Abstract
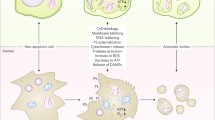
Programmed cell death (PCD) in plant cells is often accompanied by biochemical and morphological hallmarks similar to those of animal apoptosis. However, orthologs of several core components of such apoptosis have not been reported in plants. Here, we describe an ortholog of Fas-associated factor1 (FAF1), a member of the Fas-death-inducing signaling complex (Fas-DISC), found in pepper. We also examined FAF1 orthologs in other plant species. Transcripts of CaFAF1 specifically accumulated in pepper leaves infected with the avirulent pepper mild mottle virus (PMMoV) P0 pathotype. This gene was also strongly expressed in aging leaves. To determine whether those orthologs are involved in PCD, we suppressed their expression through virus-induced gene silencing, and determined the effect on the hypersensitive response (HR), a typical PCD, in pepper, tomato, and tobacco. Constitutive expression of CaFAF1 in transgenic tobacco triggered spontaneous induction of cell death lesions and induced pathogenesis-related (PR) genes. This ability to cause cell death and suppress R gene-mediated HR in its knockdown condition suggests that some features of animal and plant cell death processes may be shared. We propose that plant FAF1 is a conserved cell death regulator in both kingdoms.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abramovitch RB, Martin GB (2004) Strategies used by bacterial pathogens to suppress plant defenses. Curr Opin Plant Biol 7:356–364
Boukema IW (1980) Allelism of genes controlling resistance to TMV in Capsicum L. Euphytica 29:433–439
Boukema IW (1982) Resistance to TMV in Capsicum chacoense Hunz. is governed by an allele of the L-locus. Capsicum Newslett 3:47–48
Buchberger A, Howard MJ, Proctor M, Bycroft M (2001) The UBX domain: a widespread ubiquitin-like module. J Mol Biol 16:17–24
Chomczynsk i P, Sacchi N (1987) Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem 162:156–159
Chu K, Niu X, Williams LT (1995) A Fas-associated protein factor, FAF1, potentiates Fas-mediated apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 92:11894–11898
Chung E, Seong E, Kim YC, Chung EJ, Oh SK, Lee S, Park JM, Joung YH, Choi D (2004) A method of high frequency virus-induced gene silencing in chili pepper (Capsicum annuum L. cv. Bukang). Mol Cells 17:377–380
Dardick CD, Taraporewala Z, Lu B, Culver JN (1999) Comparison of tobamovirus coat protein structural features that affect elicitor activity in pepper, eggplant, and tobacco. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 12:247–251
del Pozo O, Pedley KF, Martin GB (2004) MAPKKKα is a positive regulator of cell death associated with both plant immunity and disease. EMBO J 23:3072–3082
Deveraux QL, Reed JC (1999) IAP family proteins-suppressors of apoptosis. Genes Dev 13:239–252
Ekengren SK, Liu T, Schiff M, Dinesh-Kumar SP, Martin GB (2003) Two MAPK cascades, NPR1, and TGA transcription factors play a role in Pto-mediated disease resistance in tomato. Plant J 36:905–917
Goodman RN, Novacky AJ (1994) The Hypersensitive Reaction in Plants to Pathogens: A Resistance Phenomenon. The American Phytopathological Society, St. Paul
Greenberg JT, Yao N (2004) The role and regulation of programmed cell death in plant-pathogen interactions. Cell Microbiol 6:201–211
Ham BK, Park JM, Lee SB, Kim MJ, Lee IJ, Kim KJ, Kwon CS, Paek KH (2006) Tobacco Tsip1, a DnaJ-type Zn finger protein, is recruited to and potentiates Tsi-mediated transcriptional activation. Plant Cell 18:2005–2020
Hengartner MO (2000) The biochemistry of apoptosis. Nature 407:770–776
Itoh N, Yonehara S, Ishii A, Yonehara M, Mizushima S, Sameshima M, Hase A, Seto Y, Nagata S (1991) The polypeptide encoded by the cDNA for human cell surface antigen Fas can mediate apoptosis. Cell 66:233–243
Jin JB, Kim YA, Kim SJ, Lee SH, Kim DH, Cheong GW, Hwang IH (2001) A new dynamin-like protein, ADL6, is involved from the trans-Golgi network to the central vacuole in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 13:1511–1525
Kim HJ, Song EJ, Lee YS, Kim E, Lee KJ (2005a) Human Fas-associated factor 1 interacts with heat shock protein 70 and negatively regulates chaperone activity. J Biol Chem 280:8125–8133
Kim MJ, Ham BK, Kim HR, Lee IJ, Kim YJ, Ryu KH, Park YI, Paek KH (2005b) In vitro and in planta interaction evidence between Nicotiana tabacum thaumatin-like protein 1 (TLP1) and Cucumber mosaic virus proteins. Plant Mol Biol 59:981–994
Lam E (2004) Controlled cell death, plant survival and development. Nature Rev Cell Biol 5:305–315
Lee GJ, Shin R, Park CJ, Yoo TH, Paek KH (2001) Induction of a pepper cDNA encoding SAR8.2 protein during the resistance response to Tobacco mosaic virus. Mol Cells 12:250–256
Lincoln JE, Richael C, Overduin B, Smith K, Bostock R, Gilchrist DG (2002) Expression of the antiapoptotic baculovirus p35 gene in tomato blocks programmed cell death and provides broad spectrum resistance to disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99:15217–15221
Liu Y, Schiff M, Dinesh-Kumar SP (2002) Virus-induced gene silencing in tomato. Plant J 31:777–786
Lorrain S, Vailleau F, Balagué C, Roby D (2003) Lesion mimic mutants: keys for deciphering cell death and defense pathways in plants? Trends Plant Sci 8:263–271
Lu R, Martin-Hernandez AM, Peart JM, Malcuit I, Baulcombe DC (2003) Virus-induced gene silencing in plants. Methods 30:296–303
Nicholson DW, Thornberry NA (2003) Apoptosis. Life and death decisions. Science 299:214–215
Opferman JT (2008) Apoptosis in the development of the immune system. Cell Death Diff 15:234–242
Park JM, Park CJ, Lee SB, Ham BK, Shin R, Paek KH (2001) Overexpression of the tobacco Tsi1 gene encoding an EREBP/AP2–type transcription factor enhances resistance against pathogen attack and osmotic stress in tobacco. Plant Cell 13:1035–1046
Park MY, Jang HD, Lee SY, Lee KJ, Kim E (2004) Fas-associated factor-1 inhibits nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) activity by interfering with nuclear translocation of the RelA (p65) subunit of NF-κB. J Biol Chem 279:2544–2549
Rast AThB (1979) Pepper strains of TMV in the Netherlands. Meded Fac Landbouwkd Rijksuniv Gent 44:617–622
Ryu SW, Chae SK, Lee KJ, Kim E (1999) Identification and characterization of human Fas associated factor1, hFAF1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 262:388–394
Ryu SW, Lee SJ, Park MY, Jun JI, Jung YK, Kim E (2003) Fas-associated Factor 1, FAF1, is a member of Fas death-inducing signaling complex. J Biol Chem 278:24003–24010
Ryu CM, Anand A, Kang L, Mysore KS (2004) Agrodrench: a novel and effective agroinoculation method for virus-induced gene silencing in root and diverse Solanaceous species. Plant J 40:322–331
Sambrook J, Russell DW (2001) Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor
Shin R, Lee GJ, Park CJ, Kim TY, You JS, Nam YW, Paek KH (2001) Isolation of pepper mRNAs differentially expressed during the hypersensitive response to tobacco mosaic virus and characterization of a proteinase inhibitor gene. Plant Sci 161:727–737
Shin R, An JM, Park CJ, Kim YJ, Joo S, Kim WT, Paek KH (2004) Capsicum annuum tobacco mosaic virus-induced clone 1 expression perturbation alters the plant’s response to ethylene and interferes with the redox homeostasis. Plant Physiol 135:561–573
Winans SC, Kerstetter RA, Nester EW (1988) Transcriptional regulation of the virA and virG genes of Agrobacterium tumefaciens. J Bacteriol 170:4047–4054
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. SP Dinesh-Kumar (Yale University) for the pTRV1 and pTRV2 vectors for gene silencing. This study was supported by a grant (R11-200-008-02006) from the Plant Signaling Network Research Center funded by the Korea Ministry of Education, Science and Technology; and a BioGreen 21 grant (R0803471) funded by the Ministry of Food, Agriculture, Forestry, and Fisheries. YJ Kim was supported by Brain Korea 21 Research Fellowships from the Korea Ministry of Education, Science and Technology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, Y.J., Park, CJ., Ham, BK. et al. Involvement of the Fas-associated Factor1 Ortholog, CaFAF1, in Regulating Programmed Cell Death in Plants. J. Plant Biol. 52, 125–134 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12374-009-9012-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12374-009-9012-3