Abstract
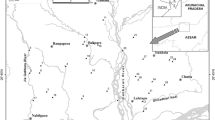
Kameng River is a high-altitude fluvial system that originates in the snow-clad mountain ranges of the eastern Himalayas in the state of Arunachal Pradesh of India. In the present research, the spatial and seasonal distributions of selected heavy metals (Fe, Cd, Cu, Mn, Pb, Zn, and As) were studied to assess their pollution status within the river basin. This study reports the first systematic evaluation of heavy metals in the Kameng River within the geographical boundary of Arunachal Pradesh. The Kameng River is a major source of water to the indigenous communities residing within the river basin. In recent years, some serious debates have been going on the issues surrounding hydro-energy exploration in the river basin. Construction of large- and medium-scale hydroelectric projects is likely to fragment the entire river course and alter the environmental flow of the river that would invariably affect the water quality regime. In order to predict the future changes in the water quality parameters, it is important to carry out water quality studies at present. In the present study, water samples were collected from 27 locations representing four sub-watersheds within the Kameng River basin. The study revealed that the river water was polluted by Cd, Pb, Mn, and Zn with respect to the safe limit prescribed by regulatory authorities. The multivariate statistical analysis using principal component analysis (PCA) and hierarchical cluster analysis (HCA) tools suggested that the concentration of the heavy metals was primarily controlled by geochemical factors that included the dissolution of phosphate rocks, weathering of carbonate rocks, and base metal mineralization. Further, the solubility mechanics of these metals were controlled by processes of co-precipitation, adsorption, and ion precipitation on pre-existing mineral surfaces. The study also indicated the contribution of heavy metals from anthropogenic sources that primarily included the leaching of pesticides from agricultural soils. This study illustrates the successful application of multivariate statistical tools in understanding the distribution of heavy metals in river basins.






Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.References
Adriano DC (1986) Trace elements in the terrestrial environment. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg
Ajmal M, Khan MA, Nomain AA (1985) Distributions of heavy metals in water and sediments of selected sites of Yamuna River (India). Environ Monit Assess 5:205–214
Aktar MW, Paramasivam M, Ganguly M, Purkait S, Sengupta D (2010) Assessment and occurrence of various heavy metals in surface water of Ganga River around Kolkata: a study for toxicity and ecological impact. Environ Monit Assess 160(1–4):207–213
American Public Health Association. APHA (1985) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. APHA, 16th. Ed., Washington.
Anazawa K, Ohmori H, Tomiyasu T, Sakamoto H (2003) Hydrochemistry at a volcanic summit area, Norikura, Central Japan. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 67(18S):17
APHA, AWWA, & WEF (2005) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 21st edn. American public health association, American Water Works Association and water environment federation, Washington
Ayeni AO, & Soneye ASO (2013). Interpretation of surface water quality using principal components analysis and cluster analysis. Journal of Geography and Regional Planning, 6(4):132
Banerjee S, Maiti SK, Kumar A (2015) Metal contamination in water and bioaccumulation of metals in the planktons, molluscs and fishes in Jamshedpur stretch of Subarnarekha River of Chotanagpur plateau, India. Water Environ J 29(2):207–213
Baruah NK, Kotoky P, Bhattacharyya KG, Borah GC (1996) Metal speciation in Jhanji River sediments. Sci Total Environ 193:1–12
Bhardwaj V, Singh DS, Singh AK (2010) Water quality of the Chhoti Gandak River using principal component analysis, Ganga Plain, India. J Earth Syst Sci 119(1):117–127
Bhattacharjee KK (2006).Ion transport by the river Siang (Arunachal Pradesh) with special reference to distribution of heavy metals in water and sediments. Unpublished Ph.D. Thesis, Gauhati University
BIS (1993). Ammendment No. 1- January 1993 to Indian Standards: Drinking Water – Specifications (First Revision) IS 10500 : 1991. Bureau of Indian Standards, pp.1-4.
Chatterjee SK, Bhattacharjee I, Chandra G (2010) Water quality assessment near an industrial site of Damodar River, India. Environ Monit Assess 161(1–4):177–189
Dekov D, Araujo F, Subramanian V, Van Grieken R (1998) Chemical composition of sediments and suspended matter from the Cauvery and Brahmaputra River (India). Sci Total Environ 212:89–105
Garizi AZ, Sheikh V, Sadoddin A (2011) Assessment of seasonal variations of chemical characteristics in surface water using multivariate statistical methods. Int J Environ Sci Technol 8(3):581–592
GSI (2010) Geology and mineral resources of Arunachal Pradesh. Geological survey of India. Miscellenous publication, no. 30, part IV, Vol I (i), Arunachal Pradesh
Gupta LP, Subramanian V (1994) Environmental geochemistry of the river Gomti: a tributary of Ganges river. Environ Geol 24:235–243
Habes G, Nigem Y (2006) Assessing Mn, Fe, cu, Zn, and cd pollution in bottom sediments of Wadi Al-Arab dam, Jordan. Chemosphere 65:2114–2121
Hawkes SJ (1997) What is a" heavy metal"? J Chem Educ 74(11):1374
Hejabi AT, Basavarajappa HT, Karbassi AR, Monavari SM (2011) Heavy metal pollution in water and sediments in the Kabini River, Karnataka, India. Environ Monit Assess 182(1–4):1–13
Hem JD (1991) Study and interpretation of the chemical characteristics of natural water: book 2254, 3rd edn. Scientific Publishers, Jodhpur
Hussain Z (2002) Geoecology of Kameng Himalaya. Regency Publication, New Delhi
Islam MS, Ahmed MK, Raknuzzaman M, Habibullah-Al-Mamun M, Islam MK (2015) Heavy metal pollution in surface water and sediment: a preliminary assessment of an urban river in a developing country. Ecol Indic 48:282–291
Joshi A, Chakraborty PP (2001). Systematic geological mapping in parts of East and West Kameng districts, Arunachal Pradesh. Geol. Surv. India Unpublished progress report for F. S, Shillong. 1999 – 2000
Khound NJ, Bhattacharyya KG (2016) Multivariate statistical evaluation of heavy metals in the surface water sources of Jia Bharali river basin, north Brahmaputra plain, India. Appl Water Sci 7:2577–2586. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-016-0453-9
Khound NJ, Phukon P, Bhattacharyya KG (2012) Physico-chemical studies on surface water quality in the Jia-Bharali River basin, north Brahmaputra plain, India. Arch Appl Sci Res 4(2):1169–1174
Khwaja, A. R., Singh, R., & Tandon, S. N. (2001). Monitoring of ganga water and sediments vis-a-vis tannery pollution at kanpur (india): A case study. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 68(1), 19–35. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010790705006
Kikuchi T, Furuichi T, Hai HT, Tanaka S (2009) Assessment of heavy metal pollution in river water of Hanoi, Vietnam using multivariate analyses. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 83(4):575–582
Konhauser KO, Powell MA, Fyfe WS, Longstaffe FJ, Tripathy S (1997) Trace element geochemistry of river sediment, Orissa state, India. J Hydrol 193(1–4):258–269
Laaksoharju M, Gurban I, Skarman C, Skarman E (1999) Multivariate mixing and mass balance (M3) calculations, a new tool for decoding hydrogeochemical information. Appl Geochem 14(7):861–871
Manoj K, Padhy PK (2014) Multivariate statistical techniques and water quality assessment: discourse and review on some analytical models. Int J Environ Sci 5(3):607
Manoj K, Padhy PK, Chaudhury S (2012) Study of heavy metal contamination of the river water through index analysis approach and environmetrics. Bull Environ Pharmacol Life Sci 1(10):7–15
Mathur A, Sharma YC, Rupainwar DC, Murthy RC, Chandra S (1987) A study of river ganga at Varanasi with special emphasis on heavy metal pollution. Pollut Res 6(1):37–44
Milana P, Dragan D, Ugljesa S, Igor L (2013) Correlation analysis of impact of natural parameters on water quality of the river Danube near nori sad for the period 2004–2011. Geogr Pannonica 17(3):74–78
Nies DH (1999) Microbial heavy-metal resistance. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 51(6):730–750
Pandey J, Singh R (2017) Heavy metals in sediments of Ganga River: up-and downstream urban influences. Appl Water Sci 7(4):1669–1678
Pekey H (2006) Heavy metal pollution assessment in sediments of the Izmit Bay, Turkey. Environ Monit Assess 123(1–3):219–231
Prasad S, Mathur A, Rupaniwar DC (1989) Heavy metal distribution in the sediment and river confluence points of river ganga in Varanasi-Mirzapur region. Asian J Water Environ Pollut 11(2):73–82
Prasad MBK, Ramanathan AL, Shrivastav SK, & Saxena, R. (2006). Metal fractionation studies in surfacial and core sediments in the Achankovil river basin in India. Environmental monitoring and assessment, 121(1-3):77-102.
Rodriguez-Barroso MR, Garcia-Morales JL, Coello Oviedo MD (2010) An assessment of heavy metal contamination in surface sediment using statistical analysis. Environ Monit Assess 163:489–501
Shanbehzadeh, S., Vahid Dastjerdi, M., Hassanzadeh, A., & Kiyanizadeh, T. (2014) Heavy metals in water and sediment: a case study of Tembi River. Journal of environmental and public health
Sharma SK, Subramanian V (2010) Source and distribution of trace metals and nutrients in Narmada and Tapti river basins, India. Environ Earth Sci 61:1337–1352. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-010-0452-3
Sharma P, Sarma HP, Mahanta C (2012) Evaluation of groundwater quality with emphasis on fluoride concentration in Nalbari district, Assam, Northeast India. Environ Earth Sci 65(7):2147–2159
Singh HP, Mahaveer LR (1997) Preliminary observations on heavy metals in water and sediments in a stretch of river ganga and some of its tributaries. J Environ Biol 18(1):49–53
Singh HP, Mahaveer LR, Mishra JP (1992) Heavy metals in sediments and water in river ganga. J Assam Sci Soc 34(2):52–56
Singh HP, Chandra R, Singh B (1993) Status of heavy metals in water, sediments, and fish flesh in the middle stretch of the river Ganga. J Inland Fish Soc (India) 25(1):62–65
Singh V, Singh K, Mohan D (2004) Status of heavy metals in water and bed sediments of river Gomti—a tributary of the ganga river, India. Environ Monit Assess 105:43–67
Srivastava SK, Mohan D, Gupta VA (1994) Status of some toxic heavy metal ions in the upper reaches of river Ganges. Indian J Chem Soc 71:29–34
Subramanian V, Van Girieken R, Vant dack L (1987) Heavy metals distribution in the sediments of Ganges and Brahmaputra rivers. Environ Geol Water Sci 9:93–108
Suthar S, Sharma J, Chabukdhara M, Nema AK (2010) Water quality assessment of river Hindon at Ghaziabad, India: impact of industrial and urban wastewater. Environ Monit Assess 165(1–4):103–112
Talukdar R (2012) Geomorphological study of the Jia Bharali River catchment N E India. Unpublished Ph.D. Thesis, Gauhati University
Wang H, Wang J, Liu R, Yu W, Shen Z (2015) Spatial variation, environmental risk and biological hazard assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments of the Yangtze River estuary. Mar Pollut Bull 93(1):250–258
WHO (2011) Guidelines for drinking water-quality - 4th ed.. Geneva: World Health Organisation, pp.307-433.
Zhao Z-W, Cui F-Y (2009) Multivariate statistical analysis for the surface water quality of the Luan River, China. J Zhejiang Univ Sci A 10(1):142–148
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to the Head, Department of Environmental Science of Gauhati University, for allowing us to use the laboratory facilities for this research work. We also acknowledge the reviewers for providing valuable suggestions for improving the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sharma, B.B., Sarma, H.P. Assessment of heavy metal pollution in a Himalayan river using multivariate statistical tools: a case study of the Kameng River in Arunachal Pradesh, India. Arab J Geosci 11, 308 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-018-3556-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-018-3556-9