Abstract
Background
The ratio of mitral peak velocity of early filling (E) to early diastolic mitral annular velocity (e′, E/e′ ratio) as estimated by tissue Doppler imaging is a noninvasive surrogate for the left ventricular diastolic function. Because diastolic dysfunction usually precedes systolic dysfunction in cardiovascular diseases, we investigated whether monitoring the E/e′ ratio can help to predict the risk of trastuzumab-induced cardiotoxicity.
Methods
E/e′ ratio on tissue Doppler imaging was retrospectively reviewed to assess its value for early detection of the left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) decline in women with human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)-positive breast cancer who received trastuzumab with or without cytotoxic chemotherapy. Echocardiography was performed at baseline and every 3 months after treatment began.
Results
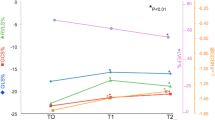
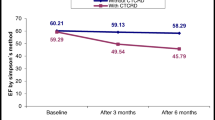
Among 129 patients, LVEF declined in 25 (19 %) during trastuzumab treatment; the decline was grade 2 in 23 patients and grade 3 in 2. Elevation of the E/e′ ratio to more than 15 was detected in 17 patients (13 %), 7 of whom (5.4 % of total) concurrently had LVEF decline. A weak negative correlation was observed between E/e′ elevation and the worst LVEF decline (P = 0.0077), which was confirmed by multiple regression analysis (P = 0.023). E/e′ ratio at baseline or 3 months after beginning trastuzumab treatment was not significantly associated with the subsequent LVEF decline.
Conclusion
Monitoring of the left ventricular diastolic function on the basis of the E/e′ ratio at baseline or 3 months after is unlikely to predict LVEF decline in patients who receive trastuzumab. However, there is a potential chronological relation between E/e′ elevation and LVEF decline, implying that the degree of E/e′ elevation could have a role as a surrogate marker for predicting the LVEF decline characteristic of trastuzumab-induced cardiotoxicity.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen J, Long JB, Hurria A, Owusu C, Steingart RM, Gross CP. Incidence of heart failure or cardiomyopathy after adjuvant trastuzumab therapy for breast cancer. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2012;60:2504–12.
Bowles EJ, Wellman R, Feigelson HS, Onitilo AA, Freedman AN, Delate T, Allen LA, Nekhlyudov L, Goddard KA, Davis RL, Habel LA, Yood MU, McCarty C, Magid DJ, Wagner EH. Pharmacovigilance Study Team. Risk of heart failure in breast cancer patients after anthracycline and trastuzumab treatment: a retrospective cohort study. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2012;104:1293–305.
Chavez-MacGregor M, Zhang N, Buchholz TA, Zhang Y, Niu J, Elting L, Smith BD, Hortobagyi GN, Giordano SH. Trastuzumab-related cardiotoxicity among older patients with breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2013;31:4222–8.
Curigliano G, Cardinale D, Suter T, Plataniotis G, de Azambuja E, Sandri MT, Criscitiello C, Goldhirsch A, Cipolla C, Roila F, ESMO Guidelines Working Group. Cardiovascular toxicity induced by chemotherapy, targeted agents and radiotherapy: ESMO clinical practice guidelines. Ann Oncol. 2012;23(Suppl 7):vii155–66.
Geisberg CA, Lenihan DJ. Neuregulin in heart failure: reverse translation from cancer cardiotoxicity to new heart failure therapy. Herz. 2011;36:306–10.
Perez EA, Suman VJ, Davidson NE, Sledge GW, Kaufman PA, Hudis CA, Martino S, Gralow JR, Dakhil SR, Ingle JN, Winer EP, Gelmon KA, Gersh BJ, Jaffe AS, Rodeheffer RJ. Cardiac safety analysis of doxorubicin and cyclophosphamide followed by paclitaxel with or without trastuzumab in the North Central Cancer Treatment Group N9831 adjuvant breast cancer trial. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26:1231–8.
Bonow RO, Bacharach SL, Green MV, Kent KM, Rosing DR, Lipson LC, Leon MB, Epstein SE. Impaired left ventricular diastolic filling in patients with coronary artery disease: assessment with radionuclide angiography. Circulation. 1981;64:315–23.
Inouye I, Massie B, Loge D, Topic N, Silverstein D, Simpson P, Tubau J. Abnormal left ventricular filling: an early finding in mild to moderate systemic hypertension. Am J Cardiol. 1984;53:120–6.
Kasner M, Westermann D, Steendijk P, Gaub R, Wilkenshoff U, Weitmann K, Hoffmann W, Poller W, Schultheiss HP, Pauschinger M, Tschope C. Utility of Doppler echocardiography and tissue Doppler imaging in the estimation of diastolic function in heart failure with normal ejection fraction: a comparative Doppler-conductance catheterization study. Circulation. 2007;116(6):637–47.
Cardinale D, Colombo A, Torrisi R, Sandri MT, Civelli M, Salvatici M, Lamantia G, Colombo N, Cortinovis S, Dessanai MA, Nolè F, Veglia F, Cipolla CM. Trastuzumab-induced cardiotoxicity: clinical and prognostic implications of troponin I evaluation. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28:3910–6.
Nousiainen T, Vanninen E, Jantunen E, Puustinen J, Remes J, Rantala A, Vuolteenaho O, Hartikainen J. Natriuretic peptides during the development of doxorubicin-induced left ventricular diastolic dysfunction. J Intern Med. 2002;251:228–34.
Cochet A, Quilichini G, Dygai-Cochet I, Touzery C, Toubeau M, Berriolo-Riedinger A, Coudert B, Cottin Y, Fumoleau P, Brunotte F. Baseline diastolic dysfunction as a predictive factor of trastuzumab-mediated cardiotoxicity after adjuvant anthracycline therapy in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2011;130(3):845–54.
Reuvekamp EJ, Bulten BF, Nieuwenhuis AA, Meekes MR, de Haan AF, Tol J, Maas AH, Elias-Smale SE, de Geus-Oei LF. Does diastolic dysfunction precede systolic dysfunction in trastuzumab-induced cardiotoxicity? Assessment with multigated radionuclide angiography (MUGA). J Nucl Cardiol. 2015. doi:10.1007/s12350-015-0164-x
Serrano JM, González I, Del Castillo S, Muñiz J, Morales LJ, Moreno F, Jiménez R, Cristóbal C, Graupner C, Talavera P, Curcio A, Martínez P, Guerra JA, Alonso JJ. Diastolic dysfunction following anthracycline-based chemotherapy in breast cancer patients: incidence and predictors. Oncologist. 2015;20(8):864–72.
Telli ML, Hunt SA, Carlson RW, Guardino AE. Trastuzumab-related cardiotoxicity: calling into question the concept of reversibility. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25:3525–33.
Acknowledgments
We thank Ms. Yuka Murasaki for her technical assistance. This work was supported in part by a Grant-in-Aid from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan (Training Program for Oncology Professionals).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Yuichi Ando received research funding and honoraria from Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
About this article
Cite this article
Honda, K., Takeshita, K., Murotani, K. et al. Assessment of left ventricular diastolic function during trastuzumab treatment in patients with HER2-positive breast cancer. Breast Cancer 24, 312–318 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12282-016-0705-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12282-016-0705-4