Abstract
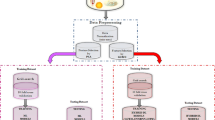
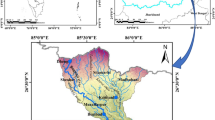
Turkey is one of several countries frequently facing significant earthquakes because of its geological and tectonic position on earth. Especially, graben systems of Western Turkey occur as a result of seismically quite active tensional tectonics. The prediction of earthquakes has been one of the most important subjects concerning scientists for a long time. Although different methods have already been developed for this task, there is currently no reliable technique for finding the exact time and location of an earthquake epicenter. Recently artificial intelligence (AI) methods have been used for earthquake studies in addition to their successful application in a broad spectrum of data intensive applications from stock market prediction to process control. In this study, earthquake data from one part of Western Turkey (37–39.30° N latitude and 26°–29.30° E longitude) were obtained from 1975 to 2009 with a magnitude greater than M ≥ 3. To test the performance of AI in time series, the monthly earthquake frequencies of Western Turkey were calculated using catalog data from the region and then the obtained data set was evaluated with two neural networks namely as the multilayer perceptron neural networks (MLPNNs) and radial basis function neural networks (RBFNNs) and adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system (ANFIS). The results show that for monthly earthquake frequency data prediction, the proposed RBFNN provides higher correlation coefficients with real data and smaller error values.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexandridis A, Chondrodima E, Efthimiou E, Papadakis G, Vallianatos F, Triantis D (2014) Large earthquake occurrence estimation based on radial basis function neural networks. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 52(9)
Alptekin O, Ilkışık M, Ezen U, Uçer SB (1990) Heat flow, seismicity and the crustal structure of western Anatolia. In: Savascin MY & Eronat AH (eds) Proc. Internat. Earth Sc. Congr. on Aegean Regions, Izmir/Turkey, v.II. p. 1–12
Alves EI (2006) Earthquake forecasting using neural networks: results and future work. Nonlinear Dynamics 44:341–349
Bodri B (2001) A neural network model for earthquake occurrence. J Geodyn 32:289–310
Buscema PM, Massini G, Maurelli G (2015) Artificial adaptive systems to predict the magnitude of earthquakes. Boll Geofis Teor Appl 56(n. 2):227–256
Ham MF, Kostanic I (2000) Principles of neurocomputing for science & engineering. McGraw-Hill
Haykin S (1999) Neural network: a comprehensive foundation. Prentice Hall, New Jersey
Jang JS R (1993) ANFIS: adaptive-network-based fuzzy inference system. IEEE Trans Syst, Man, Cybern 23(3)
Kandilli Observatory and Earthquake Research Institute Database, http://www.koeri.boun.edu.tr, Boğaziçi University, İstanbul
Koçyiğit A, Yusufoğlu H, Bozkurt E (1999) Evidence from the Gediz graben for episodic two-stage extension in western Turkey. J Geol Soc Lond 156:605–616
Külahçı F, İnceöz M, Doğru M, Aksoy E, Baykara O (2009) Artificial neural networks model for earthquake prediction with radon monitoring. Appl Radiat Isot 67(1):212–219
Morales-Esteban A, Martinez-Alvarez F, Reyes J (2013) Earthquake prediction in seismogenic areas of the Iberian Peninsula based on computational intelligence. Tectonophysics 593:121–134
Qiang L (2000) The application of neural network to the analysis of earthquake precursor chaotic time series. Acta Seismol Sin 13(4):434–439
Republic of Turkey Prime Ministry Disaster and Emergency Management Presidency Database, http://www.deprem.gov.tr, Ankara
Reyes J, Morales-Esteban A, Martinez-Alvarez F (2013) Neural networks to predict earthquakes in Chile. Appl Soft Comput 13:1314–1328
Royden L (1993a) The tectonic of slab pull at continental convergent boundaries. Tectonics 12:303–325
Royden L (1993b) Evolution of retreating subduction boundaries formed during continenta collision. Tectonics 12:629–638
Sayıl N, Osmanşahin I (2008) An investigation of seismicity for Western Anatolia. Nat Hazards 44:51–64
Sri Lakshmi S, Tiwari RK (2009) Model dissection from earthquake time series: a comparative analysis using modern non-linear forecasting and artificial neural network approaches. Comput Geosci 35:191–204
Wang FWM, Wang Y, Shen Z-K (2015) Earthquake potential of the Sichuan-Yunnan region, western China. J Asian Earth Sci 107:232–243
Yıldırım E, Gülbağ A, Horasan G, Doğan E (2011) Discrimination of quarry blasts and earthquakes in the vicinity of Istanbul using soft computing techniques. Comput Geosci 37:1209–1217
Zakeri N S S, Pashazadeh S (2015) Application of neural network based on genetic algorithm in predicting magnitude of earthquake in North Tabriz Fault (NW Iran). Res Commun 109(9)
Zamani A, Sorbi MR, Safavi AA (2013) Application of neural network and ANFIS model for earthquake occurrence in Iran. Earth Sci Inf. doi:10.1007/s12145-013-0112-8
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kaftan, I., Şalk, M. & Şenol, Y. Processing of earthquake catalog data of Western Turkey with artificial neural networks and adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system. Arab J Geosci 10, 243 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-017-3021-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-017-3021-1