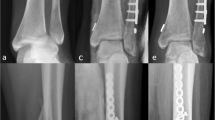
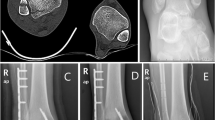
Abstract
Purpose
Ten percentage of all ankle fractures sustain an associated syndesmotic injury. TightRope is a relatively new technique for syndesmosis fixation, characterized by a non-absorbable FibreWire held tight between two cortical metal buttons. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the results obtained with the use of this device.
Methods
From January 2011 to December 2015, 54 patients with ankle diastases were treated. Eighteen patients were excluded from the study. Fractures of the fibula or tibia requiring fixation were internally fixed using standard AO techniques. Preoperative and the most recent postoperative ankle radiographs were reassessed for measurements of the tibiofibular clear space (TFCS), medial clear space (MCS) and tibiofibular overlap (TFO). Clinical outcomes were assessed at the time of follow-up using the American Orthopaedic Foot and Ankle Society (AOFAS) score, a self-administered Foot and Ankle Disability Index (FADI) score and patients satisfaction.
Results
The mean follow-up was 28, 64 months. Mean values for MCS, TFCS and TFO were 1.51–1.53 and 0.25 cm, respectively. The mean AOFAS score was 93.11, and the mean FADI score was 130.11. Twenty-nine (80.6 %) patients reported their outcome as excellent or very good.
Conclusions
TightRope technique can achieve flexible fixation of the syndesmosis and permit full range of motion of the tibiofibular joint. Patients can start rehabilitation exercise at an early stage after operation. The results of this study indicate that TightRope fixation is a valid option for syndesmotic injuries.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fong DTP, Hong Y, Chan LK, Yung PSH, Chan KM (2007) A systematic review on ankle injury and ankle sprain in sports. Sports Med 37(1):73–94
Magnan B, Samaila E, Bondi M, Vecchini E, Micheloni GM, Bartolozzi P (2012) Three-dimensional matrix-induced autologous chondrocytes implantation for osteochondral lesions of the talus: midterm results. Adv Orthop 2012:942174. doi:10.1155/2012/942174
Nelson AJ, Collins CL, Yard EE, Fields SK, Comstock RD (2007) Ankle injuries among United States high school sports athletes, 2005–2006. J Athl Train 42(3):381–387
Rammelt S, Zwipp H, Grass R (2008) Injuries to the distal tibiofibular syndesmosis: an evidence-based approach to acute and chronic lesions. FCL 13:611–633 (vii–viii)
Stuart K, Panchbhavi V (2011) The fate of syndesmotic screws. Foot Ankle Int 32:S519–S525
Wagener M, Beumer A, Swierstra B (2011) Chronic instability of the anterior tibiofibular syndesmosis of the ankle: arthroscopic findings and results of anatomical reconstruction. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 12:212–225
Dattani R, Patnaik S, Kantak A, Srikanth B, Selvan TP (2008) Injuries to the tibiofibular syndesmosis. J Bone Joint Surg Br 90:405–410
Sman AD, Hiller CE, Refshauge KM (2012) Diagnostic accuracy of clinical tests for diagnosis of ankle syndesmosis injury: a systematic review. Br J Sports Med Jul 47(10):620–628
Han SH, Lee JW, Kim S, Suh J-S, Choi YR (2007) Chronic tibiofibular syndesmosis injury: the diagnostic efficiency of magnetic resonance imaging and comparative analysis of operative treatment. Foot Ankle Int 28:336–342
Magan A, Golano P, Maffulli N, Khanduja V (2014) Evaluation and management of injuries of the tibiofibular syndesmosis. Br Med Bull 111(1):101–115. doi:10.1093/bmb/ldu020
Black EM, Antoci V, Lee JT, Weaver MJ, Johnson AH, Susarla SM, Kwon JY (2013) Role of preoperative computed tomography scans in operative planning for malleolar ankle fractures. Foot Ankle Int 34(5):697–704. doi:10.1177/1071100713475355
Porter DA (2009) Evaluation and treatment of ankle syndesmosis injuries. Instr Course Lect 58:575–581
Mukhopadhyay S, Metcalfe A, Guha A, Mohanty K, Hemmadi S, Lyons K, O’Doherty D (2011) Malreduction of syndesmosisdare we considering the anatomical variation? Inj Int J Care Inj 42:1073–1076
Ahmad J, Raikin SM, Pour AE, Haytmanek C (2009) Bioabsorbable screw fixation of the syndesmosis in unstable ankle injuries. Foot Ankle Int 30:99–105
Beumer A, Campo MM, Niesing R, Day J, Kleinrensink GJ, Swierstra BA (2005) Screw fixation of the syndesmosis: a cadaver model comparing stainless steel and titanium screws and three and four cortical fixation. Injury 36:60–64
Cox S, Mukherjee DP, Ogden AL, Mayuex RH, Sadasivan KK, Albright JA, Pietrzak WS (2005) Distal tibiofibular syndesmosis fixation: a cadaveric, simulated fracture stabilization study comparing bioabsorbable and metallic single screw fixation. J Foot Ankle Surg 44:144–151
Naqvi GA, Cunningham P, Lynch B, Galvin R, Awan N (2012) Fixation of ankle syndesmotic injuries: comparison of tightrope fixation and syndesmotic screw fixation for accuracy of syndesmotic reduction. Am J Sports Med 40:2828–2835
Rigby RB, Cottom JM (2013) Does the arthrex TightRope provide maintenance of the distal tibiofibular syndesmosis? a 2-year follow-up of 64 TightRopes in 37 patients. J Foot Ankle Surg 52:563–567
Storey P, Gadd RJ, Blundell C, Davies MB (2012) Complications of suture button ankle syndesmosis stabilization with modifications of surgical technique. Foot Ankle Int 33:717–721
Bell DP, Wong MK (2006) Syndesmotic screw fixation in Weber C ankle injuries—should the screw be removed before weight bearing? Injury 37(9):891–898
Manjoo A, Sanders D, Tieszer C (2010) Functional and radiographic results of patients with syndesmotic screw fixation: implications for screw removal. J Orthop Trauma 24:2–6
Melvin J, Downing K, Ogilvie K (2008) A technique for removal of broken cannulated tricortical syndesmotic screws. J Orthop Trauma 22:648–651
Schepers T (2012) Acute distal tibiofibular syndesmosis injury: a systematic review of suture-button versus syndesmotic screw repair. Int Orthop (SICOT) 36:1199–1206
Casillas M (2006) Operative treatment of acute syndesmotic injuries with screw fixation and without direct exposure or repair of the syndesmotic ligaments. Tech Foot Ankle Surg 5:27–33
Fanter N, Inouye S, McBryde A (2010) Safety of ankle trans-syndesmotic fixation. Foot Ankle Int 31:433–440
Hoiness P, Stromsoe K (2004) Tricortical versus quadricortical syndesmosis fixation in ankle fractures: a prospective, randomized study comparing two methods of syndesmosis fixation. J Orthop Trauma 18:331–337
Schepers T (2011) To retain or remove the syndesmotic screw: a review of literature. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 131:879–883
Scranton P (2002) Isolated syndesmotic injuries: diastasis of the ankle in the athlete. Tech Foot Ankle Surg 1:88–93
Teramoto A, Suzuki D, Kamiya T, Chikenji T, Watanabe K, Yamashita T (2011) Comparison of different fixation methods of the suture-button implant for tibiofibular syndesmosis injuries. Am J Sports Med 39:2226–2232
Thordarson D, Samuelson M, Shepherd L, Merkle P, Lee J (2001) Bioabsorbable versus stainless steel screw fixation of the syndesmosis in pronation-lateral rotation ankle fractures: a prospective randomized trial. Foot Ankle Int 22:335–338
Thornes B, McCartan D (2006) Ankle syndesmosis injuries treated with the TightRope suture-button kit. Tech Foot Ankle Surg 5:45–53
Weening B, Bhandari M (2005) Predictors of functional outcome following transsyndesmotic screw fixation of ankle fractures. J Orthop Trauma 19:102–108
De Vil J, Bonte F, Claes H, Bongaerts W, Verstraete K, Verdonk R (2009) Bolt fixation for syndesmotic injuries. Injury 40:1176–1179
DeGroot H, Al-Omari A, Ghazaly S (2011) Outcomes of suture button repair of the distal tibiofibular syndesmosis. Foot Ankle Int 32:250–256
Naqvi GA, Shafqat A, Awan N (2012) Tightrope fixation of ankle syndesmosis injuries: clinical outcome, complications and technique modification. Injury 43:838–842
Thornes B, Shannon F, Guiney AM, Hession P, Masterson E (2005) Suture-button syndesmosis fixation: accelerated rehabilitation and improved outcomes. Clin Orthop Relat Res 431:207–212
Willmott HJ, Singh B, David LA (2009) Outcome and complications of treatment of ankle diastasis with tightrope fixation. Injury 40:1204–1206
Cottom JM, Hyer CF, Philbin TM, Berlet GC (2008) Treatment of syndesmotic disruptions with the Arthrex Tightrope: a report of 25 cases. Foot Ankle Int 29(8):773–780
Bayer T, McKenna J (2015) Technical tips for the removal of TightRope ankle syndesmosis fixation. Foot Ankle Surg 21(3):214–215
Jordan T, Talarico R, Schuberth J (2011) The radiographic fate of the syndesmosis after trans-syndesmotic screw removal in displaced ankle fractures. J Foot Ankle Surg 50:407–412
Lin CF, Gross ML, Weinhold P (2006) Ankle syndesmosis injuries: anatomy, biomechanics, mechanism of injury, and clinical guidelines for diagnosis and intervention. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther 36:372–384
Arthrex. Surgical Technique. (Online): www.ankletightrope.com
Martin RL, Burdett RG, Irrgang JJ (1999) Development of the foot and ankle disability index (FADI). J Orthop Sports Phys Ther 29:A32–A33
Sheri AH, Hertel J (2005) Reliability and sensitivity of the foot and ankle disability index in subjects with chronic ankle instability. J Athl Train 40(1):35–40
Coughlin MJ (1991) Treatment of bunionette deformity with longitudinal diaphyseal osteotomy with distal soft tissue repair. Foot Ankle 11(4):195–203
Wiker_y A, Hoiness P, Andreassen G, Hellund J, Madsen J (2010) No difference in functional and radiographic results 8.4 years after quadricortical compared with tricortical syndesmosis fixation in ankle fractures. J Orthop Trauma 24:17–23
Forsythe K, Freedman K, Stover M, Patwardhan A (2008) Comparison of a novel FiberWire-button construct versus metallic screw fixation in a syndesmotic injury model. Foot Ankle Int 29:49–54
Klitzman R, Zhao H, Zhang L, Strohmeyer G, Vora A (2010) Suture-button versus screw fixation of the syndesmosis: a biomechanical analysis. Foot Ankle Int 31:69–75
Miller A, Paul O, Boraiah S, Parker R, Helfet D, Lorich D (2010) Functional outcomes after syndesmotic screw fixation and removal. J Orthop Trauma 24:12–16
Teramoto A, Kura H, Uchiyama E, Suzuki D, Yamashita T (2008) Three-dimensional analysis of ankle instability after tibiofibular syndesmosis injuries: a biomechanical experimental study. Am J Sports Med 36:348–352
Coetzee C, Ebeling P (2009) Treatment of syndesmosis disruptions: a prospective, randomized study comparing conventional screw fixation vs TightRope_ fiber wire fixation-medium term results. SA Ortho J 33:32–37
Miller RS, Weinhold PS, Dahners LE (1999) Comparison of tricortical screw fixation versus a modified suture construct for fixation of ankle syndesmosis injury: a biomechanical study. J Orthop Trauma 13:39–42
Schepers T, Van Lieshout E, de Vries M, Van der Elst M (2011) Complications of syndesmotic screw removal. Foot Ankle Int 32:1040–1044
Hsu YT, Wu CC, Lee WC, Fan KF, Tseng IC, Lee PC (2011) Surgical treatment of syndesmotic diastasis: emphasis on effect of syndesmotic screw on ankle function. Int Orthop 35:359–364
Welck MJ, Ray P (2013) Tibialis anterior tendon entrapment after ankle tightrope insertion for acute syndesmosis injury. Foot Ankle Spec 6(3):242–246. doi:10.1177/1938640013477131
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors certify that they have no affiliations with or involvement in any organization or entity with any financial interest or non-financial interest (such as personal or professional relationships, affiliations, knowledge or beliefs) in the subject matter or materials discussed in this manuscript.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bondi, M., Rossi, N., Pizzoli, A. et al. The use of TightRope fixation for ankle syndesmosis injuries: our experience. Musculoskelet Surg 100, 217–222 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12306-016-0421-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12306-016-0421-4