Abstract
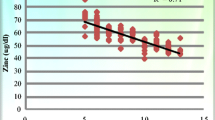
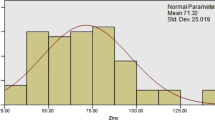
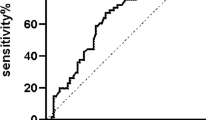
Decompensation followed by death is the most serious outcome in patients suffering from cirrhosis of the liver. Alteration of trace elements may play a vital role in the process of decompensation. To examine the change in status of trace elements during the decompensation process, we analysed the zinc, copper, iron, magnesium, bilirubin and albumin levels in the serum of compensated (n = 34) and decompensated (n = 31) liver cirrhosis patients and compared them with healthy control group (n = 36) by post hoc ANOVA. We observed significant alteration in the selected micronutrients in the diseased group relative to healthy controls (P < 0.05). Moreover, mean serum zinc and iron levels were significantly lower with a higher level of serum copper in decompensated cirrhosis group than in compensated group (P < 0.05). However, no significant decrease of serum magnesium was found between the two diseased groups. Our findings imply that the trace elements like zinc, copper and iron might exert important contributory roles in decompensation process in liver cirrhosis and hence, may be utilized as important biomarkers for these patients. Furthermore, we propose that replacements of those micronutrients at an early stage can delay or prevent the severe outcomes like hepatic encephalopathy, gastrointestinal bleeding, severe jaundice or ascites in these patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sullivan JF, Blotcky AJ, Jetton MM, Hahn HK, Burch RE. Serum levels of selenium, calcium, copper magnesium, manganese and zinc in various human diseases. J Nutr. 1979;109(8):1432–7.
Rahelic D, Kujundzic M, Romic Z, Brkic K, Petrovecki M. Serum concentration of zinc, copper, manganese and magnesium in patients with liver cirrhosis. Coll Antropol. 2006;30(3):523–8.
Pasqualetti P, Casale R, Colantonio D, Di Lauro G, Festuccia V, Natali L, et al. Serum levels of magnesium in hepatic cirrhosis. Quad Sclavo Diagn. 1987;23(1):12–7.
Buyukasik NS, Nadir I, Akin FE, Cakal B, Kav T, Ersoy O, et al. Serum iron parameters in cirrhosis and chronic hepatitis: detailed description. Turk J Gastroenterol. 2011;22(6):606–11.
Machado MV, Ravasco P, Martins A, Almeida MR, Camilo ME, Cortez-Pinto H. Iron homeostasis and H63D mutations in alcoholics with and without liver disease. World J Gastroenterol. 2009;15(1):106–11.
Basaki M, Saeb M, Nazifi S, Shamsaei HA. Zinc, copper, iron, and chromium concentrations in young patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2012;148(2):161–4.
Mukerji AN, Patel V, Jain A. Improving survival in decompensated cirrhosis. Int J Hepatol. 2012;2012:318627.
Lindeman RD, Baxter DJ, Yunice AA, Kraikitpanitch S. Serum concentrations and urinary excretions of zinc in cirrhosis, nephrotic syndrome and renal insufficiency. Am J Med Sci. 1978;275(1):17–31.
Iron JF. In: Cook JD, editor. Methods in hematology. New York: Churchill Livingstone; 1980. p. 15–43.
Khayam-Bashi H, Liu TZ, Walter V. Measurement of serum magnesium with a centrifugal analyzer. Clin Chem. 1977;23:289–91.
Abe A, Yamashita S, Noma A. Sensitive, direct colorimetric assay for copper in serum. Orient Pharm Exp Med. 1989;35(4):552–4.
Tolman KGRR. Tietz textbook of clinical chemistry. 3rd ed. In: Burtis CA, Ashwood ER, editors. Liver function. Philadelphia: W.B Saunders Company; 1999. p. 1125–77.
Doumas BT, Watson WA, Biggs HG. Albumin standards and the measurement of serum albumin with bromcresol green. Clin Chim Acta. 1971;31(1):87–96.
Nomura F, Takekoshi K. Zinc and selenium metabolism in liver cirrhosis. Nihon Rinsho. 1994;52(1):165–9.
Paik YH, Yoon YJ, Lee HC, Jung MK, Kang SH, Chung SI, et al. Antifibrotic effects of magnesium lithospermate B on hepatic stellate cells and thioacetamide-induced cirrhotic rats. Exp Mol Med. 2011;43(6):341–9.
Kalbfleisch JM, Lindeman RD, Ginn HE, Smith WO. Effects of ethanol administration on urinary excretion of magnesium and other electrolytes in alcoholic and normal subjects. J Clin Investig. 1963;42:1471–5.
Koivisto M, Valta P, Hockerstedt K, Lindgren L. Magnesium depletion in chronic terminal liver cirrhosis. Clin Transplant. 2002;16(5):325–8.
Rocchi E, Borella P, Borghi A, Paolillo F, Pradelli M, Farina F, et al. Zinc and magnesium in liver cirrhosis. Eur J Clin Invest. 1994;24(3):149–55.
Lin CC, Huang JF, Tsai LY, Huang YL. Selenium, iron, copper, and zinc levels and copper-to-zinc ratios in serum of patients at different stages of viral hepatic diseases. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2006;109(1):15–24.
Chetri K, Choudhuri G. Role of trace elements in hepatic encephalopathy: zinc and manganese. Indian J Gastroenterol. 2003;22(Suppl 2):S28–30.
Capocaccia L, Merli M, Piat C, Servi R, Zullo A, Riggio O. Zinc and other trace elements in liver cirrhosis. Ital J Gastroenterol. 1991;23(6):386–91.
Zowczak M, Iskra M, Torlinski L, Cofta S. Analysis of serum copper and zinc concentrations in cancer patients. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2001;82(1–3):1–8.
Poo JL, Rosas-Romero R, Montemayor AC, Isoard F, Uribe M. Diagnostic value of the copper/zinc ratio in hepatocellular carcinoma: a case control study. J Gastroenterol. 2003;38(1):45–51.
Gubler CJ, Brown H, Markowitz H, Cartwright GE, Wintrobe MM. Studies on copper metabolism. XXIII. Portal (Laennec’s) cirrhosis of the liver. J Clin Investig. 1957;36(8):1208–16.
Schilsky ML, Irani AN, Gorla GR, Volenberg I, Gupta S. Biliary copper excretion capacity in intact animals: correlation between ATP7B function, hepatic mass, and biliary copper excretion. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2000;14(4):210–4.
Eagon PK, Teepe AG, Elm MS, Tadic SD, Epley MJ, Beiler BE, et al. Hepatic hyperplasia and cancer in rats: alterations in copper metabolism. Carcinogenesis. 1999;20(6):1091–6.
Florianczyk B. Copper and metallothioneins in cancer cells. Annales Universitatis Mariae Curie-Sklodowska Sectio D. 2003;58(2):390–3.
Wu T, Sempos CT, Freudenheim JL, Muti P, Smit E. Serum iron, copper and zinc concentrations and risk of cancer mortality in US adults. Ann Epidemiol. 2004;14(3):195–201.
Gonzalez-Casas R, Jones EA, Moreno-Otero R. Spectrum of anemia associated with chronic liver disease. World J Gastroenterol. 2009;15(37):4653–8.
Jandl JH. The anemia of liver disease: observations on its mechanism. J Clin Investig. 1955;34(3):390–404.
Guo SB, Duan ZJ, Li Q, Sun XY. Effect of heme oxygenase-1 on renal function in rats with liver cirrhosis. World J Gastroenterol. 2011;17(3):322–8.
Ozaki I, Motomura M, Setoguchi Y, Fujio N, Yamamoto K, Kariya T, et al. Albumin mRNA expression in human liver diseases and its correlation to serum albumin concentration. Gastroenterol Japonica. 1991;26(4):472–6.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kar, K., Dasgupta, A., Vijaya Bhaskar, M. et al. Alteration of Micronutrient Status in Compensated and Decompensated Liver Cirrhosis. Ind J Clin Biochem 29, 232–237 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12291-013-0349-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12291-013-0349-5