Abstract
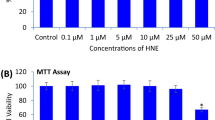
Three known 2-arylbenzofurans, moracin P (1), moracin O (2) and mulberrofuran Q (3) were isolated from the MeOH extract of the Mori Cortex Radicis. These compounds 1–3 enhanced cell viability in dose-dependent manner against oxygen-glucose deprivation (OGD)-induced cell death in neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells, which was measured by MTT reduction assay. (EC50 values of 10.4, 12.6, and 15.9 μM, respectively). In addition, the compounds 1–3 were examined for their inhibitory effect on OGD-induced ROS production by FACS analysis. We observed these compounds reduced ROS production in OGD-induced cell death (IC50 values of 1.9, 0.3 and 12.1 μM, respectively). Consequently, reactive oxygen species (ROS) were overexpressed in OGD-induced cells and all three compounds reduced ROS induced by OGD in dosedependent manner. Taken together, compounds 1–3 might protect neuronal cell death against the oxidative stress induced by OGD, though further studies in vitro and in vivo models are necessary.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albrecht, J., Hanganu, I. L., Heck, N., and Luhmann, H. J., Oxygen and glucose deprivation induces major dysfunction in the somatosensory cortex of the newborn rat. Eur. J. Neurosci., 22, 2295–2305 (2005).
Asano, N., Yamashita, T., Yasuda, K., Ikeda, K., Kizu, H., Kameda, Y., Kato, A., Nash, R. J., Lee, H. S., and Ryu, K. S., Polyhydroxylated alkaloids isolated from mulberry trees (Morusalba L.) and silkworms (Bombyx mori L.). J. Agric. Food Chem., 49, 4208–4213 (2001).
Bass, D. A., Parce, J. W., Dechatelet, L. R., Szejda, P., Seeds, M. C., and Thomas, M., Flow cytometric studies of oxidative product formation by neutrophils: a graded response to membrane stimulation. J. Immunol., 130, 1910–1917 (1983).
Blokhina, O. and Fagerstedt, K. V., Oxidative metabolism, ROS and NO under oxygen deprivation. Plant Physiol. Biochem., 48, 359–373 (2010).
Christophe, M. and Nicolas, S., Mitochondria: a target for neuroprotective interventions in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion. Curr. Pharm. Des., 12, 739–757 (2006).
Dat, N. T., Jin, X., Lee, K., Hong, Y. S., Kim, Y. H., and Lee, J. J., Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 inhibitory benzofurans and chalcone-derived diels-alder adducts from Morus species. J. Nat. Prod., 72, 39–43 (2009).
Dobrota, D., Fedorova, T., Stvolinsky, S., Babusikova, E., Likavcanova, K., Drgova, A., Strapkova, A., and Boldyrev, A., Carnosine protects the brain of rats and Mongolian gerbils against ischemic injury: after-stroke-effect. Neurochem. Res., 30, 1283–1288 (2005).
Du, J., He, Z. D., Jiang, R. W., Ye, W. C., Xu, H. X., and But, P. P., Antiviral flavonoids from the root bark of Morus alba L. Phytochemistry, 62, 1235–1238 (2003).
El-Beshbishy, H. A., Singab, A. N., Sinkkonen, J., and Pihlaja, K., Hypolipidemic and antioxidant effects of Morus alba L. (Egyptian mulberry) root bark fractions supplementation in cholesterol-fed rats. Life Sci., 78, 2724–2733 (2006).
Fatokun, A. A., Stone, T. W., and Smith, R. A., Oxidative stress in neurodegeneration and available means of protection. Front. Biosci., 13, 3288–3311 (2008).
Fordel, E., Thijs, L., Martinet, W., Schrijvers, D., Moens, L., and Dewilde, S., Anoxia or oxygen and glucose deprivation in SH-SY5Y cells: a step closer to the unraveling of neuroglobin and cytoglobin functions. Gene, 398, 114–122 (2007).
Goldberg, M. P. and Choi, D. W., Combined oxygen and glucose deprivation in cortical cell culture: calcium-dependent and calcium-independent mechanisms of neuronal injury. J. Neurosci., 13, 3510–3524 (1993).
Hano, Y. and Nomura, T., Structure of mulberrofuran P, a novel 2-arylbenzofuran derivative from the cultivated mulberry tree (Morus alba L.). Heterocycles, 24, 1381–1386 (1986).
Hano, Y., Hirakura, K., Someya, T., and Nomura, T., Structure of mulberrofuran M, a novel 2-arylbenzofuran derivative from the cultivated mulberry Tree (Morus alba L.). Heterocycles, 24, 1251–1255 (1986).
Hano, Y., Nomura, T., and Ueda, S., Two new Diels-Alder type adducts, mulberrofuran T and kuwanol E, from callus tissues of Morus alba L. Heterocycles, 29, 2035–2041 (1989a).
Hano, Y., Suzuki, S., Nomura, T., and Ueda, S., Two new phenolic compounds, kuwanols C and D, from the root bark of a mulberry tree redifferentiated from the callus tissues. Heterocycles, 29, 807–813 (1989b).
Hirakura, K., Fujimoto, Y., Fukai, T., and Nomura, T., Two phenolic glycosides from the root bark of the cultivated mulberry tree (Morus lhou). J. Nat. Prod., 49, 218–224 (1986).
Kang, T. H., Oh, H. R., Jung, S. M., Ryu, J. H., Park, M. W., Park, Y. K., and Kim, S. Y., Enhancement of neuroprotection of mulberry leaves (Morus alba L.) prepared by the anaerobic treatment against ischemic damage. Biol. Pharm. Bull., 29, 270–274 (2006).
Koo, U., Lee, H. J., Lee, D., Lee, H. J., Ham, A. R., and Mar, W. C., Neuroprotective effects of some plant extracts against dopamine-induced oxidative stress on neuronal cell. Kor. J. Pharmacogn., 40, 41–45 (2009).
Kusano, G., Orihara, S., Tsukamoto, D., Shibano, M., Coskun, M., Guvenc, A., and Erdurak, C. S., Five new nortropane alkaloids and six new amino acids from the fruit of Morus alba LINNE growing in Turkey. Chem. Pharm. Bull., 50, 185–192 (2002).
Lecht, S., Arien-Zakay, H., Marcinkiewicz, C., Lelkes, P. I., and Lazarovici, P., Nerve growth factor-induced protection of brain capillary endothelial cells exposed to oxygen-glucose deprivation involves attenuation of Erk phosphorylation. J. Mol. Neurosci., 41, 183–192 (2010).
Lee, S. H., Choi, S. Y., Kim, H., Hwang, J. S., Lee, B. G., Gao, J. J., and Kim, S. Y., Mulberroside F isolated from the leaves of Morus alba inhibits melanin biosynthesis. Biol. Pharm. Bull., 25, 1045–1048 (2002).
Li, G., Zou, L. Y., Cao, C. M., and Yang, E. S., Coenzyme Q10 protects SHSY5Y neuronal cells from beta amyloid toxicity and oxygen-glucose deprivation by inhibiting the opening of the mitochondrial permeability transition pore. Biofactors, 25, 97–107 (2005).
Miglio, G., Varsaldi, F., Francioli, E., Battaglia, A., Canonico, P. L., and Lombardi, G., Cabergoline protects SH-SY5Y neuronal cells in an in vitro model of ischemia. Eur. J. Pharmacol., 489, 157–165 (2004).
Nomura, T., Fukai, T., Matsumoto, J., and Ohmori, T., Constituents of the cultivated mulberry tree. Planta Med., 46, 28–32 (1982).
Oh, H., Ko, E. K., Jun, J. Y., Oh, M. H., Park, S. U., Kang, K. H., Lee, H. S., and Kim, Y. C., Hepatoprotective and free radical scavenging activities of prenylflavonoids, coumarin, and stilbene from Morus alba. Planta Med., 68, 932–934 (2002).
Oshima, Y., Konno, C., and Hikino, H., Structure of moracenin D, a hypotensive principle of Morus root barks. Heterocycles, 16, 979–982 (1981).
Park, K. M., You, J. S., Lee, H. Y., Baek, N. I., and Hwang, J. K., Kuwanon G: an antibacterial agent from the root bark of Morus alba against oral pathogens. J. Ethnopharmacol., 84, 181–185 (2003).
Park, W. J., Lee, H. J., and Yang, S. G., The inhibitory effect of sanggenon C from the root-bark of Morus alba L. on the growth and the cellular adherence of Streptococcus mutans. Yakhakhoe Chi, 34, 434–438 (1990).
Qiu, F., Komatsu, K., Kawasaki, K., Saito, K., Yao, X., and Kano, Y., A novel stilbene glucoside, oxyresveratrol 3′-O-beta-glucopyranoside, from the root bark of Morus alba. Planta Med., 62, 559–561 (1996).
Stvolinsky, S. L. and Dobrota, D., Anti-ischemic activity of carnosine. Biochemistry (Mosc), 65, 849–855 (2000).
Stvolinsky, S. L., Bulygina, E. R., Fedorova, T. N., Meguro, K., Sato, T., Tyulina, O. V., Abe, H., and Boldyrev, A. A., Biological activity of novel synthetic derivatives of carnosine. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol., 30, 395–404 (2010).
Tabakman, R., Jiang, H., Shahar, I., Arien-Zakay, H., Levine, R. A., and Lazarovici, P., Neuroprotection by NGF in the PC12 in vitro OGD model: involvement of mitogen-activated protein kinases and gene expression. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci., 1053, 84–96 (2005).
Taylor, C. P., Burke, S. P., and Weber, M. L., Hippocampal slices: glutamate overflow and cellular damage from ischemia are reduced by sodium-channel blockade. J. Neurosci. Methods, 59, 121–128 (1995).
Ueda, S., Nomura, T., Fukai, T., and Matsumoto, J., Kuwanon J, a new diels-alder adduct and Chalcomoracin from callus culture of Morus alba L. Chem. Pharm. Bull., 30, 3042–3045 (1982).
Ueda, S., Matsumoto, J., and Nomura, T., Four new natural diels-alder type adducts, Mulberrofuran E, Kuwanon Q, R, and V from callus culture of Morus alba L. Chem. Pharm. Bull., 32, 350–353 (1984).
Valko, M., Leibfritz, D., Moncol, J., Cronin, M. T., Mazur, M., and Telser, J., Free radicals and antioxidants in normal physiological functions and human disease. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol., 39, 44–84 (2007).
Zhang, M., Wang, R. R., Chen, M., Zhang, H. Q., Sun, S., and Zhang, L. Y., A New flavanone glycoside with antiproliferation activity from the root bark of Morus alba. Chin. J. Nat. Med., 7, 105–107 (2009).
Zhu, Y., Hoell, P., Ahlemeyer, B., Sure, U., Bertalanffy, H., and Krieglstein, J., Implication of PTEN in production of reactive oxygen species and neuronal death in in vitro models of stroke and Parkinson’s disease. Neurochem. Int., 50, 507–516 (2007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, H.J., Lyu, D.H., Koo, U. et al. Inhibitory effect of 2-arylbenzofurans from the Mori Cortex Radicis (Moraceae) on oxygen glucose deprivation (OGD)-induced cell death of SH-SY5Y cells. Arch. Pharm. Res. 34, 1373–1380 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-011-0818-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-011-0818-4