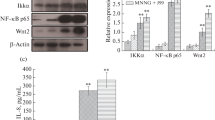
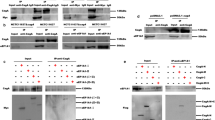
Abstract
Helicobacter pylori is a major pathogen causing various gastric diseases including gastric cancer. Infection of H. pylori induces pro-inflammatory cytokine IL-8 expression in gastric epithelial cells in the initial inflammatory process. It has been known that H. pylori can modulate Ras-Raf-Mek-Erk signal pathway for IL-8 induction. Recently, it has been shown that another signal molecule, cancer Osaka thyroid oncogene/tumor progression locus 2 (Cot/Tpl2) kinase, activates Mek and Erk and plays a role in the Erk pathway, similar to MAP3K signal molecule Raf kinase. Therefore, the objective of this study was to determine whether Cot kinase might be involved in IL-8 induction caused by H. pylori infection. AGS gastric epithelial cells were infected by H. pylori strain G27 or its isogenic mutants lacking cagA or type IV secretion system followed by treatment with Cot kinase inhibitor (KI) or siRNA specific for Cot kinase. Activation of Erk was assessed by Western blot analysis and expression of IL-8 was measured by ELISA. Treatment with Cot KI reduced both transient and sustained Erk activation. It also reduced early and late IL-8 secretion in the gastric epithelial cell line. Furthermore, siRNA knockdown of Cot inhibited early and late IL-8 secretion induced by H. pylori infection. Taken together, these results suggest that Cot kinase might play a critical role in H. pylori type IV secretion apparatus-dependent early IL-8 secretion and CagA-dependent late IL-8 secretion as an alternative signaling molecule in the Erk pathway.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aihara, M., Tsuchimoto, D., Takizawa, H., Azuma, A., Wakebe, H., Ohmoto, Y., Imagawa, K., Kikuchi, M., Mukaida, N., and Matsushima, K. 1997. Mechanisms involved in Helicobacter pyloriinduced interleukin-8 production by a gastric cancer cell line, MKN45. Infect. Immun. 65, 3218–3224.
Allison, C.C., Kufer, T.A., Kremmer, E., Kaparakis, M., and Ferrero, R.L. 2009. Helicobacter pylori induces MAPK phosphorylation and AP-1 activation via a NOD1-dependent mechanism. J. Immunol. 183, 8099–8109.
Amieva, M.R., Salama, N.R., Tompkins, L.S., and Falkow, S. 2002. Helicobacter pylori enter and survive within multivesicular vacuoles of epithelial cells. Cell. Microbiol. 4, 677–690.
Argent, R.H., Hale, J.L., El-Omar, E.M., and Atherton, J.C. 2008. Differences in Helicobacter pylori CagA tyrosine phosphorylation motif patterns between western and east asian strains, and influences on interleukin-8 secretion. J. Med. Microbiol. 57, 1062–1067.
Ballester, A., Velasco, A., Tobeña, R., and Alemany, S. 1998. Cot kinase activates tumor necrosis factor-α gene expression in a cyclosporin A-resistant manner. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 14099–14106.
Blaser, M.J. 1998. Helicobacter pylori and gastric diseases. BMJ 316, 1507–1510.
Bodger, K. and Crabtree, J.E. 1998. Helicobacter pylori and gastric inflammation. Br. Med. Bull. 54, 139–150.
Bourzac, K.M., Botham, C.M., and Guillemin, K. 2007. Helicobacter pylori CagA induces AGS cell elongation through a cell retraction defect that is independent of Cdc42, Rac1, and Arp2/3. Infect. Immun. 75, 1203–1213.
Brandt, S., Kwok, T., Hartig, R., König, W., and Backert, S. 2005. NF-κB activation and potentiation of proinflammatory responses by the Helicobacter pylori CagA protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 102, 9300–9305.
Carpenter, B.M., McDaniel, T.K., Whitmire, J.M., Gancz, H., Guidotti, S., Censini, S., and Merrell, D.S. 2007. Expanding the Helicobacter pylori genetic toolbox: modification of an endogenous plasmid for use as a transcriptional reporter and complementation vector. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 73, 7506–7514.
Censini, S., Lange, C., Xiang, Z., Crabtree, J.E., Ghiara, P., Borodovsky, M., Rappuoli, R., and Covacci, A. 1996. Cag, a pathogenicity island of Helicobacter pylori, encodes type I-specific and disease-associated virulence factors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 93, 14648–14653.
Chiariello, M., Marinissen, M.J., and Gutkind, J.S. 2000. Multiple mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathways connect the cot oncoprotein to the c-jun promoter and to cellular transformation. Mol. Cell. Biol. 20, 1747–1758.
Correa, P. 1992. Human gastric carcinogenesis: a multistep and multifactorial process: first american cancer society award lecture on cancer epidemiology and prevention. Cancer Res. 52, 6735–6740.
Covacci, A., Censini, S., Bugnoli, M., Petracca, R., Burroni, D., Macchia, G., Massone, A., Papini, E., Xiang, Z., Figura, N., et al. 1993. Molecular characterization of the 128-kDa immunodominant antigen of Helicobacter pylori associated with cytotoxicity and duodenal ulcer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90, 5791–5795.
Crabtree, J.E. and Lindley, I.J. 1994. Mucosal interleukin-8 and Helicobacter pylori-associated gastroduodenal disease. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 6 Suppl. 1, S33–38.
Das, S., Cho, J., Lambertz, I., Kelliher, M.A., Eliopoulos, A.G., Du, K., and Tsichlis, P.N. 2005. Tpl2/cot signals activate ERK, JNK, and NF-κB in a cell-type and stimulus-specific manner. J. Biol. Chem. 280, 23748–23757.
Dumaz, N. and Marais, R. 2003. Protein kinase a blocks Raf-1 activity by stimulating 14-3-3 binding and blocking Raf-1 interaction with Ras. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 29819–29823.
Dumitru, C.D., Ceci, J.D., Tsatsanis, C., Kontoyiannis, D., Stamatakis, K., Lin, J.H., Patriotis, C., Jenkins, N.A., Copeland, N.G., Kollias, G., et al. 2000. TNF-α induction by LPS is regulated posttranscriptionally via a Tpl2/ERK-dependent pathway. Cell 103, 1071–1083.
Eliopoulos, A.G., Wang, C.C., Dumitru, C.D., and Tsichlis, P.N. 2003. Tpl2 transduces CD40 and TNF signals that activate ERK and regulates IgE induction by CD40. EMBO J. 22, 3855–3864.
Fan, X.G., Chua, A., Fan, X.J., and Keeling, P.W. 1995. Increased gastric production of interleukin-8 and tumour necrosis factor in patients with Helicobacter pylori infection. J. Clin. Pathol. 48, 133–136.
Fischer, W., Püls, J., Buhrdorf, R., Gebert, B., Odenbreit, S., and Haas, R. 2001. Systematic mutagenesis of the Helicobacter pylori cag pathogenicity island: essential genes for CagA translocation in host cells and induction of interleukin-8. Mol. Microbiol. 42, 1337–1348.
Galgani, M., Busiello, I., Censini, S., Zappacosta, S., Racioppi, L., and Zarrilli, R. 2004. Helicobacter pylori induces apoptosis of human monocytes but not monocyte-derived dendritic cells: role of the cag pathogenicity island. Infect. Immun. 72, 4480–4485.
Higashi, H., Nakaya, A., Tsutsumi, R., Yokoyama, K., Fujii, Y., Ishikawa, S., Higuchi, M., Takahashi, A., Kurashima, Y., Teishikata, Y., et al. 2004. Helicobacter pylori CagA induces Ras-independent morphogenetic response through SHP-2 recruitment and activation. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 17205–17216.
Higashi, H., Tsutsumi, R., Fujita, A., Yamazaki, S., Asaka, M., Azuma, T., and Hatakeyama, M. 2002a. Biological activity of the Helicobacter pylori virulence factor CagA is determined by variation in the tyrosine phosphorylation sites. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 99, 14428–14433.
Higashi, H., Tsutsumi, R., Muto, S., Sugiyama, T., Azuma, T., Asaka, M., and Hatakeyama, M. 2002b. SHP-2 tyrosine phosphatase as an intracellular target of Helicobacter pylori CagA protein. Science 295, 683–686.
Johannessen, C.M., Boehm, J.S., Kim, S.Y., Thomas, S.R., Wardwell, L., Johnson, L.A., Emery, C.M., Stransky, N., Cogdill, A.P., Barretina, J., et al. 2010. COT drives resistance to RAF inhibition through MAP kinase pathway reactivation. Nature 468, 968–972.
Kaiser, F., Cook, D., Papoutsopoulou, S., Rajsbaum, R., Wu, X., Yang, H.T., Grant, S., Ricciardi-Castagnoli, P., Tsichlis, P.N., Ley, S.C., et al. 2009. TPL-2 negatively regulates interferon-β production in macrophages and myeloid dendritic cells. J. Exp. Med. 206, 1863–1871.
Kuipers, E.J. 1997. Helicobacter pylori and the risk and management of associated diseases: gastritis, ulcer disease, atrophic gastritis and gastric cancer. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 11 Suppl. 1, 71–88.
Lee, H.W., Choi, H.Y., Joo, K.M., and Nam, D.H. 2015. Tumor progression locus 2 (Tpl2) kinase as a novel therapeutic target for cancer: double-sided effects of Tpl2 on cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 16, 4471–4491.
Lee, I.O., Kim, J.H., Choi, Y.J., Pillinger, M.H., Kim, S.Y., Blaser, M.J., and Lee, Y.C. 2010. Helicobacter pylori CagA phosphorylation status determines the gp130-activated SHP2/ERK and JAK/STAT signal transduction pathways in gastric epithelial cells. J. Biol. Chem. 285, 16042–16050.
Lin, X., Cunningham, E.T.Jr., Mu, Y., Geleziunas, R., and Greene, W.C. 1999. The proto-oncogene Cot kinase participates in CD3/CD28 induction of NF-κB acting through the NF-κB-inducing kinase and IκB kinases. Immunity 10, 271–280.
Marshall, B.J. and Warren, J.R. 1984. Unidentified curved bacilli in the stomach of patients with gastritis and peptic ulceration. Lancet 1, 1311–1315.
Meyer-ter-Vehn, T., Covacci, A., Kist, M., and Pahl, H.L. 2000. Helicobacter pylori activates mitogen-activated protein kinase cascades and induces expression of the proto-oncogenes c-fos and c-jun. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 16064–16072.
Naito, M., Eguchi, H., Goto, Y., Kondo, T., Nishio, K., Ishida, Y., Kawai, S., Okada, R., Hishida, A., Wakai, K., et al. 2010. Associations of plasma IL-8 levels with Helicobacter pylori seropositivity, gastric atrophy, and IL-8 T-251A genotypes. Epidemiol. Infect. 138, 512–518.
Neel, B.G., Gu, H., and Pao, L. 2003. The ‘Shp’ing news: SH2 domain-containing tyrosine phosphatases in cell signaling. Trends Biochem. Sci. 28, 284–293.
Nozawa, Y., Nishihara, K., Peek, R.M.Jr., Nakano, M., Uji, T., Ajioka, H., Matsuura, N., and Miyake, H. 2002. Identification of a signaling cascade for interleukin-8 production by Helicobacter pylori in human gastric epithelial cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 64, 21–30.
Odenbreit, S., Püls, J., Sedlmaier, B., Gerland, E., Fischer, W., and Haas, R. 2000. Translocation of Helicobacter pylori CagA into gastric epithelial cells by type IV secretion. Science 287, 1497–1500.
Olbermann, P., Josenhans, C., Moodley, Y., Uhr, M., Stamer, C., Vauterin, M., Suerbaum, S., Achtman, M., and Linz, B. 2010. A global overview of the genetic and functional diversity in the Helicobacter pylori cag pathogenicity island. PLoS Genet. 6, e1001069.
Papadakos, K.S., Sougleri, I.S., Mentis, A.F., Hatziloukas, E., and Sgouras, D.N. 2013. Presence of terminal EPIYA phosphorylation motifs in Helicobacter pylori CagA contributes to IL-8 secretion, irrespective of the number of repeats. PLoS One 8, e56291.
Patriotis, C., Makris, A., Bear, S.E., and Tsichlis, P.N. 1993. Tumor progression locus 2 (Tpl-2) encodes a protein kinase involved in the progression of rodent T-cell lymphomas and in T-cell activation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90, 2251–2255.
Pillinger, M.H., Marjanovic, N., Kim, S.Y., Lee, Y.C., Scher, J.U., Roper, J., Abeles, A.M., Izmirly, P.I., Axelrod, M., Pillinger, M.Y., et al. 2007. Helicobacter pylori stimulates gastric epithelial cell MMP-1 secretion via CagA-dependent and -independent ERK activation. J. Biol. Chem. 282, 18722–18731.
Ruggiero, P. 2010. Helicobacter pylori and inflammation. Curr. Pharm. Des. 16, 4225–4236.
Salmerón, A., Ahmad, T.B., Carlile, G.W., Pappin, D., Narsimhan, R.P., and Ley, S.C. 1996. Activation of MEK-1 and SEK-1 by Tpl-2 proto-oncoprotein, a novel MAP kinase kinase kinase. EMBO J. 15, 817–826.
Selbach, M., Moese, S., Meyer, T.F., and Backert, S. 2002. Functional analysis of the Helicobacter pylori cag pathogenicity island reveals both VirD4-CagA-dependent and VirD4-CagA-independent mechanisms. Infect. Immun. 70, 665–671.
Sharma, S.A., Tummuru, M.K., Blaser, M.J., and Kerr, L.D. 1998. Activation of IL-8 gene expression by Helicobacter pylori is regulated by transcription factor nuclear factor-κB in gastric epithelial cells. J. Immunol. 160, 2401–2407.
Suerbaum, S. and Michetti, P. 2002. Helicobacter pylori infection. New Engl. J. Med. 347, 1175–1186.
Torok, A.M., Bouton, A.H., and Goldberg, J.B. 2005. Helicobacter pylori induces interleukin-8 secretion by toll-like receptor 2-and toll-like receptor 5-dependent and -independent pathways. Infect. Immun. 73, 1523–1531.
Tsutsumi, R., Takahashi, A., Azuma, T., Higashi, H., and Hatakeyama, M. 2006. Focal adhesion kinase is a substrate and downstream effector of SHP-2 complexed with Helicobacter pylori CagA. Mol. Cell. Biol. 26, 261–276.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jang, S., Kim, J. & Cha, JH. Cot kinase plays a critical role in Helicobacter pylori-induced IL-8 expression. J Microbiol. 55, 311–317 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-017-7052-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-017-7052-9