Abstract
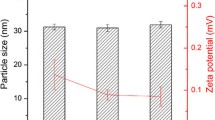
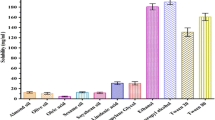
Fenofibrate is indicated in hypercholesterolemia and hypertriglyceridemia alone or combined (types IIa, IIb, III, IV, and V dyslipidemias). However, due to its low solubility in water, it has low bioavailability after oral administration. In order to improve the dissolution rate, fenofibrate was formulated into a self-microemulsifying drug delivery system (SMEDDS). We used pseudoternary phase diagrams to evaluate the area of microemulsification, and an in vitro dissolution test was used to investigate the dissolution rate of fenofibrate. The optimized formulation for in vitro dissolution and bioavailability assessment consisted of propylene glycol laurate (Lauroglycol FCC) (60 %), macrogol-15-hydroxystearate (Solutol HS 15) (27 %), and diethylene glycol monoethyl ether (Transcutol-P) (13 %). The mean droplet size of the oil phase in the microemulsion formed by the SMEDDS was 131.1 nm. The dissolution rate of fenofibrate from SMEDDS was significantly higher than that of the reference tablet. In vivo pharmacokinetics study of fenofibrate in beagles administered SMEDDS-A form resulted in a 3.7-fold increase in bioavailability as compared with the reference drug. Our studies suggested that the fenofibrate containing SMEDDS composition can effectively increase the solubility and oral bioavailability of poorly water-soluble drugs.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Charman, S.A., W.N. Charman, M.C. Rogge, T.D. Wilson, F.J. Dutko, and C.W. Pouton. 1992. Self-emulsifying drug delivery systems: formulation and biopharmaceutic evaluation of an investigational lipophilic compound. Pharmaceutical Research 9: 87–93.
Chi, S.C. 1999. Enhanced dissolution rate of biphenyl dimethyl dicarboxylate using SMEDDS. Bulletin Technique Gattefossé 92: 75–80.
Constantinides, P.P. 1995. Lipid microemulsions for improving drug dissolution and oral absorption: physical and biopharmaceutical aspects. Pharmaceutical Research 12: 1561–1572.
Craig, D.M.Q. 1993. The use of self-emulsifying systems as a means of improving drug delivery. Bulletin Technique Gattefossé 86: 21–31.
Curtet B, Teillaud E, Reginault P (1980) inventors. Fournier Innovation et Synergie, assignee. Novel dosage form of fenofibrate. US patent 4895726., January 23.
Danielsson, I., and B. Lindman. 1981. The definition of microemulsion. Colloids and Surfaces 3: 391–392.
Georgakopoulos, E., N. Farah, and G. Vergnault. 1992. Oral anhydrous nonionic microemulsions administrated in softgel capsules. Bulletin Technique Gattefossé 85: 11–20.
Gershanik, T., S. Benzeno, and S. Benita. 1998. Interaction of a self-emulsifying lipid drug delivery system with the inverted rat intestinal mucosa as a function of droplet size and surface charge. Pharmaceutical Research 15: 863–869.
Groves, M.J., and D.A. de Galindez. 1976. The self-emulsifying action of mixed surfactants in oil. Acta Pharmaceutica Suecica 13: 361–372.
Guay, D.R. 2002. Update on fenofibrate. Cardiovascular Drug Reviews 20: 281–302.
Hanafy, A., H. Spahn-Langguth, G. Vergnault, P. Grenier, M. Tubic Grozdanis, T. Lenhardt, and P. Langguth. 2007. Pharmacokinetic evaluation of oral fenofibrate nanosuspensions and SLN in comparison to conventional suspensions of micronized drug. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews 59: 419–426.
Kang, B.K., J.S. Lee, S.K. Chon, S.Y. Jeong, S.H. Yuk, G. Khang, H.B. Lee, and S.H. Cho. 2004. Development of self-microemulsifying drug delivery systems (SMEDDS) for oral bioavailability enhancement of simvastatin in beagle dogs. International Journal of Pharmaceutics 274: 65–73.
Kasim, N.A., M. Whitehouse, C. Ramachandran, M. Bermejo, H. Lennernäs, A.S. Hussain, H.E. Junginger, S.A. Stavchansky, K.K. Midha, V.P. Shah, and G.L. Amidon. 2004. Molecular properties of WHO essential drugs and provisional biopharmaceutical classification. Molecular Pharmaceutics 1: 85–96.
Kawakami, K., T. Yoshikawa, Y. Moroto, E. Kanaoka, K. Takahashi, Y. Nishihara, and K. Masuda. 2002. Microemulsion formulation for enhanced absorption of poorly soluble drugs. I. Prescription design. Journal of Controlled Release 81: 65–74.
Kim, H.J., K.A. Yoon, M. Hahn, E.S. Park, and S.C. Chi. 2000. Preparation and in vitro evaluation of self microemulsifying drug delivery systems containing idebenone. Drug Development and Industrial Pharmacy 26: 523–529.
Kim, K.H., Y.S. Rhee, J.H. Bae, S.C. Chi, and E.S. Park. 1999. Improvement of dissolution rate of poorly water soluble drug using self-microemulsifying drug delivery system. Journal of Korean Pharmaceutical Sciences 29: 37–45.
Kreuter, J. (ed.). 1997. Colloidal drug delivery systems, 31–65. New York: Marcel Dekker.
Korea (2007) Food and Drug Administration, K-BE Test 2007 and BA Calc.
Law, D., W. Wang, E.A. Schmitt, Y. Qiu, S.L. Krill, and J.J. Fort. 2003. Properties of rapidly dissolving eutectic mixtures of poly(ethylene glycol) and fenofibrate: the eutectic microstructure. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 92: 505–515.
Mayer, D. 1988. Surfactant science and technology, 174–175. New York: VCH Publishers, Inc.
Najib, J. 2002. Fenofibrate in the treatment of dyslipidemia: a review of the data as they relate to the new suprabioavailable tablet formulation. Clinical Therapeutics 24: 2022–2050.
Patel, A.R., and P.R. Vavia. 2006. Effect of hydrophilic polymer on solubilization of fenofibrate by cyclodextrin complexation. Journal of Inclusion Phenomena and Macrocyclic Chemistry 56: 247–251.
Physician’s Desk Reference (2000) 54th ed Medical Economics Company, Montvale, NJ. 476–477.
Porter, C.J.H., A.M. Kaukonen, B.J. Boyd, G.A. Edwards, and W.N. Charman. 2004. Susceptibility to lipase-mediated digestion reduces the oral bioavailability of danazol after administration as a medium-chain lipid-based microemulsion formulation. Pharmaceutical Research 21: 1405–1412.
Pouton, C.W. 2000. Lipid formulations for oral administration of drugs: nonemulsifying, self-emulsifying and ‘self-microemulsifying’ drug delivery systems. European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 11: S93–S98.
Sarciaux, J.M., L. Acar, and P.A. Sado. 1995. Using microemulsion formulations for oral drug delivery of therapeutic peptides. International Journal of Pharmaceutics 120: 127–136.
Schulman, J.H., and J.B. Montagne. 1961. Formation of microemulsions by amino alkyl alcohols. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences 92: 366–371.
Schulman, J.H., W. Stoekenius, and L.M.J. Prince. 1959. Mechanism of formation and structure of micro emulsions by electron microscopy. Journal of Physical Chemistry 63: 1677–1678.
Shah, N.H., M.T. Carvajal, C.I. Patel, M.H. Infeld, and A.W. Malick. 1994. Selfemulsifying drug delivery systems (SEDDS) with polyglycolyzed glycerides for improving in vitro dissolution and oral absorption of lipophilic drugs. International Journal of Pharmaceutics 106: 15–23.
Torrado, S., M.L. Lopez, G. Torrado, F. Bolas, S. Torrado, and R. Cadorniga. 1997. A novel formulation of albendazole solution: oral bioavailability and efficacy evaluation. International Journal of Pharmaceutics 156: 181–187.
TriCor (2002) (fenofibrate) [package insert]. Abbott Laboratories, North Chicago, IL.
Vetter, R.D., M.C. Carey, and J.S. Patton. 1985. Coassimilation of dietary fat and benzo(a)pyrene in the small intestine: an absorption model using the killifish. Journal of Lipid Research 26: 428–434.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cho, YD., Park, YJ. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of a self-microemulsifying drug delivery system for the poorly soluble drug fenofibrate. Arch. Pharm. Res. 37, 193–203 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-013-0169-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-013-0169-4