Abstract
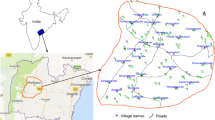
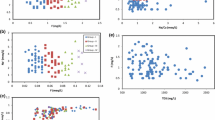
This paper reports occurrence of high fluoride concentration in groundwater of Gharbar Village, Dhanbad District, Jharkhand, India. The concentration of fluoride varied from 0.3 to 14.9 mg/L in 27 groundwater samples. The correlation studies demonstrate that fluoride has strong positive correlation with pH and sodium and negative correlation with calcium. It indicates dominance of ion exchange activity and rock water interaction. Thermodynamic consideration shows that all the samples were oversaturated with calcite and most of the samples were under saturated with fluorite. The results indicate that occurrence of high concentration of fluoride is leading by geochemical composition of rocks, alkaline environmental condition, weathering of rocks and ion exchange processes.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed S, Sreedevi PD (2002) Cyclic variation of fluoride contents in a granite aquifer in semi-arid region. ICWRMA, Kuwait
APHA (1992) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. American Public Health Association, Washington
BIS (2003) Indian standard specifications for drinking water. Bureau of Indian Standards, New Delhi
Brindha, K., Elango, L. (2011) Fluoride in groundwater: causes, implications and mitigation measures. In: Monroy SD (ed) Fluoride properties, applications and environmental management, 1st edn. Nova, New York, p 111–136
Brown E, Skougstad MW, Fishman MJ (1970) Methods for collection and analysis of water samples for dissolved minerals and gases. In: Techniques of Water Resources Investigations of the U.S. Geological Survey. United States Goverment Printing Office, Washington
CGWB (2013) Groundwater information booklet-Dhanbad district. Jharkhand state, Ministry of Water Resources, Patna
Chae G-T, Yun S-T, Mayer B, Kim K-H, Kim S-Y, Kwon J-S, Kim K, Koh Y-K (2007) Fluorine geochemistry in bedrock groundwater of South Korea. Sci Total Environ 385(1–3):272–283
Coetsiers M, Kilonzo F, Walraevens K (2008) Hydrochemistry and source of high fluoride in groundwater of the Nairobi area, Kenya. Hydrol Sci J 53(6):1230–1240
Dinesh C (1998) Fluoride and human health-cause for concern. Ind J Environ Protec 2(19):81–89
Duraiswami RA, Patankar UR (2011) Occurrence of fluoride in the drinking water sources from Gad River basin, Maharashtra, India. J Geol Soc India 77(2):167–174
Freeze RA, Cherry JA (1979) Groundwater. Prentice-Hall, Inc., Englewood Cliffs
Guo Q, Wang Y, Ma T, Ma R (2007) Geochemical processes controlling the elevated fluoride concentrations in groundwaters of the Taiyuan Basin, northern China. J Geochem Explor 93(1):1–12
Gupta S, Banerjee S (2009) Fluoride accumulation in paddy irrigated with fluoride-contaminated groundwater in the Birbhum District, West Bengal. Res Rep Fluoride 42(3):224–227
Handa BK (1975) Geochemistry and genesis of fluoride containing groundwater in India. Groundwater 3(13):275–281
Hem JD (1991) Study and interpretation of the chemical characteristics of natural water (3rd edn.). United States Geological Survey Professional Paper 2254, Scientific Pub, Jodhpur, India
Jacks G, Bhattacharya P, Chaudhary V, Singh KP (2005) Controls on the genesis of some high-fluoride groundwaters in India. Appl Geochem 20:221–228
Karanth KR (1989) Hydrogeology. McGraw-Hill, New Delhi, p 720
Khan SMMN, Ravikumar A (2013) Role of alkalinity for the release of fluoride in the groundwater of Tiruchengode Taluk, Namakkal District, Tamilnadu, India. Chem Sci Trans 2(S1):S302–S308
Lloyd JA, Heathcote JA (1985) Natural inorganic hydrochemistry in relation to groundwater: an introduction. Oxford University Press, New York
María G, Laura B (2015) Chapter 1: Fluoride in the context of the environment. In book: Fluorine: Chemistry, Analysis, Function and Effects. Royal Society of Chemistry, Cambridge, p 3–21
Meenakshi RC, Maheshwari J (2006) Fluoride in drinking water and its removal. J Haz Mater 137:456–463
Mondal NC, Prasad RK, Saxena VK, Singh Y, Singh VS (2009) Appraisal of highly fluoride zones in groundwater of Kurmapalli watershed, Nalgonda district, Andhra Pradesh (India). Environ Earth Sci 59(1):63–73
Pande G, Sinha A, Agrawal S (2015) Impacts of leachate percolation on ground water quality: a case study of Dhanbad City. Global Nest J 17(1):162–174
Rainwater FH, Thatcher LL (1960) Methods for collection and analysis of water samples. U.S. Geological Survey Water Supply Paper No.1454, 301
Ramesam V, Rajagopalan K (1985) Fluoride ingestion into the natural waters of hard-rock areas, Peninsular India. J Geol Soc India 26:125–132
Rao NVR, Rao N, Rao SP, Schuiling RD (1993) Fluorine distributionin waters of Nalgonda District, Andhra Pradesh, India. Environ Geol 21:84–89
Singh R, Maheshwari R (2001) Defluoridation of drinking water—a review. Ind J Environ Protec 11(21):983–991
Singh AK, Mondal GC, Singh S, Singh PK, Singh TB, Tewary BK, Sinha A (2007) Aquatic geochemistry of Dhanbad, Jharkhand: source evaluation and quality assessment. J Geol Soc India 69:1088–1102
Srinivasa RN (1997) The occurrence and behaviour of fluoride in the groundwater of the lower Vamsadhara River basin. India Hydrol Sci J 6(42):877–892
Srivastava VK, Giri DN, Bhardwaj P (2012) Study and mapping of ground water prospect using remote sensing, GIS and geoelectrical resistivity techniques—a case study of Dhanbad district, Jharkhand. India J Ind Geophys Union 16(2):55–63
WHO (2004) Guidelines for drinking water quality. World Health Organization, Geneva
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Patolia, P., Sinha, A. Fluoride contamination in Gharbar Village of Dhanbad District, Jharkhand, India: source identification and management. Arab J Geosci 10, 381 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-017-3164-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-017-3164-0