Abstract
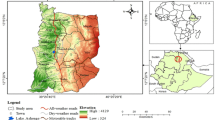
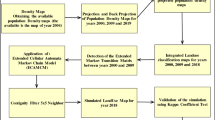
The rapid development of cities in developing countries results in deteriorating of agricultural lands. The majority of these agricultural lands are converted to urban areas, which affects the ecosystems. In this research, an integrated model of Markov chain and cellular automata models was applied to simulate urban land use changes and to predict their spatial patterns in Tripoli metropolitan area, Libya. It is worth mentioning that there is not much research has been done about land use/cover change in Libyan cities. In this study, the performance of integrated CA–Markov model was assessed. Firstly, the Markov chain model was used to simulate and predict the land use change quantitatively; then, the CA model was applied to simulate the dynamic spatial patterns of changes explicitly. The urban land use change from 1984 to 2010 was modelled using the CA–Markov model for calibration to compute optimal transition rules and to predict future land use change. In validation process, the model was validated using Kappa index statistics which resulted in overall accuracy more than 85 %. Finally, based on transition rules and transition area matrix produced from calibration process, the future land use changes of 2020 and 2025 were predicted and mapped. The findings of this research showed reasonably good performance of employed model. The model results demonstrate that the study area is growing very rapidly especially in the recent decade. Furthermore, this rapid urban expansion results in remarkable continuous decrease of agriculture lands.





Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.References
Al-shalabi M, Billa L, Pradhan B, Mansor S, Al-Sharif AAA (2012) Modelling urban growth evolution and land-use changes using GIS based cellular automata and SLEUTH models: the case of Sana’a metropolitan city, Yemen. Environ Earth Sci:1–13. doi:10.1007/s12665-012-2137-6
Al-sharif AAA, Pradhan B (2013) Urban sprawl analysis of Tripoli Metropolitan city (Libya) using remote sensing data and multivariate logistic regression model. J Indian Soc of Remote Sens:1–15. doi 10.1007/s12524-013-0299-7
Al-sharif AAA, Pradhan B, Shafri HZM, Mansor S (2013) Spatio-temporal analysis of urban and population growths in Tripoli using remotely sensed data and GIS. Indian J Sci Technol 6(8):5134–5142
Araya YH, Cabral P (2010) Analysis and modeling of urban land cover change in Setúbal and Sesimbra, Portugal. Remote Sens 2:1549–1563. doi:10.3390/rs2061549
Arnous MO (2013) Geotechnical site investigations for possible urban extensions at Suez City, Egypt using GIS. Arab J Geosci 6:1349–1369. doi:10.1007/s12517-011-0441-1
Arsanjani JJ, Kainz W, Mousivand AJ (2011) Tracking dynamic land-use change using spatially explicit Markov Chain based on cellular automata: the case of Tehran. Int J Image Data Fusion 2:329–345. doi:10.1080/19479832.2011.605397
Barredo JI, Demicheli L (2003) Urban sustainability in developing countries’ megacities: modelling and predicting future urban growth in Lagos. Cities 20:297–310. doi:10.1016/S0264-2751(03)00047-7
Barredo JI, Kasanko M, McCormick N, Lavalle C (2003) Modelling dynamic spatial processes: simulation of urban future scenarios through cellular automata. Landscape Urban Plan 64:145–160
Batty M, Couclelis H, Eichen M (1997) Urban systems as cellular automata. Environ Plan B 24:159–164
Biro K, Pradhan B, Buchroithner M, Makeschin F (2011) Land use/land cover change analysis and its impact on soil properties in the Northern Part of Gadarif Region, Sudan. Land Degrad Dev 24:90–102. doi:10.1002/ldr.1116
Chen J, Gong P, He C, Luo W, Tamural M, Shi P (2002) Assessment of the urban development plan of Beijing by using a CA-based urban growth model. PE & RS- Photogram Eng Remote Sens 68:1063–1073
Clarke K (1997) A self-modifying cellular automaton model of historical. Environ Plan B 24:247–261
Clarke KC, Gaydos LJ (1998) Loose-coupling a cellular automaton model and GIS: long-term urban growth prediction for San Francisco and Washington/Baltimore. Int J Geogr Inf Sci 12:699–714. doi:10.1080/136588198241617
Coppedge BR, Engle DM, Fuhlendorf SD (2007) Markov models of land cover dynamics in a southern Great Plains grassland region. Landscape Ecol 22:1383–1393. doi:10.1007/s10980-007-9116-4
Dadhich PN, Hanaoka S (2011) Spatio-temporal urban growth modeling of Jaipur, India. J Urban Technol 18:45–65. doi:10.1080/10630732.2011.615567
Deng X, Su H, Zhan J (2008) Integration of multiple data sources to simulate the dynamics of land systems. Sensors 8:620–634. doi:10.3390/s8020620
Ettema D, de Jong K, Timmermans H, Bakema A (2007) PUMA: multi-agent modelling of urban systems. Modelling land-use change. Springer. pp 237–258. doi:10.1007/978-1-4020-5648-2_14
Fan F, Wang Y, Wang Z (2008) Temporal and spatial change detecting (1998–2003) and predicting of land use and land cover in Core corridor of Pearl River Delta (China) by using TM and ETM + images. Environ Monit Assess 137:127–147. doi:10.1007/s10661-007-9734-y
Guan D, Li H, Inohae T, Su W, Nagaie T, Hokao K (2011) Modeling urban land use change by the integration of cellular automaton and Markov model. Ecol Model 222:3761–3772. doi:10.1016/j.ecol model.2011.09.009
He C, Okada N, Zhang Q, Shi P, Li J (2008) Modelling dynamic urban expansion processes incorporating a potential model with cellular automata. Landscape Urban Plan 86:79–91. doi:10.1016/j.landurbplan.2007.12.010
He C, Okada N, Zhang Q, Shi P, Zhang J (2006) Modeling urban expansion scenarios by coupling cellular automata model and system dynamic model in Beijing, China. Appl Geogr 26:323–345. doi:10.1016/j.apgeog.2006.09.006
Jianping L, Bai Z, Feng G (2005) RS-and-GIS-supported forecast of grassland degradation in southwest Songnen Plain by Markov model. Geo-spatial Info Sci 8:104–109. doi:10.1007/BF02826848
Kamusoko C, Aniya M, Adi B, Manjoro M (2009) Rural sustainability under threat in Zimbabwe – Simulation of future land use/cover changes in the Bindura district based on the Markov-cellular automata model. Appl Geogr 29:435–447. doi:10.1016/j.apgeog.2008.10.002
Kawy WAMA, El-Magd IHA (2012) Use of satellite data and GIS for assessing the agricultural potentiality of the soils South Farafra Oasis, Western Desert, Egypt. Arab J Geosci 6:2299–2311. doi:10.1007/s12517-012-0518-5
Kelarestaghi A, Jeloudar ZJ (2011) Land use/cover change and driving force analyses in parts of northern Iran using RS and GIS techniques. Arab J Geosci 4:401–411. doi:10.1007/s12517-009-0078-5
Li X, Gar-On Yeh A (2004) Data mining of cellular automata's transition rules. Int J Geogr Inf Sci 18:723–744. doi:10.1080/13658810410001705325
Li X, Yeh AG-O (2002) Neural-network-based cellular automata for simulating multiple land use changes using GIS. Int J Geogr Inf Sci 16:323–343. doi:10.1080/13658810210137004
Liu X, Li X, Yeh AG-O, He J, Tao J (2007) Discovery of transition rules for geographical cellular automata by using ant colony optimization. Sci China Ser D Earth Sci 50:1578–1588. doi:10.1007/s11430-007-0083-z
López E, Bocco G, Mendoza M, Duhau E (2001) Predicting land-cover and land-use change in the urban fringe: A case in Morelia city, Mexico. Landscape Urban Plan 55:271–285. doi:10.1016/S0169-2046(01)00160-8
Mitsova D, Shuster W, Wang X (2011) A cellular automata model of land cover change to integrate urban growth with open space conservation. Landscape Urban Plan 99:141–153. doi:10.1016/j.landurbplan.2010.10.001
Muller MR, Middleton J (1994) A Markov model of land-use change dynamics in the Niagara Region, Ontario, Canada. Landscape Ecol 9:151–157. doi:10.1007/BF00124382
Myint SW, Wang L (2006) Multicriteria decision approach for land use land cover change using Markov chain analysis and a cellular automata approach. Can J Remote Sens 32:390–404
Othman AA, Al-Saady YI, Al-Khafaji AK, Gloaguen R (2013) Environmental change detection in the central part of Iraq using remote sensing data and GIS. Arab Geosci:1–12. doi:10.1007/s12517-013-0870-0
Pradhan B, Suleiman Z (2009) Landcover mapping and spectral analysis using multi-sensor satellite data: a case study in Tioman Island, Malaysia. J Geomatics 3(2):71–78
Qiu B, Chen C (2008) Land use change simulation model based on MCDM and CA and its application. ACTA Geogr Sin 63:165–174
Sang L, Zhang C, Yang J, Zhu D, Yun W (2011) Simulation of land use spatial pattern of towns and villages based on CA–Markov model. Math Comput Modell 54:938–943. doi:10.1016/j.mcm.2010.11.019
Sui DZ, Zeng H (2001) Modeling the dynamics of landscape structure in Asia’s emerging desakota regions: a case study in Shenzhen. Landscape Urban Plann 53:37–52. doi:10.1016/S0169-2046(00)00136-5
Sun H, Forsythe W, Waters N (2007) Modeling urban land use change and urban sprawl: Calgary, Alberta, Canada. Networks and spatial economics 7:353–376
Tehrany MS, Pradhan B, Jebu MN (2013a) A comparative assessment between object and pixel-based classification approaches for land use/land cover mapping using SPOT 5 imagery. Geocarto Int.:1–19. doi:10.1080/10106049.2013.768300
Tehrany MS, Pradhan B, Jebur MN (2013b) Remote sensing data reveals eco-environmental changes in urban areas of Klang Valley, Malaysia: contribution from object based analysis. J Ind Soc Remote Sens (article online first available). doi:10.1007/s12524-013-0289-9
UPA, Libya (2009) Tripoli Agglomeration Plan, (3rd Generation Planning Project).
Verburg PH, de Koning GHJ, Kok K, Veldkamp A, Bouma J (1999) A spatial explicit allocation procedure for modelling the pattern of land use change based upon actual land use. Ecol Model 116:45–61. doi:10.1016/S0304-3800(98)00156-2
Verburg PH, Soepboer W, Veldkamp A, Limpiada R, Espaldon V, Mastura SS (2002) Modeling the spatial dynamics of regional land use: the CLUE-S model. Environ Manage 30:391–405. doi:10.1007/s00267-002-2630-x
Wakode HB, Baier K, Jha R, Azzam R (2013) Analysis of urban growth using Landsat TM/ETM data and GIS—a case study of Hyderabad, India. Arab J Geosci:1–13. doi: 10.1007/s12517-013-0843-3
Wang SQ, Zheng XQ, Zang XB (2012) Accuracy assessments of land use change simulation based on Markov-cellular automata model. Procedia Environ Sci 13:1238–1245. doi:10.1016/j.proenv.2012.01.117
Ward DP, Murray AT, Phinn SR (2000) A stochastically constrained cellular model of urban growth. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst 24:539–558. doi:10.1016/S0198-9715(00)00008-9
Weng Q (2002) Land use change analysis in the Zhujiang Delta of China using satellite remote sensing, GIS and stochastic modelling. J Environ Manage 64:273–284. doi:10.1006/jema.2001.0509
White R, Engelen G (1993) Cellular automata and fractal urban form: a cellular modelling approach to the evolution of urban land-use patterns. Environ Plan A 25:1175–1199. doi:10.1068/a251175
White R, Engelen G (1997) Cellular automata as the basis of integrated dynamic regional modelling. Environ Plan B 24:235–246. doi:10.1068/b240235
White R, Engelen G (2000) High-resolution integrated modelling of the spatial dynamics of urban and regional systems. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst 24:383–400. doi:10.1016/S0198-9715(00)00012-0
Wu F (2002) Calibration of stochastic cellular automata: the application to rural–urban land conversions. Int J Geogr Inf Sci 16:795–818. doi:10.1080/13658810210157769
Wu Q, Li H-q, Wang R-s, Paulussen J, He Y, Wang M, Wang B-h, Wang Z (2006) Monitoring and predicting land use change in Beijing using remote sensing and GIS. Landscape Urban Plan 78:322–333. doi:10.1016/j.landurbplan.2005.10.002
Xian G, Crane M (2005) Assessments of urban growth in the Tampa Bay watershed using remote sensing data. Remote Sens Environ 97:203–215. doi:10.1016/j.rse.2005.04.017
Q-s Y, Li X (2007) Integration of multi-agent systems with cellular automata for simulating urban land expansion. Sci Geogr Sin 27:542
Yang X, Zheng X-Q, Lv L-N (2012) A spatiotemporal model of land use change based on ant colony optimization, Markov chain and cellular automata. Ecol Model 233:11–19. doi:10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2012.03.011
Youssef AM, Pradhan B, Tarabees E (2011) Integrated evaluation of urban development suitability based on remote sensing and GIS techniques: contribution from the analytic hierarchy process. Arab J Geosci 4:463–473. doi:10.1007/s12517-009-0118-1
Yuan F (2009) Urban growth monitoring and projection using remote sensing and geographic information systems: a case study in the twin cities metropolitan area, Minnesota. Geocarto Int 25:213–230. doi:10.1080/10106040903108445
Zhang Q, Ban Y, Liu J, Hu Y (2011) Simulation and analysis of urban growth scenarios for the Greater Shanghai Area, China. Comput Environ Urban Syst 35:126–139. doi:10.1016/j.compenvurbsys.2010.12.002
Acknowledgements
Thanks to two anonymous reviewers for their helpful comments which helped to improve the quality of previous version of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Al-sharif, A.A.A., Pradhan, B. Monitoring and predicting land use change in Tripoli Metropolitan City using an integrated Markov chain and cellular automata models in GIS. Arab J Geosci 7, 4291–4301 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-013-1119-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-013-1119-7
Keywords
Profiles
- Biswajeet Pradhan View author profile