Abstract
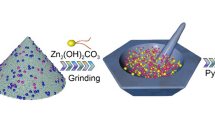
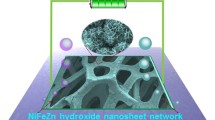
Fabrication of single-crystalline metal-organic framework (MOF) hollow nanostructures with two-dimensional (2D) morphologies is a challenging task. Herein, twin-like MOF nanobricks, a quasi-hollow 2D architecture, with multi-metal nodes and replaceable organic ligands, are uniformly and firmly grown on conductive Ni foam through a generic one-pot approach. The formation process of twin-like MOF nanobricks mainly includes selective epitaxial growth of Fe-rich MOF layer and simultaneously dissolution of the pre-formed Ni-rich metal-organic frameworks (MOFs), all of which can be ascribed to a special self-templated mechanism. The fantastic structural merits of twin-like MOF nanobrick arrays, featuring highly exposed active sites, remarkable electrical conductivity, and hierarchical porosities, enable this material for efficient electrocatalysis. Using bimetallic NiFe-MOFs grown on Ni foam as an example, the resultant twin-like nanobrick arrays can be directly utilized as three-dimensional (3D) integrated electrode for high-performance water oxidation in 1 M KOH with a low overpotential, fast reaction kinetics (28.5 mV·dec−1), and superb stability. Interestingly, the unstable NiFe-MOFs were served as an oxygen evolution reaction (OER) pre-catalyst and the single-crystalline NiFe-MOF precursor can be in-situ topochemically regulated into porous and low-crystalline NiFeOx nanosheets during the OER process. This work extends the hollowing strategy to fabricate hollow MOFs with 2D architectures and highlights their direct utilization for advanced electrocatalysis.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yang, H. Z.; Wang, X. Secondary-component incorporated hollow MOFs and derivatives for catalytic and energy-related applications. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1800743.
Furukawa, H.; Ko, N.; Go, Y. B.; Aratani, N.; Choi, S. B.; Choi, E.; Yazaydin, A. Ö.; Snurr, R. Q.; O’Keeffe, M.; Kim, J. et al. Ultrahigh porosity in metal-organic frameworks. Science 2010, 329, 424–428.
Cheng, W. R.; Zhao, X.; Su, H.; Tang, F. M.; Che, W.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Q. H. Lattice-strained metal-organic-framework arrays for bifunctional oxygen electrocatalysis. Nat. Energy 2019, 4, 115–122.
Zhao, S. L.; Wang, Y.; Dong, J. C.; He, C. T.; Yin, H. J.; An, P. F.; Zhao, K.; Zhang, X. F.; Gao, C.; Zhang, L. J. et al. Ultrathin metalorganic framework nanosheets for electrocatalytic oxygen evolution. Nat. Energy 2016, 1, 16184.
Chen, Z. J.; Cao, G. X.; Gan, L. Y.; Dai, H.; Xu, N.; Zang, M. J.; Dai, H. B.; Wu, H.; Wang, P. Highly dispersed platinum on honeycomb-like NiO@Ni film as a synergistic electrocatalyst for the hydrogen evolution reaction. ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 8866–8872.
Duan, J. J.; Chen, S.; Zhao, C. Ultrathin metal-organic framework array for efficient electrocatalytic water splitting. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15341.
Zhao, S. L.; Tan, C. H.; He, C. T.; An, P. F.; Xie, F.; Jiang, S.; Zhu, Y. F.; Wu, K. H.; Zhang, B. W.; Li, H. J. et al. Structural transformation of highly active metal-organic framework electrocatalysts during the oxygen evolution reaction. Nat. Energy 2020, 5, 881–890.
Yang, Y. C.; Yang, Y. W.; Liu, Y. Y.; Zhao, S. L.; Tang, Z. Y. Metal-organic frameworks for electrocatalysis: Beyond their derivatives. Small Sci. 2021, 2100015.
Wang, X. J.; Feng, J.; Bai, Y. C.; Zhang, Q.; Yin, Y. D. Synthesis, properties, and applications of hollow micro-/nanostructures. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 10983–11060.
Hai, G. T.; Jia, X. L.; Zhang, K. Y.; Liu, X.; Wu, Z. Y.; Wang, G. High-performance oxygen evolution catalyst using two-dimensional ultrathin metal-organic frameworks nanosheets. Nano Energy 2018, 44, 345–352.
Zhou, L.; Zhuang, Z. C.; Zhao, H. H.; Lin, M. T.; Zhao, D. Y.; Mai, L. Q. Intricate hollow structures:Controlled synthesis and applications in energy storage and conversion. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1602914.
Liu, D.; Wan, J. W.; Pang, G. S.; Tang, Z. Y. Hollow metal-organic-framework micro/nanostructures and their derivatives: Emerging multifunctional materials. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1803291.
Zhang, Z. C.; Chen, Y. F.; He, S.; Zhang, J. C.; Xu, X. B.; Yang, Y.; Nosheen, F.; Saleem, F.; He, W.; Wang, X. Hierarchical Zn/Ni-MOF-2 nanosheet-assembled hollow nanocubes for multicomponent catalytic reactions. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2014, 126, 12725–12729.
Liu, W. X.; Huang, J. J.; Yang, Q.; Wang, S. J.; Sun, X. M.; Zhang, W. N.; Liu, J. F.; Huo, F. W. Multi-shelled hollow metal-organic frameworks. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 5512–5516.
Jin, H. Y.; Guo, C. X.; Liu, X.; Liu, J. L.; Vasileff, A.; Jiao, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Qiao, S Z. Emerging two-dimensional nanomaterials for electrocatalysis. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 6337–6408.
Li, Y. Z.; Fu, Z. H.; Xu, G. Metal-organic framework nanosheets: Preparation and applications. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2019, 388, 79–106.
Zhao, M. T.; Huang, Y.; Peng, Y. W.; Huang, Z. Q.; Ma, Q. L.; Zhang, H. Two-dimensional metal-organic framework nanosheets: Synthesis and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 6267–6295.
Fang, W. S.; Huang, L.; Zaman, S.; Wang, Z. T.; Han, Y. J.; Xia, B. Y. Recent progress on two-dimensional electrocatalysis. Chem. Res. Chin. Univ. 2020, 36, 611–621.
Sun, F. Z.; Wang, G.; Ding, Y. Q.; Wang, C.; Yuan, B. B.; Lin, Y. Q. NiFe-based metal-organic framework nanosheets directly supported on nickel foam acting as robust electrodes for electrochemical oxygen evolution reaction. Adv. Energy Mater. 2018, 8, 1800584.
Raja, D. S.; Chuah, X. F.; Lu, S. Y. In situ grown bimetallic MOF-based composite as highly efficient bifunctional electrocatalyst for overall water splitting with ultrastability at high current densities. Adv. Energy Mater. 2018, 8, 1801065.
Mesbah, A.; Rabu, P.; Sibille, R.; Lebegue, S.; Mazet, T.; Malaman, B.; Francois, M. From hydrated Ni3(OH)2(C8H4O4)2(H2O)4 to anhydrous Ni2(OH)2(C8H4O4): Impact of structural transformations on magnetic properties. Inorg. Chem. 2014, 53, 872–881.
Carton, A.; Mesbah, A.; Mazet, T.; Porcher, F.; François, M. Ab initio crystal structure of nickel(II) hydroxy-terephthalate by synchrotron powder diffraction and magnetic study. Solid State Sci. 2007, 9, 465–471.
Tranchemontagne, D. J.; Hunt, J. R.; Yaghi, O. M. Room temperature synthesis of metal-organic frameworks: MOF-5, MOF-74, MOF-177, MOF-199, and IRMOF-0. Tetrahedron 2008, 44, 8553–8557.
Bordiga, S.; Lamberti, C.; Ricchiardi, G.; Regli, L.; Bonino, F.; Damin, A.; Lillerud, K. P.; Bjorgen, M.; Zecchina, A. Electronic and vibrational properties of a MOF-5 metal-organic framework: ZnO quantum dot behaviour. Chem. Commun. 2004, 2300–2301.
Yu, L.; Wu, H. B.; Lou, X. W. Self-templated formation of hollow structures for electrochemical energy applications. Acc. Chem. Res. 2017, 50, 293–301.
Ma, F. X.; Hu, H.; Wu, H. B.; Xu, C. Y.; Xu, Z. C.; Zhen, L.; Lou, X. W. Formation of uniform Fe3O4 hollow spheres organized by ultrathin nanosheets and their excellent lithium storage properties. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 4097–4101.
Suen, N. T.; Hung, S. F.; Quan, Q.; Zhang, N.; Xu, Y. J.; Chen, H. M. Electrocatalysis for the oxygen evolution reaction: Recent development and future perspectives. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 337–365.
Jiao, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Jaroniec, M.; Qiao, S. Z. Design of electrocatalysts for oxygen-and hydrogen-involving energy conversion reactions. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 2060–2086.
Dionigi, F.; Strasser, P. NiFe-based (oxy) hydroxide catalysts for oxygen evolution reaction in non-acidic electrolytes. Adv. Energy Mater. 2016, 6, 1600621.
Zou, X.; Liu, Y. P.; Li, G. D.; Wu, Y. Y.; Liu, D. P.; Li, W.; Li, H. W.; Wang, D. J.; Zhang, Y.; Zou, X. X. Ultrafast formation of amorphous bimetallic hydroxide films on 3D conductive sulfide nanoarrays for large-current-density oxygen evolution electrocatalysis. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1700404.
Liang, H. F.; Gandi, A. N.; Xia, C.; Hedhili, M. N.; Anjum, D. H.; Schwingenschlögl, U.; Alshareef, H. N. Amorphous NiFe-OH/NiFeP electrocatalyst fabricated at low temperature for water oxidation applications. ACS Energy Lett. 2017, 2, 1035–1042.
Jin, S. Are metal chalcogenides, nitrides, and phosphides oxygen evolution catalysts or bifunctional catalysts. ACS Energy Lett. 2017, 2, 1937–1938.
Song, F.; Hu, X. L. Exfoliation of layered double hydroxides for enhanced oxygen evolution catalysis. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4477.
Tareen, A. K.; Priyanga, G. S.; Khan, K.; Pervaiz, E.; Thomas, T.; Yang, M. H. Nickel-based transition metal nitride electrocatalysts for the oxygen evolution reaction. ChemSusChem 2019, 12, 3941–3954.
Liu, M.; Kong, L. J.; Wang, X. M.; He, J.; Bu, X. H. Engineering bimetal synergistic electrocatalysts based on metal-organic frameworks for efficient oxygen evolution. Small 2019, 15, 1903410.
Zhao, J.; Zhang, J. J.; Li, Z. Y.; Bu, X. H. Recent progress on NiFe-based electrocatalysts for the oxygen evolution reaction. Small 2020, 16, 2003916.
Gong, L. Q.; Yang, H.; Wang, H. M.; Qi, R. J.; Wang, J. L.; Chen, S. H.; You, B.; Dong, Z. H.; Liu, H. F.; Xia, B. Y. Corrosion formation and phase transformation of nickel-iron hydroxide nanosheets array for efficient water oxidation. Nano Res. 2021.
Yang, H.; Gong, L. Q.; Wang, H. M.; Dong, C. L.; Wang, J. L.; Qi, K.; Liu, H. F.; Guo, X. P.; Xia, B. Y. Preparation of nickel-iron hydroxides by microorganism corrosion for efficient oxygen evolution. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5075.
Li, F. L.; Shao, Q.; Huang, X. Q.; Lang, J. P. Nanoscale trimetallic metal-organic frameworks enable efficient oxygen evolution electrocatalysis. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 1888–1892.
Yang, Z. K.; Chen, B. X.; Chen, W. X.; Qu, Y. T.; Zhou, F. Y.; Zhao, C. M.; Xu, Q.; Zhang, Q. H.; Duan, X. Z.; Wu, Y. Directly transforming copper (I) oxide bulk into isolated single-atom copper sites catalyst through gas-transport approach. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3734.
Wang, B. Q.; Shang, J.; Guo, C.; Zhang, J. Z.; Zhu, F. N.; Han, A. J.; Liu, J. F. A general method to ultrathin bimetal-MOF nanosheets arrays via in situ transformation of layered double hydroxides arrays. Small 2019, 15, 1804761.
Li, F. L.; Wang, P. T.; Huang, X. Q.; Young, D. J.; Wang, H. F.; Braunstein, P.; Lang, J. P. Large-scale, bottom-up synthesis of binary metal-organic framework nanosheets for efficient water oxidation. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 7051–7056.
Qian, Q. Z.; Li, Y. P.; Liu, Y.; Yu, L.; Zhang, G. Q. Ambient fast synthesis and active sites deciphering of hierarchical foam-like trimetal-organic framework nanostructures as a platform for highly efficient oxygen evolution electrocatalysis. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1901139.
Wang, Y.; Liu, B. R.; Shen, X. J.; Arandiyan, H.; Zhao, T. W.; Li, Y. B.; Garbrecht, M.; Su, Z.; Han, L.; Tricoli, A. et al. Engineering the activity and stability of MOF-nanocomposites for efficient water oxidation. Adv. Energy Mater. 2021, 11, 2003759.
Louie, M. W.; Bell, A. T. An investigation of thin-film Ni-Fe oxide catalysts for the electrochemical evolution of oxygen. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 12329–12337.
Zhang, F.; Shi, Y. M.; Xue, T.; Zhang, J. F.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, B. In situ electrochemically converting Fe2O3-Ni(OH)2 to NiFe2O4-NiOOH: A highly efficient electrocatalyst towards water oxidation. Sci. China Mater. 2017, 60, 324–334.
Qiu, Z.; Tai, C. W.; Niklasson, G. A.; Edvinsson, T. Direct observation of active catalyst surface phases and the effect of dynamic self-optimization in NiFe-layered double hydroxides for alkaline water splitting. Energy Environ. Sci. 2019, 12, 572–581.
Thangavel, P.; Ha, M. R.; Kumaraguru, S.; Meena, A.; Singh, A. N.; Harzandi, A. M.; Kim, K. S. Graphene-nanoplatelets-supported NiFe-MOF: High-efficiency and ultra-stable oxygen electrodes for sustained alkaline anion exchange membrane water electrolysis. Energy Environ. Sci. 2020, 13, 3447–3458.
Cai, W. Z.; Chen, R.; Yang, H. B.; Tao, H. B.; Wang, H. Y.; Gao, J. J.; Liu, W.; Liu, S.; Hung, S. F.; Liu, B. Amorphous versus crystalline in water oxidation catalysis: A case study of NiFe alloy. Nano Lett. 2020, 20, 4278–4285.
Dionigi, F.; Zeng, Z. H.; Sinev, I.; Merzdorf, T.; Deshpande, S.; Lopez, M. B.; Kunze, S.; Zegkinoglou, I.; Sarodnik, H.; Fan, D. X. et al. In-situ structure and catalytic mechanism of NiFe and CoFe layered double hydroxides during oxygen evolution. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2522.
Liu, X.; Meng, J. S.; Zhu, J. X.; Huang, M.; Wen, B.; Guo, R. T.; Mai, L. Q. Comprehensive understandings into complete reconstruction of precatalysts: Synthesis, applications, and characterizations. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2007344.
Acknowledgements
This work was jointly supported by Shenzhen-Hong Kong Science and Technology Innovation Cooperation Zone Shenzhen Park Project (No. HZQB-KCZYB-2020030), the National Key R&D Program of China (Project No. 2017YFA0204403), Innovation and Technology Commission of HKSAR through Hong Kong Branch of National Precious Metals Material Engineering Research Centre and Shenzhen Science and Technology Innovation Committee (No. JCYJ20200109113212238).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic Supplementary Material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, FX., Lyu, F., Diao, Y. et al. Self-templated formation of twin-like metal-organic framework nanobricks as pre-catalysts for efficient water oxidation. Nano Res. 15, 2887–2894 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-021-3885-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-021-3885-y