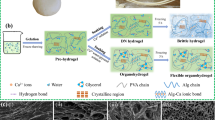
Abstract
Organohydrogels have demonstrated superior environmental adaptability and frost resistance compared to conventional hydrogels, thereby prompting considerable interests in the development and design of innovative organohydrogels. Herein, we report an effective one-pot method for fabricating MXene/polyacrylamide (MXene/PAM) composite organohydrogel (MAOH) by employing Ga liquid metals (Ga LMs) as a highly reactive component in the induced free radical polymerization reaction, without the need for additional heating or cross-linking agents. This synthetic protocol addresses the time-consuming and organic solvent waste concerns associated with traditional solvent displacement methods for organohydrogel preparation. The incorporation of MXene not only highly enhances the conductivity but also confers improved mechanical properties of MAOH. The MAOH exhibits excellent environmental adaptability (> 7 d), sustained moisture retention, remarkable self-healing capabilities, and outstanding mechanical properties under low temperatures (−20 °C). It demonstrates exceptional performance in micro-motion monitoring, rapid response time (125 ms), superior stretchability, and a broad range of strains (0.3%–600%). Therefore, the designed MAOH has great potential for applications in diverse fields such as prosthetics, electronic skin, human–machine interaction, and smart terminals.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lim, H. R.; Kim, H. S.; Qazi, R.; Kwon, Y. T.; Jeong, J. W.; Yeo, W. H. Advanced soft materials, sensor integrations, and applications of wearable flexible hybrid electronics in healthcare, energy, and environment. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1901924.
Dai, X. H.; Long, Y.; Jiang, B.; Guo, W. B.; Sha, W.; Wang, J. W.; Cong, Z. F.; Chen, J. W.; Wang, B. J.; Hu, W. G. Ultra-antifreeze, ultra-stretchable, transparent, and conductive hydrogel for multifunctional flexible electronics as strain sensor and triboelectric nanogenerator. Nano Res. 2022, 15, 5461–5468.
Lai, Y. C.; Ye, B. W.; Lu, C. F.; Chen, C. T.; Jao, M. H.; Su, W. F.; Hung, W. Y.; Lin, T. Y.; Chen, Y. F. Extraordinarily sensitive and low-voltage operational cloth-based electronic skin for wearable sensing and multifunctional integration uses: A tactile-induced insulating-to-conducting transition. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 1286–1295.
Luo, J. C.; Gao, S. J.; Luo, H.; Wang, L.; Huang, X. W.; Guo, Z.; Lai, X. J.; Lin, L. W.; Li, R. K. Y.; Gao, J. F. Superhydrophobic and breathable smart MXene-based textile for multifunctional wearable sensing electronics. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 406, 126898.
Zhang, Y. J.; He, P.; Luo, M.; Xu, X. W.; Dai, G. Z.; Yang, J. L. Highly stretchable polymer/silver nanowires composite sensor for human health monitoring. Nano Res. 2020, 13, 919–926.
Zhou, K. K.; Dai, K.; Liu, C. T.; Shen, C. Y. Flexible conductive polymer composites for smart wearable strain sensors. Smartmat 2020, 1, 1010.
Hou, C.; Xu, Z. J.; Qiu, W.; Wu, R. H.; Wang, Y. N.; Xu, Q. C.; Liu, X. Y.; Guo, W. X. A biodegradable and stretchable protein-based sensor as artificial electronic skin for human motion detection. Small 2019, 15, 1805084.
Lim, Y. W.; Jin, J.; Bae, B. S. Optically transparent multiscale composite films for flexible and wearable electronics. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1907143.
Chen, S. W.; Wu, N.; Lin, S. Z.; Duan, J. J.; Xu, Z. S.; Pan, Y.; Zhang, H. B.; Xu, Z. H.; Huang, L.; Hu, B. et al. Hierarchical elastomer tuned self-powered pressure sensor for wearable multifunctional cardiovascular electronics. Nano Energy 2020, 70, 104460.
Wang, L. R.; Xu, T. L.; Zhang, X. J. Multifunctional conductive hydrogel-based flexible wearable sensors. Trends Analyt. Chem. 2021, 134, 116130.
Hao, S. W.; Shao, C. Y.; Meng, L.; Cui, C.; Xu, F.; Yang, J. Tannic acid-silver dual catalysis induced rapid polymerization of conductive hydrogel sensors with excellent stretchability, self-adhesion, and strain–sensitivity properties. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 56509–56521.
Xu, T. J.; Zhang, L.; Song, B. W.; Bai, X.; Huang, Z. X.; Bu, X. D.; Chen, T. T.; Fu, H.; Guo, P. P. High-strain sensitive zwitterionic hydrogels with swelling-resistant and controllable rehydration for sustainable wearable sensor. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 620, 14–23.
Zeng, W. J.; Jiang, C. G.; Wu, D. F. Heterogeneity regulation of bilayer polysaccharide hydrogels for integrating pH- and humidity-responsive actuators and sensors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 16097–16108.
Li, S. N.; Zhou, X.; Dong, Y. M.; Li, J. H. Flexible self-repairing materials for wearable sensing applications: Elastomers and hydrogels. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2020, 41, 2000444.
Rong, Q. F.; Lei, W. W.; Chen, L.; Yin, Y. A.; Zhou, J. J.; Liu, M. J. Anti-freezing, conductive self-healing organohydrogels with stable strain-sensitivity at subzero temperatures. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 14159–14163.
Han, L.; Liu, K. Z.; Wang, M. H.; Wang, K. F.; Fang, L. M.; Chen, H. T.; Zhou, J.; Lu, X. Mussel-inspired adhesive and conductive hydrogel with long-lasting moisture and extreme temperature tolerance. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1704195.
Chen, M. Z.; Qian, X. Y.; Cai, J.; Zhou, J. P.; Lu, A. Electronic skin based on cellulose/KCl/sorbitol organohydrogel. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 292, 119645.
Jiang, C. G.; Ding, X. X.; Xie, W. Y.; Wu, D. F. Ultrastretchable composite organohydrogels with dual cross-links enabling multimodal sensing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 55143–55154.
Kong, W. Q.; Wang, C. W.; Jia, C.; Kuang, Y. D.; Pastel, G.; Chen, C. J.; Chen, G. G.; He, S. M.; Huang, H.; Zhang, J. H. et al. Muscle-inspired highly anisotropic, strong, ion-conductive hydrogels. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1801934.
Wang, Y.; Zhang, L. N.; Lu, A. Transparent, antifreezing, ionic conductive cellulose hydrogel with stable sensitivity at subzero temperature. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 41710–41716.
Dang, C.; Wang, M.; Yu, J.; Chen, Y. A.; Zhou, S. H.; Feng, X.; Liu, D. T.; Qi, H. S. Transparent, highly stretchable, rehealable, sensing, and fully recyclable ionic conductors fabricated by one-step polymerization based on a small biological molecule. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1902467.
Sun, H. L.; Zhao, Y.; Jiao, S. L.; Wang, C. F.; Jia, Y. P.; Dai, K.; Zheng, G. Q.; Liu, C. T.; Wan, P. B.; Shen, C. Y. Environment tolerant conductive nanocomposite organohydrogels as flexible strain sensors and power sources for sustainable electronics. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2101696.
Xia, S.; Song, S. X.; Gao, G. H. Robust and flexible strain sensors based on dual physically cross-linked double network hydrogels for monitoring human-motion. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 354, 817–824.
Wu, J.; Huang, W. X.; Wu, Z. X.; Yang, X.; Kottapalli, A. G. P.; Xie, X.; Zhou, Y. B.; Tao, K. Hydrophobic and stable graphene-modified organohydrogel based sensitive, stretchable, and self-healable strain sensors for human-motion detection in various scenarios. ACS Mater. Lett. 2022, 4, 1616–1629.
Liu, J.; Chen, Z.; Chen, Y. J.; Rehman, H. U.; Guo, Y. T.; Li, H.; Liu, H. Z. Ionic conductive organohydrogels with dynamic pattern behavior and multi-environmental stability. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2101464.
Zhan, X. Q.; Fu, Q.; Ran, Z. Q.; Chen, H.; Ma, N.; Tsai, F. C. Self-recoverable, highly adhesive, anti-freezing/drying, organohydrogel stretchable sensors. Appl. Mater. Today 2023, 31, 101777.
Liao, H.; Guo, X. L.; Wan, P. B.; Yu, G. H. Conductive MXene nanocomposite organohydrogel for flexible, healable, low-temperature tolerant strain sensors. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1904507.
Guo, R.; Han, X. Y.; Yuan, P.; He, X. X.; Li, Q.; Sun, J.; Dang, L. Q.; Liu, Z. H.; Zhang, Y. T.; Lei, Z. B. Filling Ti3C2Tx nanosheets into melamine foam towards a highly compressible all-in-one supercapacitor. Nano Res. 2022, 15, 3254–3263.
Zhang, Y. Z.; El-Demellawi, J. K.; Jiang, Q.; Ge, G.; Liang, H. F.; Lee, K.; Dong, X. C.; Alshareef, H. N. MXene hydrogels: Fundamentals and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 7229–7251.
Zhang, Y. F.; Gong, M.; Wan, P. B. MXene hydrogel for wearable electronics. Matter 2021, 4, 2655–2658.
Li, S. N.; Yu, Z. R.; Guo, B. F.; Guo, K. Y.; Li, Y.; Gong, L. X.; Zhao, L.; Bae, J.; Tang, L. C. Environmentally stable, mechanically flexible, self-adhesive, and electrically conductive Ti3C2Tx MXene hydrogels for wide-temperature strain sensing. Nano Energy 2021, 90, 106502.
Xu, X. W.; Chen, Y. C.; He, P.; Wang, S.; Ling, K.; Liu, L. H.; Lei, P. F.; Huang, X. J.; Zhao, H.; Cao, J. Y. et al. Wearable CNT/Ti3C2Tx MXene/PDMS composite strain sensor with enhanced stability for real-time human healthcare monitoring. Nano Res. 2021, 14, 2875–2883.
Chen, F.; Zhou, D.; Wang, J. H.; Li, T. Z.; Zhou, X. H.; Gan, T. S.; Handschuh-Wang, S.; Zhou, X. C. Rational fabrication of anti-freezing, non-drying tough organohydrogels by one-pot solvent displacement. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 6568–6571.
Gao, H. N.; Zhao, Z. G.; Cai, Y. D.; Zhou, J. J.; Hua, W. D.; Chen, L.; Wang, L.; Zhang, J. Q.; Han, D.; Liu, M. J. et al. Adaptive and freeze-tolerant heteronetwork organohydrogels with enhanced mechanical stability over a wide temperature range. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15911.
Ma, J.; Lin, Y. L.; Kim, Y. W.; Ko, Y.; Kim, J.; Oh, K. H.; Sun, J. Y.; Gorman, C. B.; Voinov, M. A.; Smirnov, A. I. et al. Liquid metal nanoparticles as initiators for radical polymerization of vinyl monomers. ACS Macro Lett. 2019, 8, 1522–1527.
Peng, H.; Xin, Y. M.; Xu, J.; Liu, H. Z.; Zhang, J. Y. Ultrastretchable hydrogels with reactive liquid metals as asymmetric forcesensors. Mater. Horiz. 2019, 6, 618–625.
Chen, B.; Liu, G. L.; Wu, M. Y.; Cao, Y. D.; Zhong, H. B.; Shen, J. F.; Ye, M. X. Liquid metal-based organohydrogels for wearable flexible electronics. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2023, 8, 2201919.
Xu, S.; Zong, Y.; Ma, J. Z.; Liu, L. P. A multifunctional skin-like sensor based on liquid metal activated gelatin organohydrogel. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 9, 2201212.
Zhang, Z. X.; Tang, L.; Chen, C.; Yu, H. T.; Bai, H. H.; Wang, L.; Qin, M. M.; Feng, Y. Y.; Feng, W. Liquid metal-created macroporous composite hydrogels with self-healing ability and multiple sensations as artificial flexible sensors. J. Mater. Chem. A 2021, 9, 875–883.
Cademartiri, L.; Thuo, M. M.; Nijhuis, C. A.; Reus, W. F.; Tricard, S.; Barber, J. R.; Sodhi, R. N. S.; Brodersen, P.; Kim, C.; Chiechi, R. C. et al. Electrical resistance of AgTS-S(CH2)n−1CH3//Ga2O3/EGaIn tunneling junctions. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 10848–10860.
Park, J. E.; Kang, H. S.; Koo, M.; Park, C. Autonomous surface reconciliation of a liquid-metal conductor micropatterned on a deformable hydrogel. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 2002178.
Rahim, M. A.; Centurion, F.; Han, J. L.; Abbasi, R.; Mayyas, M.; Sun, J.; Christoe, M. J.; Esrafilzadeh, D.; Allioux, F. M.; Ghasemian, M. B. et al. Polyphenol-induced adhesive liquid metal inks for substrate-independent direct pen writing. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2007336.
Wu, M. Y.; Zhang, Q.; Fang, Y. Y.; Deng, C.; Zhou, F. Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X. D.; Tang, Y.; Wang, Y. J. Polylysine-modified MXene nanosheets with highly loaded glucose oxidase as cascade nanoreactor for glucose decomposition and electrochemical sensing. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 586, 20–29.
Xu, H. T.; Xiao, R.; Huang, J. R.; Jiang, Y.; Zhao, C. X.; Yang, X. F. In situ construction of protonated g-C3N4/Ti3C2 MXene Schottky heterojunctions for efficient photocatalytic hydrogen production. Chin. J. Catal. 2021, 42, 107–114.
Zhi, W. Q.; Xiang, S. L.; Bian, R. J.; Lin, R. Z.; Wu, K. H.; Wang, T. W.; Cai, D. Y. Study of MXene-filled polyurethane nanocomposites prepared via an emulsion method. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2018, 168, 404–411.
Wang, L. Y.; Gao, J. P.; An, Z. L.; Zhao, X. X.; Yao, H. D.; Zhang, M.; Tian, Q.; Zhai, X. G.; Liu, Y. Polymer microsphere for water-soluble drug delivery via carbon dot-stabilizing W/O emulsion. J. Mater. Sci. 2019, 54, 5160–5175.
Chen, Z.; Chen, Y. J.; Hedenqvist, M. S.; Chen, C.; Cai, C.; Li, H.; Liu, H. Z.; Fu, J. Multifunctional conductive hydrogels and their applications as smart wearable devices. J. Mater. Chem. B 2021, 9, 2561–2583.
Cao, Y. D.; Chen, B.; Zhong, H. B.; Pei, L. Y.; Liu, G. L.; Xu, Z. L.; Shen, J. F.; Ye, M. X. Ti2C3Tx/polyurethane constructed by gas–liquid interface self-assembly for underwater sensing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 24659–24667.
Wu, L.; Hu, Y. P.; Tang, P.; Wang, H.; Bin, Y. Z. High stretchable, pH-sensitive and self-adhesive rGO/CMCNa/PAA composite conductive hydrogel with good strain-sensing performance. Compos. Commun. 2021, 24, 100669.
Zhang, J. F.; Xue, W.; Dai, Y. Q.; Wu, L.; Liao, B.; Zeng, W.; Tao, X. M. Double network hydrogel sensors with high sensitivity in large strain range. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2021, 306, 2100486.
Maleski, K.; Mochalin, V. N.; Gogotsi, Y. Dispersions of two-dimensional titanium carbide MXene in organic solvents. Chem. Mater. 2017, 29, 1632–1640.
Zhang, Q. X.; Lai, H. R.; Fan, R. Z.; Ji, P. Y.; Fu, X. L.; Li, H. High concentration of Ti3C2Tx MXene in organic solvent. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 5249–5262.
Kim, D.; Ko, T. Y.; Kim, H.; Lee, G. H.; Cho, S.; Koo, C. M. Nonpolar organic dispersion of 2D Ti3C2Tx MXene flakes via simultaneous interfacial chemical grafting and phase transfer method. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 13818–13828.
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (No. 2018YFA0209402) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 22088101, 22175132, and 22072028).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic Supplementary Material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, M., Chen, B., Fan, X. et al. Liquid-metals-induced formation of MXene/polyacrylamide composite organohydrogels for wearable flexible electronics. Nano Res. 17, 1913–1922 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-023-6010-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-023-6010-6