Abstract
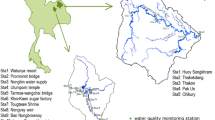
The current study presents the application of selected chemometric techniques—hierarchical cluster analysis (HCA) and principal component analysis (PCA)—to evaluate the spatial variation of the water chemistry and to classify the pollution sources in the Langat River. The HCA rendered the sampling stations into two clusters (group 1 and group 2) and identified the vulnerable stations that are under threat. Group1 (LY 1 to LY 14) is associated with seawater intrusion, while group 2 (LY 15 to LY 30) is associated with agricultural and industrial pollution. PCA analysis was applied to the water datasets for group 1 resulting in four components, which explained 85 % of the total variance while group 2 extracted six components, explaining 88 % of the variance. The components obtained from PCA indicated that seawater intrusion, agricultural and industrial pollution, and geological weathering were potential sources of pollution to the study area. This study demonstrated the usefulness of the chemometric techniques on the interpretation of large complex datasets for the effective management of water resources.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdullah MI, Royle LG (1974) A study of the dissolved and particulate trace elements in the Bristol Channel. J Mar Biol Assoc UK 54(3):581–597. doi:10.1017/S0025315400022761
Akbal F, Gürel L, Bahadır T et al (2011) Multivariate statistical techniques for the assessment of surface water quality at the mid-Black Sea Coast of Turkey. Water Air Soil Poll 216(1):21–37. doi:10.1007/s11270-010-0511-0
Alkarkhi A, Ahmad A, Easa A (2009a) Assessment of surface water quality of selected estuaries of Malaysia: multivariate statistical techniques. Environmentalist 29(3):255–262. doi:10.1007/s10669-008-9190-4
Alkarkhi A, Ismail N, Ahmed A, Easa A (2009b) Analysis of heavy metal concentrations in sediments of selected estuaries of Malaysia—a statistical assessment. Environ Monit Assess 153(1):179–185. doi:10.1007/s10661-008-0347-x
Alloway BJ (1995) Heavy metals in soils. Blackie Academic & Professional, London
Altın A, Filiz Z, Iscen CF (2009) Assessment of seasonal variations of surface water quality characteristics for Porsuk Stream. Environ Monit Assess 158(1–4):51–65. doi:10.1007/s10661-008-0564-3
APHA (2005) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 21st edn. American Water Works Association, Water Environment Federation, Washington
Aris AZ, Abdullah MH, Ahmed A, Woong KK (2007) Controlling factors of groundwater hydrochemistry in a small island’s aquifer. Int J Environ Sci Technol 4(4):441–450
Aris AZ, Praveena SM, Abdullah MH, Radojevic M (2012) Statistical approaches and hydrochemical modelling of groundwater system in small tropical island. J Hydroinform 14(1):206–220. doi:10.2166/hydro.2011.072
Berandah FE, Yap CK, Ismail A (2010) Bioaccumulation and distribution of heavy metals (Cd, Cu, Fe, Ni, Pb and Zn) in the different tissues of Chicoreus capucinus Lamarck (Mollusca: Muricidae) collected from Sungai Janggut, Kuala Langat, Malaysia. Environ Asia 3(1):65–71
Boyacioglu H, Boyacioglu H (2008) Water pollution sources assessment by multivariate statistical methods in the Tahtali Basin, Turkey. Environ Geol 54(2):275–282. doi:10.1007/s00254-007-0815-6
Bu H, Tan X, Li S, Zhang Q (2010) Water quality assessment of the Jinshui River (China) using multivariate statistical techniques. Environ Earth Sci 60(8):1631–1639. doi:10.1007/s12665-009-0297-9
Campbel PGC, Stokes PM (1985) Acidification and toxicity of metals to aquatic biota. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 42(12):2034–2049. doi:10.1139/f85-251
Connell DW, Miller GJ (1984) Chemistry and ecotoxicology of pollution. Wiley, New York
Davis JC (1986) Statistics and data analysis in geology, 2nd edn. Wiley, New York
Debels P, Figueroa R, Urrutia R et al (2005) Evaluation of water quality in the Chillán River (Central Chile) using physicochemical parameters and a modified water quality index. Environ Monit Assess 110(1–3):301–322. doi:10.1007/s10661-005-8064-1
Diagomanolin V, Farhang M, Ghazi-Khansari M et al (2004) Heavy metals (Ni, Cr, Cu) in the Karoon waterway river, Iran. Toxicol Lett 151(1):63–67. doi:10.1016/j.toxlet.2004.02.018
DOA (1995) Landuse of Selangor and Negeri Sembilan. Department of Agriculture, Kuala Lumpur
Elder JF (1988) Metal biogeochemistry in surface-water systems: a review of principles and concepts. In: U.S. Geological Survey circular, Issue 1013. Department of the Interior, U.S. Geological Survey, Washington, D.C,
Gobbett DJ, Hutchison CS (1973) Geology of the Malay Peninsula: West Malaysia and Singapore. Wiley-Interscience, New York
Goh BPL, Chou LM (1997) Heavy metal levels in marine sediments of Singapore. Environ Monit Assess 44(1):67–80. doi:10.1023/a:1005763918958
Hait J, Jana RK, Sanyal SK (2009) Processing of copper electrorefining anode slime: a review. Miner Process Extract Metall Rev 118(4):240–252. doi:10.1179/174328509X431463
Huang J, Ho M, Du P (2011) Assessment of temporal and spatial variation of coastal water quality and source identification along Macau peninsula. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 25(3):353–361. doi:10.1007/s00477-010-0373-4
Hussain M, Ahmed SM, Abderrahman W (2008) Cluster analysis and quality assessment of logged water at an irrigation project, eastern Saudi Arabia. J Environ Manag 86(1):297–307. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2006.12.007
JICA and MGDM (2002) The study on the sustainable groundwater resources and environmental management for the Langat Basin in Malaysia. Final Report. vol 3. Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia
Juahir H, Zain S, Yusoff M et al (2011) Spatial water quality assessment of Langat River Basin (Malaysia) using environmetric techniques. Environ Monit Assess 173(1):625–641. doi:10.1007/s10661-010-1411-x
Kazi TG, Arain MB, Jamali MK et al (2009) Assessment of water quality of polluted lake using multivariate statistical techniques: a case study. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 72(2):301–309. doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2008.02.024
Krishna AK, Satyanarayanan M, Govil PK (2009) Assessment of heavy metal pollution in water using multivariate statistical techniques in an industrial area: a case study from Patancheru, Medak District, Andhra Pradesh, India. J Hazard Mater 167(1–3):366–373. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.12.131
Langner BE (2000) Selenium and selenium compounds. In: Ullmann’s encyclopedia of industrial chemistry. Wiley, Weinheim. doi:10.1002/14356007.a23_525
Lee YH, Abdullah MP, Chai SY, Mokhtar MB, Ahmad R (2006) Development of possible indicators for sewage pollution for the assessment of Langat River ecosystem health. Malays J Anal Sci 10(1):15–26
Mokhtar MB, Aris AZ, Munusamy V, Praveena SM (2009) Assessment level of heavy metals in Penaeus monodon and Oreochromis spp. in selected aquaculture ponds of high densities development area. Eur J Sci Res 30(3):348–360
Najar I, Khan A (2012) Assessment of water quality and identification of pollution sources of three lakes in Kashmir, India, using multivariate analysis. Environ Earth Sci 66(8):2367–2378. doi:10.1007/s12665-011-1458-1
Osman R, Saim N, Juahir H, Abdullah M (2012) Chemometric application in identifying sources of organic contaminants in Langat river basin. Environ Monit Assess 184(2):1001–1014. doi:10.1007/s10661-011-2016-8
Praveena SM, Abdullah MH, Bidin K, Aris AZ (2011) Understanding of groundwater salinity using statistical modeling in a small tropical island, East Malaysia. Environmentalist 31(3):279–287. doi:10.1007/s10669-011-9332-y
Praveena SM, Ahmed A, Radojevic M et al (2008) Multivariate and geoaccumulation index evaluation in mangrove surface sediment of Mengkabong Lagoon, Sabah. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 81(1):52–56. doi:10.1007/s00128-008-9460-3
Reghunath R, Murthy TRS, Raghavan BR (2002) The utility of multivariate statistical techniques in hydrogeochemical studies: an example from Karnataka, India. Water Res 36(10):2437–2442. doi:10.1016/S0043-1354(01)00490-0
Reza R, Singh G (2010) Heavy metal contamination and its indexing approach for river water. Int J Environ Sci Technol 7(4):785–792
Saim N, Osman R, Sari AbgSpian DR et al (2009) Chemometric approach to validating faecal sterols as source tracer for faecal contamination in water. Water Res 43(20):5023–5030. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2009.08.052
Sarmani S (1989) The determination of heavy metals in water, suspended materials and sediments from Langat River, Malaysia. Hydrobiologia 176–177(1):233–238. doi:10.1007/bf00026558
Sarmani S, Abdullah MP, Baba I, Majid AA (1992) Inventory of heavy metals and organic micropollutants in an urban water catchment drainage basin. Hydrobiologia 235–236(1):669–674. doi:10.1007/bf00026255
Shazili NAM, Yunus K, Ahmad AS et al (2006) Heavy metal pollution status in the Malaysian aquatic environment. Aquat Ecosyst Health Manag 9(2):137–145. doi:10.1080/14634980600724023
Shokrzadeh M, Saeedi Saravi SS (2009) The study of heavy metals (zinc, lead, cadmium, and chromium) in water sampled from Gorgan coast (Iran), Spring 2008. Toxicol Environ Chem 91(3):405–407. doi:10.1080/02772240902830755
Shrestha S, Kazama F (2007) Assessment of surface water quality using multivariate statistical techniques: a case study of the Fuji river basin, Japan. Environ Model Softw 22(4):464–475. doi:10.1016/j.envsoft.2006.02.001
Simeonov V, Tsakovski S, Lavric T et al (2004) Multivariate statistical assessment of air quality: a case study. Microchim Acta 148(3–4):293–298. doi:10.1007/s00604-004-0279-2
Singh KP, Malik A, Mohan D, Sinha S (2004) Multivariate statistical techniques for the evaluation of spatial and temporal variations in water quality of Gomti River (India)—a case study. Water Res 38(18):3980–3992. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2004.06.011
Singh KP, Malik A, Singh VK et al (2005) Chemometric analysis of groundwater quality data of alluvial aquifer of Gangetic plain, North India. Anal Chimica Acta 550(1–2):82–91. doi:10.1016/j.aca.2005.06.056
Taha M (2003) Groundwater and geoenvironmental quality issues in the Langat Basin, Malaysia. In: Kono I, Nishigaki M, Komatsu M (eds) Groundwater engineering-recent advances: Proceedings of the International Symposium, Okayama, Japan, 2003. Taylor & Francis
UPUM (2002) Program Pencegahan dan Peningkatan Kualiti Air Sungai Langat. Final Draft Report. Universiti Malaya Consultancy Unit, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia
Varol M, Gökot B, Bekleyen A, Şenc B (2012) Spatial and temporal variations in surface water quality of the dam reservoirs in the Tigris River basin, Turkey. Catena 92:11–21. doi:10.1016/j.catena.2011.11.013
Zulkifli S, Mohamat-Yusuff F, Arai T et al (2010) An assessment of selected trace elements in intertidal surface sediments collected from the Peninsular Malaysia. Environ Monit Assess 169(1):457–472. doi:10.1007/s10661-009-1189-x
Acknowledgments
This research was funded by the Research University Grant Scheme vot no. 9199751, no. project 03-01-11-1142RU from Universiti Putra Malaysia and the Academy of Sciences for the Developing World (TWAS) project number 09-09 RG/EAS/AS_C/UNESCO FR:3240231216. The first author sincerely acknowledges the support from Graduate Research Fellowship Scholarship awarded by Universiti Putra Malaysia for her study. Rainfall data and field services provided by the Department of Drainage and Irrigation (JPS), Malaysia is greatly appreciated.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lim, W.Y., Aris, A.Z. & Praveena, S.M. Application of the chemometric approach to evaluate the spatial variation of water chemistry and the identification of the sources of pollution in Langat River, Malaysia. Arab J Geosci 6, 4891–4901 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-012-0756-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-012-0756-6