Abstract
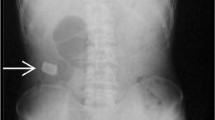
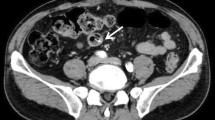
A 45-year-old woman visited our hospital complaining of abdominal pain 1 week after undergoing an annual medical checkup. Her vital signs and blood test results were normal, but tenderness was found in the lower abdomen. A high-density round structure found at the midline of the lower abdomen on an abdominal radiograph was thought to be an accumulation of barium (a barolith) from upper gastrointestinal barium radiography. Two liters of an oral gastrointestinal cleaning agent was administered, but defecation did not occur. Lower gastrointestinal endoscopy revealed that the barolith was impacted at the sigmoid colon. We unsuccessfully attempted to move it using a pressurized water jet and forceps, but it was too large to be captured by the net. Therefore, we broke it down using a snare. After a successful endoscopic procedure, 120 mL of a glycerin enema solution was injected through the forceps opening, causing the barolith to be excreted. There is only one similar case of successful endoscopic treatment of a barolith in the literature.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ott DJ, Gelfand DW. Gastrointestinal contrast agents. Indications, uses, and risks. JAMA. 1983;249:2380–4.
Kunisaki C, Ishino J, Nakajima S, et al. Outcomes of mass screening for gastric carcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol. 2006;13:221–8.
Levine MS, Rubesin SE, Laufer I. Barium esophagography: a study for all seasons. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008;6:11–25.
Katzka DA. The role of barium esophagography in an endoscopy world. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am. 2014;24:563–80.
Levine MS, Carucci LR, DiSantis DJ, et al. Consensus statement of society of abdominal radiology disease-focused panel on barium esophagography in gastroesophageal reflux disease. Am J Roentgenol. 2016;207:1009–15.
Cove JK, Snyder RN. Fatal barium intravasation during barium enema. Radiology. 1974;112:9–10.
Gelfand DW. Complications of gastrointestinal radiologic procedures: I. Complications of routine fluoroscopic studies. Gastrointest Radiol. 1980;5:293–315.
Vallarades CDP. Bariolitos. Rev Bras Gastroenterol. 1950;2:595–608.
Cheney CP, Murphy JR, Wong RK. Colonoscopic dissolution of a barolith. J Clin Gastroenterol. 1994;19:265–6.
Kurer MA, Davey C, Chintapatla S. Intestinal obstruction from inspissated barium (Barolith): a systematic review of all cases from 1950 to 2006. Colorectal Dis. 2008;10:431–9.
Shaughnessy GF, Cho P, Francis DL. A rare complication of a barium-contrast study. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015;13:e67–8.
Ince V, Işık B, Koç C, Başkıran A, Onur A. Barolith as a rare cause of acute appendicitis: a case report. Ulus Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg. 2013;19:86–8.
Kurer MA, Miller GV, Petty DR, Chintapatla S. An update of the systematic review of Barolith intestinal obstruction. Colorectal Dis. 2008;10:523–4.
McDonnell WM, Jung F. Images in clinical medicine. Barium impaction in the sigmoid colon. N Engl J Med. 1997;337:1278.
Kurer MA, Chintapatla S. Images in clinical medicine. Intestinal obstruction due to inspissated barium. N Engl J Med. 2007;356:1656.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest:
Iida T, Hirano T, Onodera K, Kubo T, Yamashita K, Yamano H, and Nakase H declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Human Rights:
All procedures followed have been performed in accordance with the ethical standards laid down in the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments.
Informed Consent:
Informed consent was obtained from the patient for being included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Iida, T., Hirano, T., Onodera, K. et al. Endoscopic removal of an impacted barolith at the sigmoid colon: a rare case report. Clin J Gastroenterol 10, 361–363 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12328-017-0752-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12328-017-0752-1