flow forecasting through conceptual models part I—A discussion of principles. Journal of Hydrology, 10(3), 282–290.
Nijssen, B., Lettenmaier, D. P., Liang, X., Wetzel, S. W., & Wood, E. F. (1997). Streamflow simulation for continental-scale river basins. Water Resources Research, 33(4), 711–724.
Nijssen, B., Schnur, R., & Lettenmaier, D. P. (2001). Global retrospective estimation of soil moisture using the variable infiltration capacity land surface model, 1980–1993. Journal of Climate, 14(8), 1790–1808.
Nikam, B. R., Garg, V., Jaya, K., Gupta, P. K., Srivastav, S. K., Thakur, P. K., et al. (2018). Analyzing future water availability and hydrological extremes in Krishna basin under changing climatic conditions. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 11(19), 581. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-018-3936-1.
Nikam, V. V., Nikam, B. R., Garg, V. & Aggarwal, S. P. (2015). Assimilation of remote sensing derived soil moisture in macroscale hydrological model. In: Proceedings of ‘Hydro International 2015’, 20th international conference on hydraulics. Water Resources and River Engineering organized at IIT Roorkee, India, 17–19 December, 2015.
Njoku, E. G., Jackson, T. J., Lakshmi, V., Chan, T. K., & Nghiem, S. V. (2003). Soil moisture retrieval from AMSR-E. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 41(2), 215–229.
Pai, D. S., Sridhar, L., Rajeevan, M., Sreejith, O. P., Satbhai, N. S., & Mukhopadyay, B. (2014). Development of a new high spatial resolution (0.25° × 0.25°) Long Period (1901–2010) daily gridded rainfall data set over India and its comparison with existing data sets over the region. Mausam, 65(1), 1–18.
Panciera, R., Walker, J. P., & Merlin, O. (2009). Improved understanding of soil surface roughness parameterization for L-band passive microwave soil moisture retrieval. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 6(4), 625–629.
Pauwels, V. R., Hoeben, R., Verhoest, N. E., & De Troch, F. P. (2001). The importance of the spatial patterns of remotely sensed soil moisture in the improvement of discharge predictions for small-scale basins through data assimilation. Journal of Hydrology, 251(1), 88–102.
Pauwels, V., Hoeben, R., Verhoest, N. E., De Troch, F. P., & Troch, P. A. (2002). Improvement of TOPLATS-based discharge predictions through assimilation of ERS-based remotely sensed soil moisture values. Hydrological Processes, 16(5), 995–1013.
Rahmoune, R., Ferrazzoli, P., Kerr, Y. H., & Richaume, P. (2013). SMOS level 2 retrieval algorithm over forests: Description and generation of global maps. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 6(3), 1430–1439.
Rao, P. G. (1993). Climatic changes and trends over a major river basin in India. Climate Research, 2, 215–223.
Reichle, R. H., & Koster, R. D. (2004). Bias reduction in short records of satellite soil moisture. Geophysical Research Letters. https://doi.org/10.1029/2004gl020938.
Sabater, J. M., De Rosnay, P., & Balsamo, G. (2011). Sensitivity of L-band NWP forward modelling to soil roughness. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 32(19), 5607–5620.
Sahoo, A. K., De Lannoy, G. J., Reichle, R. H., & Houser, P. R. (2013). Assimilation and downscaling of satellite observed soil moisture over the Little River Experimental Watershed in Georgia, USA. Advances in Water Resources, 52, 19–33.
Sheffield, J., Pan, M., Wood, E. F., Mitchell, K. E., Houser, P. R., Schaake, J. C., et al. (2003). Snow process modeling in the North American Land Data Assimilation System (NLDAS): 1. Evaluation of model-simulated snow cover extent. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres. https://doi.org/10.1029/2002jd003274.
Sheffield, J., & Wood, E. F. (2008). Global trends and variability in soil moisture and drought characteristics, 1950–2000, from observation-driven simulations of the terrestrial hydrologic cycle. Journal of Climate, 21(3), 432–458.
Srivastava, A. K., Rajeevan, M., & Kshirsagar, S. R. (2009). Development of a high resolution daily gridded temperature data set (1969–2005) for the Indian region. Atmospheric Science Letters, 10(4), 249–254.
Su, F., Adam, J. C., Bowling, L. C., & Lettenmaier, D. P. (2005). Streamflow simulations of the terrestrial Arctic domain. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 110(D08112), 1–25.
Todini, E. (1996). The ARNO rainfall—runoff model. Journal of Hydrology, 175(1–4), 339–382.
Wagner, W., Hahn, S., Kidd, R., Melzer, T., Bartalis, Z., Hasenauer, S., et al. (2013). The ASCAT soil moisture product: A review of its specifications, validation results, and emerging applications. Meteorologische Zeitschrift, 22(1), 5–33.
Walker, J. P., Willgoose, G. R., & Kalma, J. D. (2001). One-dimensional soil moisture profile retrieval by assimilation of near-surface measurements: A simplified soil moisture model and field application. Journal of Hydrometeorology, 2(4), 356–373.
Wang, J. R., O’Neill, P. E., Jackson, T. J., & Engman, E. T. (1983). Multifrequency measurements of the effects of soil moisture, soil texture, and surface roughness. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1, 44–51.
Wigneron, J. P., Pardé, M., Waldteufel, P., Chanzy, A., Kerr, Y., Schmidl, S., et al. (2004). Characterizing the dependence of vegetation model parameters on crop structure, incidence angle, and polarization at L-band. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 42(2), 416–425.
Wood, E. F., Lettenmaier, D., Liang, X., Nijssen, B., & Wetzel, S. W. (1997). Hydrological modeling of continental-scale basins. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 25(1), 279–300.
Wood, E. F., Roundy, J. K., Troy, T. J., Van Beek, L. P. H., Bierkens, M. F., Blyth, E., et al. (2011). Hyperresolution global land surface modeling: Meeting a grand challenge for monitoring Earth’s terrestrial water. Water Resources Research, 47(5), 1–5. https://doi.org/10.1029/2010wr010090.
Xie, Z., Yuan, F., Duan, Q., Zheng, J., Liang, M., & Chen, F. (2007). Regional parameter estimation of the VIC land surface model: Methodology and application to river basins in China. Journal of Hydrometeorology, 8(3), 447–468.
Yuan, F., Xie, Z., Liu, Q., Yang, H., Su, F., Liang, X., et al. (2004). An application of the VIC-3L land surface model and remote sensing data in simulating streamflow for the Hanjiang River basin. Canadian Journal of Remote Sensing, 30(5), 680–690.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
About this article
Cite this article
Behera, S.S., Nikam, B.R., Babel, M.S. et al. The Assimilation of Remote Sensing-Derived Soil Moisture Data into a Hydrological Model for the Mahanadi Basin, India. J Indian Soc Remote Sens 47, 1357–1374 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12524-019-00954-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12524-019-00954-2