Abstract
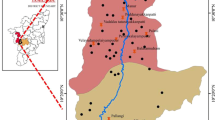
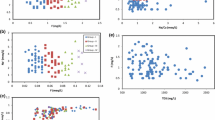
Groundwater samples were collected from Mettur taluk of Salem district, Tamilnadu, India for two different seasons (pre-monsoon and post-monsoon) and analyzed for fluoride ion along with other chemical parameters. The major litho units of the study area are Charnockites, peninsular gneiss, and calc gneiss of meta-sedimentary group. The fluoride concentration ranges from 0.1 to 2.8 mg/L and 0.4 to 4.0 mg/L during pre-monsoon (PRM) and post-monsoon (POM) seasons, respectively. Results showed that collected water samples were contaminated by the presence of fluoride ion. During PRM and POM, 21% and 56% of samples recorded higher fluoride when compared with Indian Drinking Water Standard (1 mg/L) and (9% and 35%) of samples recorded higher fluoride when compared with World Health Organization tolerance limit (1.5 mg/L). The ratio of Na/Ca indicates high sodium content in groundwater enhances the dissolution of fluoride at higher pH. Hydrogeochemical facies indicates water-rock interaction as main source for high fluoride in groundwater. A positive correlation between pH, Mg, and F indicates high alkaline nature of water promotes fluoride leaching from source rocks into ground water. Factor analysis indicates hydro-geochemical processes like weathering, ion exchange, and anthropogenic contributes to groundwater chemistry. The saturation index indicates dissolution and precipitation contributes fluoride dissolution along with mixing.
Abstract
[متّور] [تلوك] من سالم منطقة, [تميلندو], هند لاثنان فصول مختلفة ([بر] ريح موسميّة وموقعة ريح موسميّة) وحلّلت ل [فلووريد يون] مع أخرى معلمات كيميائيّ. الكبريات [ليثو] وحدات من الدراسة منطقة [شرنوكيتس], صخر نايس شبه جزيري و [كلك] صخر نايس من ميتا مجموعة رسوبيّة. الفلوريد يتراوح تركيز من 0.1 إلى 2.8 [مغ/ل] و0.4 [تو] 4.0 [مغ/ل] أثناء [برم] و [بوم] فصول على التّوالي. نتيجات أبدوا أنّ لوّنت يجمع [وتر سمبل] كان بالوجود ال [فلووريد يون]. سجّل أثناء [برم] و [بوم] 21% و56% من عينات فلوريد [هيغر] [وهن كمبرد ويث] [درينك وتر] هنديّة معياريّة (1 [مغ/ل]) و(9% و35%) من عينات سجّل فلوريد [هيغر] [وهن كمبرد ويث] [وورلد هلث ورغنيزأيشن] [تولرنس ليميت] (1.5 [مغ/ل]). يشير النسبة ال [ن/ك] عال صوديوم محتوى في ماء جوفيّ يحسن الإنحلال الفلوريد في [ف.] [هيغر]. يشير سحنة مائيّ جوفيّ كيميائيّ [وتر-روك] تفاعل كمصدر رئيسيّة لفلوريد عال في ماء جوفيّ. يشير إرتباط إيجابيّة بين [ف], [مغ] و [ف], طبيعة عال قلويّة ماء يروّج فلوريد يرشح من مصدر صخورة داخل [غرووند وتر]. [فكتور نلسس] يشير يسهم عمليات [هدرو-جوشميكل] مثل [وثرينغ], [إيون-إكسشنج] و [أنثروبوجنيك] إلى ماء جوفيّ كيمياء. التشبع يشير فهرسة إنحلال وترسيب يسهم فلوريد إنحلال مع يمزج.






Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.References
Apha (1995) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 19th edn. APHA, Washington DC, USASS
Appelo CAJ, Postma D (1996) Geochemistry, groundwater and pollution. Balkema, Rotterdam, 536pp
Babulal Das, Jitu Talukdar, Surashree Sarma, Biren Gohain, Robin K. Dutta, Himangshu B. Das, Subhash C. Das (2003) Fluoride and other inorganic constituents in groundwater of Guwahati, Assam, India. Curr Sci Vol.85, Paper 5
Balasubramanian A, Sharma KK, Sastri JCV (1985) Geoelectrical and Hydrogeochemicalevaluation of Coastal aquifers of Tambraparni basin, Tamilnadu. Geophysical Research Bull 23:203–209
BIS Bureau of Indian Standards Drinking water-specification (2003) IS: 10500, New Delhi
Bouwer H (1978) Groundwater quality, groundwater hydrology. Kogakusha Ltd, Mc.Graw-Hill, pp 339–375
Carrillo-Rivera JJ, Cardona A, Edmunds WM (2002) Use of abstraction regime and knowledge of hydrogeological conditions to control high-fluoride concentration in abstracted groundwater:San Luis Potosi basin, Mexico. J Hydrol 261:24–47
Craig E, Anderson MP (1979) The effects of urbanization of ground water quality. A case study of ground water ecosystems. Environ Conserv 30(2):104–130
Davis JC (1986) Statistics and data analysis in geology. Wiley, NewYork
Dhiman SD, Keshari AK (2006) GIS assisted inverse geochemical modeling for plausible phase transfers in aquifers. Environ Geol 50:1211–1219. doi:10.1007/s00254-006-0293-2
Dissanayake CB (1991) The fluoride problem in the groundwater of Sri Lanka—environmental management and health. Int J Environ Stud 38:137–156
Drever JI (1988) The geochemistry of natural waters, 2nd edn. Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs
EPA (1997) Public health global for fluoride in drinking water. Pesticide and environmental toxicology. Section Office of Environmental Health Hazard Assessment, California Environmental Protection Agency
Farooqi A, Masuda H, Firdous N (2007) Toxic fluoride and arsenic contaminated groundwater in the Lahore and Kasur districts, Punjab, Pakistan and possible contaminant sources. J Environ Pollut 145:839–849
Gibbs RJ (1970) Mechanisms controlling world water chemistry. Science 170:1088–1090
Gizaw B (1996) The origin of high bicarbonate and fluoride concentrations in waters of the main Ethiopian Rift Valley. J Afr Earth Sci 22:391–402
Guo Q, Wang Y, Ma T, Ma R (2007) Geochemical processes controlling the elevated fluoride concentration in groundwaters of the Taiyuan Basin, Northern China. J Geochem Explor 93:1–12
Gupta S, Banerjee S, Saha R, Datta JK, Mondal N (2006) Fluoride geochemistry of groundwater in Birbhum, West Bengal, India. Fluoride 39:318–320
Hounslow AW (1995) Water quality data: analysis and interpretation. CRC Press LLC, Lewis publishers, 397 p
Jacks G, Rajagopalan K, Alveteg T, Jönsson M (1993) Genesis of high F groundwater, Southern India. App Geochem 2, Paper 3
Karanth KR (1987) Quality of groundwater and groundwater exploration. Tata McGraw – Hill Publishing Co.Ltd, New Delhi, pp 217–275, 437–509
Karro E, Indermitte E, Saava A, Haamer K, Marandi A (2006) Fluoride occurrence in publicly supplied drinking water in Estonia. Environ Geol 50(3):389–396
Kim K, Jeong GY (2005) Factors influencing natural occurrence of fluoride-rich groundwaters: a case study in the southeastern part of the Korean Peninsula. Chemos 58:1399–1408
Kumar S, Syed A (1989) Distribution of fluoride in shallow aquifers in and around district Rohtak, Haryana state, India. In: Gupta CP, Shakeel A, Rao VVSG, Raja MT (eds) Workshop on appropriate methodologies for development and management of groundwater resources in developing countries. National Geophysical research Institute, Hyderabad, pp 33–38
Kundu MC, Mandal B (2008) Assessment of potential hazards of fluoride contamination in drinking groundwater of an intensively cultivated district in West Bengal, India. Env Mon and Assess. doi:10.1007/s10661-008-0299-1
Lawrence FW, Upchurch SB (1982) Identification of recharge areas using geochemical factor analysis. Groundwat 20:680–687
Madhnure P, Sirsikar DY, Tiwari AN, Ranjan B, Malpe DB (2007) Occurrence of fluoride in the groundwaters of Pandharkawada area, Yavatmal district, Maharashtra, India. Curr Sci 92(5):675–679
Meenakshi RC (2006) Fluoride in drinking water and its removal. J Hazard Mater B137:456–463
Miller GT (1979) Living in the environment. Wadsworth Publishing Company, Belmond California
Misra AK, Mishra A, Premraj (2006) Escalation of groundwater fluoride in the Ganga alluvial plain of India. Fluoride 39(1):35–38
Moghaddam A, Fijani E (2008) Distribution of fluoride in groundwater of Maku area, northwest of Iran. Environ Geol 56:281–287
Mor S, Ravindra K, Dahiya RP, Chandra A (2006) Leachate characterization and assessment of groundwater pollution near municipal solid waste landfill site. Env Monit and Assess 118:435–456
Nanyaro JT, Aswathanarayana U, Mungere JS, Lahermo P (1984) A geochemical model for the abnormal fluoride concentrations in waters in parts of northern Tanzania. J Arf Earth Sci 2:129–140
Ozsvath D (2006) Fluoride concentrations in a crystalline bedrock aquifer Marathon County. Wisconsin, Environ Geol 50:132–138
Pickering WF, Slavek J, Waller P (1988) The effect of ion exchange on the solubility of fluoride compounds. Wat Air Soil Poll 39:323–336
Piper AM (1994) A graphic procedure in the geochemical interpretation of water analysis. Trans Geophysics union 25:914–923
Plummer LN, Jones BF, Truesdell AH (1976) WATEQF – A FORTRAN IV Version of WATEQ, A computer program for calculating chemical equilibrium of natural waters. USGS Wat Res Invest 76:13–61
Rajiv Gandhi National Drinking Water Mission (RGNDWM) (1993) Prevention and control of fluorisis in India, (unpublished report)
Ramamohana Rao NV, Suhasini Reddy V, Navneeth Rao T, Surya prakash Rao (1996) Hydrogeochemistry of fluorine in Nalgonda district of Andhra Pradesh, India. Proc of the International Symposium on Applied Geochemistry, 255–262pp
Ramanaiah SV, Venkatamohan S, Rajkumar B, Sarma PN (2006) Monitoring of fluoride concentration in groundwater of Prakasham district in India: correlation with physico-chemical parameters. J Environ Sci Eng 48:129–134
Robin NS (2002) Groundwater quality in Scotland: major ion chemistry of the key groundwater bodies. Sci Total Env 294:48–49
Rukah YA, Alsokhny K (2004) Geochemical assessment of groundwater contamination with special emphasis on fluoride concentration, North Jordan. Chemie der Erde Geochem 64:171–181
Salve PR, Maurya A, Kumbhare PS, Ramteke DS, Wate SR (2008) Assessment of groundwater quality with respect to fluoride. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 81:289–293
Saxena V, Ahmed S (2003) Inferring chemical parameters for the dissolution of fluoride in groundwater. Environ Geol 43(6):731–736
Shaji E, Viju BJ, Thambi DS (2007) High fluoride in groundwater of Palghat District, Kerala. Curr Sci 92(2):240–246
Short HE, McRobert TW, Bernard AS, Mannadinayer AS (1937) Endemic fluorosis in the Madras Presidency. Ind J Med Res 25:553–561
Sreedevi PD, Ahmed S, Made B, Ladous E, Gandolfi JM (2006) Association of hydrogeological factors in temporal variations of fluoride concentration in a crystalline aquifer in India. Environ Geol 50:1–11. doi:10.1007/s00254-005-0167-z
Srinivasamoorthy K, Chidambaram S, Vasantavigar M, Prasanna V and John P (2007) Geochemistry of Fluorides in groundwater of Salem district, Tamilnadu, India, Indian J Geochem 22(2):237–246
Srinivasamoorthy K, Chidambaram M, Prasanna MV, Vasanthavigar M, John Peter A, Anandhan P (2008a) Identification of major sources controlling Groundwater Chemistry from a hard rock terrain—A case study from Mettur taluk, Salem district, Tamilnadu, India. J Earth Sys Sci 117(1):49–58
Srinivasamoorthy K, Chidambaram S, Vasanthavigar M (2008b) Geochemistry of fluorides in Salem district, Tamilnadu, India. J Envro Geol 16:25
Subba Rao N (2002) Geochemistry of groundwater in parts of Guntur Dist., A.P., India. Environ Geol 41:552–562
Susheela AK (1999a) Dark side of fluoride. The Daily Star. February 20; Features, 16 (col. 5)
Susheela AK (1999b) Fluorosis management programme in India. Curr Sci 77(10):1250–1256
Tirumalesh K, Shivanna K, Jalihal AA (2007) Isotope hydrochemical approach to understand fluoride release into groundwaters of Ilkal area, Bagalkot District, Karnataka, India. Hydrogeol J 15:589–598. doi:10.1007/s10040-006-0107-3
Valenzuela-Vasquez L, Ramırez-Hernandez J, Reyes-Lopez J, Sol-Uribe A, Lazaro-Mancilla O (2006) The origin of fluoride in groundwater supply to Hermosillo City, Sonora, Mexico. Environ Geol 51:17–27
WHO (2004) Guidelines for drinking water quality, 3rd edn. World Health Organization, Geneva
Wodeyar BK, Sreenivasan G (1996) Occurrence of Fluoride in the groundwater and its impact in peddavankahalla basin, Bellary District, Karnataka, A preliminary study. Current Science 70 No.1
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the anonymous reviewer for his help to improve the manuscript in the present form. Thanks also to Department of Science and Technology, New Delhi, India for providing this work as a Young Scientist Project to the corresponding author.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Srinivasamoorthy, K., Vijayaraghavan, K., Vasanthavigar, M. et al. Assessment of groundwater quality with special emphasis on fluoride contamination in crystalline bed rock aquifers of Mettur region, Tamilnadu, India. Arab J Geosci 5, 83–94 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-010-0162-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-010-0162-x