Abstract
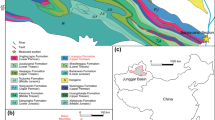
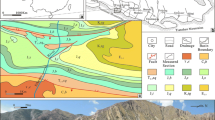
This paper focuses on the initial basin-fill processes in an extensional nonmarine back-arc basin. Sedimentary facies analysis in the southwestern part of the Gyeongsang Basin (Jinju Subbasin), Hapcheon area reveals that the succession consists of four facies assemblages. The assemblage I mainly consists of disorganized conglomerate deposited by flash floods in a streamflow-dominated alluvial fan. The assemblage II is dominated by stratified conglomerates and massive, stratified, and cross-stratified sandstones, showing architecture of stacked channels and bars. The assemblage III largely comprises massive, stratified to laminated, and trough cross-stratified sandstones, which are organized into channel-fill and bar-accretion structures. It most likely formed in sandy sinuous rivers. The assemblage IV comprises gray mudstone interlayered with fine sandstone, representing water-logged floodplains. Conglomerate and sandstone bodies formed in the fluvial systems appear to be randomly distributed within floodplain fines, displaying a great lateral and vertical lithologic variation. This study helps understand the complexity of basin-fill history, i.e., switching of fluvial networks in time and space, in contrast to the simple notion of margin-parallel stacking of lithostratigraphic units.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen, J.P., Fielding, C.R., Rygel, M.C., and Gibling, M.R., 2013, Deconvolving signals of tectonic and climatic controls from continental basins: an example from the late Paleozoic Cumberland Basin, Atlantic Canada. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 83, 847–872.
Arnott, R.W.C. and Hand, B.M., 1989, Bedforms, primary structures and grain fabric in the presence of suspended sediment rain. Journal of Sedimentary Petrology, 59, 1062–1069.
Boothroyd, J.C. and Ashley, G.M, 1975, Process, bar morphology and sedimentary structures on braided outwash fans, North-eastern Gulf of Alaska. In: Jopling, A.V. and McDonald, B.C. (eds.), Glaciofluvial and Glaciolacustrine Sedimentation. Society of Economic Paleontologists and Mineralogists, Special Publication, 23, p. 193–222.
Bridge, J.S., 1993, The interaction between channel geometry, water flow, sediment transport and deposition in braided rivers. In: Best, J.L. and Bristow, C.S. (eds.), Braided Rivers. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 75, p. 13–71.
Brierley, G.J., 1996, Channel morphology and element assemblages: a constructivist approach to facies modeling. In: Carling, P.A. and Dawson, M.R. (eds.), Advances in Fluvial Dynamics and Stratigraphy. John Wiley & Sons, Chichester, p. 263–298.
Bristow, C.S., 1993, Sedimentary structures exposed in bar tops in the Brahmaputra River, Bangladesh. In: Best, J.L. and Bristow, C.S. (eds.), Braided Rivers. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 75, p. 277–289.
Cant, D.J. and Walker, R.G., 1978, Fluvial processes and facies sequences in the sandy braided South Saskatchewan River, Canada. Sedimentology, 25, 625–648.
Chang, K.H., 1975, Cretaceous stratigraphy of southeast Korea. Journal of the Geological Society of Korea, 11, 1–23.
Chang, K.H., 1977, Late Mesozoic stratigraphy, sedimentation and tectonics of southeastern Korea. Journal of Geological Society of Korea, 13, 76–90. (in Korean with English abstract)
Choi, H.I., 1986, Sedimentation and evolution of the Cretaceous Gyeongsang Basin, southeastern Korea. Journal of the Geological Society, 143, 29–40.
Choi, S.-J., 1990, Some nonmarine fossils from the central part of Gyeongsang Basin, South Korea. Journal of the Paleontological Society of Korea, 6, 165–179.
Chough, S.K. and Sohn, Y.K., 2010, Tectonic and sedimentary evolution of a Cretaceous continental arc-backarc system in the Korean peninsula: new view. Earth Science Reviews, 101, 225–249.
Collinson, J.D., 1969, The sedimentology of the Grindslow Shales and the Kinderscout Grit: a deltaic complex in the Namurian of northern England. Journal of Sedimentary Petrology, 39, 194–221.
Heller, P.L. and Paola, C., 1996, Downstream changes in alluvial architecture: an exploration of controls on channel-stacking patterns. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 66, 297–306.
Hein, F.J. and Walker, R.G., 1977, Bar evolution and development of stratification in the gravelly, braided Kicking Horse River, British Columbia. Canadian Journal Earth Sciences, 14, 562–570.
Hickson, T.A., Sheets, B.A., Paola, C., and Kelberer, M., 2005, Experimental test of tectonic controls on three-dimensional alluvial facies architecture. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 75, 710–722.
Jo, H.R., 2003, Depositional environments, architecture, and controls of Early Cretaceous nonmarine successions in the northwestern part of Kyongsang Basin, Korea. Sedimentary Geology, 161, 269–294.
Jo, H.R. and Chough, S.K., 2001, Architectural analysis of fluvial sequences in the northwestern part of Kyongsang Basin (Early Cretaceous), SE Korea. Sedimentary Geology, 144, 307–334.
Jo, H.R., Rhee, C.W., and Chough, S.K., 1997, Distinctive characteristics of a streamflow-dominated alluvial fan deposit: Sanghori area, Kyongsang Basin (Early Cretaceous), southeastern Korea. Sedimentary Geology, 110, 51–59.
Kim, D.H., Hwang, J.H., Park, K.H., and Song, K.Y., 1998, Geological map of Pusan sheet (1:250,000). Korea Institute of Geoscience and Mineral Resources, Daejeon.
Kim, J.Y., Kim, K.S., Lockley, M.G., Yang, S.Y., Seo, S.J., Choi, H.I., and Lim, J.D., 2008, New didactyl dinosaur footprints (Dromaeosauripus hamanensis ichnogen. et ichnosp. nov.) from the Early Cretaceous Haman Formation, south coast of Korea. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology 262, 72–78.
Kim, H.J., Paik, I.S., Kim, S., and Lee, H., 2018, Sedimentary facies, paleoenvironments, and stratigraphy of the Haman Formation (Early Cretaceous) in Sopo-ri, Haman-gun, Gyeongsangnam-do, Korea. Journal of the Geological Society of Korea, 54, 1–19.
Mack, G.H. and James, W.C, 1992, Paleosols for Sedimentologists. The Geological Society of America, Short Course Manual, 127 p.
Martensen, O.J., Ryseth, A., Helland-Hansen, W., Flesche, H., Torkildsen, G., and Idil, S., 1999, Stratigraphic base level and fluvial architecture: Ericson Sandstone (Campanian), Rock Springs Uplift, SW Wyoming, USA. Sedimentology, 46, 235–259.
McLaurin, B.T. and Steel, R.J, 2007, Architecture and origin of an amalgamated fluvial sheet sand, lower Castlegate Formation, Book Cliffs, Utah. Sedimentary Geology, 197, 291–311.
Miall, A.D., 1985, Architectural-element analysis: a new method of facies analysis applied to fluvial deposits. Earth Science Reviews, 22, 261–308.
Miall, A.D., 1994, Reconstructing fluvial macroform architecture from two-dimensional outcrops: examples from the Castlegate Sandstone, Book Cliffs, Utah. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 64, 146–158.
Miall, A.D., 1996, The Geology of Fluvial Deposits. Springer, Berlin, 582 p.
Nemec, W. and Postma, G., 1993, Quaternary alluvial fans in southwestern Crete: sedimentation processes and geomorphic evolution. In: Marzo, M. and Puigdefabregas, C. (eds.), Alluvial Sedimentation. International Association of Sedimentologists, Special Publication, 17, p. 235–276.
Neuendorf, K.K.E., Mehl, J.P.Jr, and Jackson, J.A., 2005, Glossary of Geology. American Geological Institute, Alexandria, 779 p.
Paik, I.S. and Kim, H.J., 2003, Palustrine calcretes of the Cretaceous Gyeongsang Supergroup, Korea: variation and palaeoenvironmental implications. Island Arc, 12, 110–124.
Paik, I.S. and Lee, Y.I., 1998, Desiccation cracks in vertic palaeosols of the Cretaceous Hasandong Formation, Korea: genesis and palaeoenvironmental implications. Sedimentary Geology 119, 161–179.
Paik, I.S., Kim, H.J., and Lee, Y.I., 2001, Dinosaur track-bearing deposits in the Cretaceous Jindong Formation, Korea: occurrence, palaeoenvironments and preservation. Cretaceous Research 22, 79–92.
Paik, I.S., Huh, M., So, Y.H., Lee, J.E., and Kim, H.J., 2007, Traces of evaporites in Upper Cretaceous lacustrine deposits of Korea: origin and paleoenvironmental implications. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 30, 93–107.
Retallack, G.J., 1997, A Color Guide to Paleosols. John Wiley & Sons, Chichester, 175 p.
Rhee, C.W., Jo, H.R., and Chough, S.K., 1998, An allostratigraphic approach to a non-marine basin: the northwestern part of Cretaceous Kyongsang basin, SE Korea. Sedimentology, 45, 449–472.
Todd, S.P., 1989, Stream-driven, high-density gravelly traction carpets: possible deposits in the Trabeg Conglomerate Formation, SW Ireland and some theoretical considerations of their origin. Sedimentology, 36, 513–530.
Todd, S.P., 1996, Process deduction from fluvial sedimentary structures. In: Carling, P.A. and Dawson, M.R. (eds.), Advances in Fluvial Dynamics and Stratigraphy. John Wiley & Sons, Chichester, p. 299–350.
Todd, S.P. and Went, D.J., 1991, Lateral migration of sand-bed rivers: examples from the Devonian Glashabeg Formation, SW Ireland and the Cambrian Alderney Sandstone Formation, Channel Islands. Sedimentology, 38, 997–1020.
Wright, V.P. and Tucker, M.E., 1991, Calcretes: an introduction. In: Wright, V.P. and Tucker, M.E. (eds.), Calcretes. International Association of Sedimentologists, Reprint Series, 2, Blackwell Scientific Publications, Oxford, p. 1–24.
Yang, S.Y., 1976, On fossils from the Gyeongsang Group: especially on some of the molluscan fauna. Journal of Geological Society of Korea, 12, 23–30. (in Korean with English abstract)
Yang, S.Y., 1982, Geology around the type-locality of Trigonioides (s.s.) kodairai and age of the Nagdong Subgroup. Journal of Geological Society of Korea, 18, 67–72. (in Korean with English abstract)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, JH., Chough, S.K. & Jo, H.R. Development of a streamflow-dominated alluvial-fan system in the southwestern margin of Gyeongsang Basin (Lower Cretaceous): implications for initial basin-fill history. Geosci J 23, 189–200 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12303-018-0073-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12303-018-0073-5