Abstract
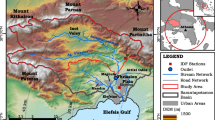
The use of radar for rainfall and runoff estimation is beneficial because of the high spatial and temporal resolution and large areal coverage; the main objective of this research is the calibration of the weather radar of Annaba for hydrological applications. To improve rainfall distribution estimation for the maritime watershed (1,129 km2) (Seybouse, Annaba), located in the north eastern of Algeria, a new technique was used based on the creation of six virtual rainfall stations uniformly throughout the area. The rainfall data for these virtual stations are estimated from raw weather radar data using a newly developed program called “Rain-Data ver1.0.” The calibrated radar-derived rainfall is used as input data in the Gridded Surface Subsurface Hydrologic Analysis model; the results show that all radar rainfall input data tend to produce more accurate runoff hydrographs than rain gauge data. Finally, the use of radar rainfall data to estimate runoff gives encouraging results, especially in regions where continuous gauge rainfall measurements are not available and rain gauges are sparsely distributed.











Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ASWR:
-
Algérien Service weather radar
References
Amiryazdani F, Khalili M, Golkar F, Kalantarzadeh M (2004) Weather radar calibration in central Iran applying ground based rain gauge data. sixth international on symposium on hydrological application of weather radar.
Atlas D, Rosenfeld D, Wolff B (1990) Climatologically tuned reflectivity-rain rate relation and links to area-time integrals. J Appl Meteorol 29:1120–1135. doi:10.1175/1520-0450(1990)029<1120:CTRRRR>2.0.CO;2
Austin PM (1987) Relation between measured radar reflectivity and surface rainfall. Weather Rev 115:1053–1070. doi:10.1175/1520-0493(1987)115<1053:RBMRRA>2.0.CO;2
Bevan KJ, et Hornberger GM (1982) Assessing the effect of spatial pattern of precipitation in modeling stream flow hydrograph. Water Resour Bull 18:823–829. doi:10.1111/j.1752-1688.1982.tb00078.x
Borga M (2008) Notes weather radar and flash flood forecasting, RIMAX OPAQUE. University of Padova Italy, Italy
Bouzeboudja O, Haddad B, Ameur S (2010) Estimation radar des precipitations par la methode des aires fractionnelles. Larhyss J 08:7–26
Calheiros RV, Zawadzki I (1987) Reflectivity rain-rate relationships for radar hydrology in Brazil. Journal of Climate. Appl Meteorol 26:118–132. doi:10.1175/1520 0450(1987)026<0118:RRRRFR>2.0.CO;2
Davis R S, Jendrowski P (1993) The operational real mean basin estimated rainfall (AMBER) module. 13th conference on weather analysis and forecasting, Vienna. Am Meteorol Soc 379-383.
Downer C W, Ogden F L (2002) GSSHA user’s manual, gridded surface subsurface hydrologic analysis version 1.43 for WMS 6.1. ERDC Technical Report. Engineering Research and Development Center Vicksburg.
Hamlin MJ (1983) The significance of rainfall in the study of hydrological processes at basin scale. J Hydrol 65:73–94. doi:10.1016/0022-1694(83)90211-1
Horritt MS, Bates PD (2011) Effect of spatial resolution on a raster based of flood flow. J Hydrol 253:239–249. doi:10.1016/S0022-1694(01)00490-5
Jorgeson J D (1999) Peak flow analysis using a two-dimensional watershed model with radar precipitation data. PhD Thesis. Colorado State University, 194pp
Julien PY, Saghafian B, Ogden FL (1995) Raster-based hydrologic modeling of spatially varied surface runoff. Water Resour Bull 31:523–535. doi:10.1111/j.1752-1688.1995.tb04039.x
Keblouti M, Ouerdachi L, Boutaghane H (2012) Spatial interpolation of annual precipitation in Annaba-Algeria-comparison and evaluation of methods. J Energy Procedia 18:468–475. doi:10.1016/j.egypro.2012.05.058
Khanchoul K, Altschul R, Assassi F (2009) Estimating suspended sediment yield, sedimentation controls and impacts in the Mellah Catchment of Northern Algeria. Arab J Geosci 2:257–271. doi:10.1007/s12517-009-0040-6
Krajewski W, Smith (1991) On the estimation of climatological Z-R relationships. J Appl Meteorol 30:1436–1445
Marshall JS, Langille RC, Palmer W (1947) Measurement of rainfall by radar. J Appl Meteorol 4:186–192. doi:10.1175/1520-0469(1947)004<0186:MORBR>2.0.CO;2
Masoud AA (2009) Runoff modeling of the wadi systems for estimating flash flood and groundwater recharge potential in Southern Sinai Egypt. Arabian journal of Geosciences 4:785–801. doi:10.1007/s12517-009-0090-9
Milford JR, Dugdale G (1989) Estimation of rainfall using geostationary satellite data Applications of Remote Sensing in Agricultural Sciences. PhD Thesis. University of Nottingham, Butterworth London
Piman T, Babel MS, Das Gupta A, Weesakul S (2007) Development of a window correlation matching method for improved radar rainfall estimation. J Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 11:1361–1372. doi:10.5194/hess-11-1361-2007
Ramli S, Tahir W (2011) Radar hydrology: new Z/R relationships for quantitative precipitation estimation in Klang River Basin, Malaysia. Int J Environ Sci Dev. doi:10.1109/CHUSER.2011.6163790
Renard F (2010) Le risque pluvial en milieu urbain. De la caractérisation de l’aléa à l’évaluation de la vulnérabilité : le cas du grand Lyon . PhD Thesis .université jean Moulin Lyon 3. 528pp
Rosenfeld D, Wolff DB, Atlas D (1993) General probability matched relations between radar reflectivity and rain rate. J Appl Meteorol 32:50–72. doi:10.1175/1520-0450(1993)032<0050:GPMRBR>2.0.CO;2
Rosenfeld D, Wolff DB, Amitai E (1994) The window probability matching method for rainfall measurements with radar. J Appl Meteorol 33:682–693. doi:10.1175/1520-0450(1994)033<0682:TWPMMF>2.0.CO;2
Sauvageot H (1994) The probability density functions of rain rate and estimation of rainfall by area integrals. J Appl Meteorol 33:1255–1262. doi:10.1175/1520 0450(1994)033 < 1255:TPDFOR > 2.0.CO;2
Sharif HO, Ogden FL, Krajewski WF, Xue M (2002) Numerical simulations of radar rainfall error propagation. Water Resour Res 38:1–14. doi:10.1029/2001WR000525
Smith JA, Baeck ML, Steiner M, Andrew JM (1996) Catastrophic rainfall from an upslope thunderstorm in the central Appalachians: the Rapidan Storm of June 27, 1995. Water Resour Res 32:3099–3113. doi:10.1029/96WR02107
WF K, Bertrand V, Seo B-C, Gabriele V (2011) Statistical model of the range-dependent error in radar-rainfall estimates due to the vertical profile of reflectivity. journal of hydrology 402:306–316. doi:10.1016/j.jhydrol.2011.03.024
Zawadzki I (1984) Factors affecting the precision of radar measurements of rain. Preprints 22nd Radar Meteorology Conference.
Acknowledgments
The first and the last authors gratefully acknowledge Leila Sadouki, Hamza Atoui and Ahmed Chargui for their help, and Azzeddine Amri chef Sétif Meteorological Department (SMD) for providing data radar list to laboratory of hydraulic and hydraulics construction. The authors also thank National Agency of Water Resources (NAWR) for providing the rain gauge and discharge data.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Keblouti, M., Ouerdachi, L. & Berhail, S. The use of weather radar for rainfall-runoff modeling, case of Seybouse watershed (Algeria). Arab J Geosci 8, 1–11 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-013-1224-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-013-1224-7