Abstract
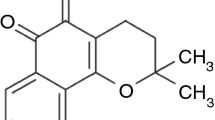
This investigation describes a novel approach to prepare solid dispersions of tanshinone IIA using a laboratory-scale planetary ball mill. Poloxamer 188 was employed as the surfactant carrier to improve the solubility and dissolution of the poorly soluble drug, tanshinone IIA. Solubility and dissolution were evaluated compared to the corresponding physical mixtures and pure drug. Furthermore, the physicochemical properties of the solid dispersions were investigated using scanning electron microscopy, powder X-ray diffraction, differential scanning calorimetry, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and ultraviolet spectrophotometry. The solid dispersion significantly enhanced drug solubility and dissolution compared with pure drug and the physical mixtures. Scanning electron microscopy, powder X-ray diffraction, differential scanning calorimetry and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy analyses of tanshinone IIA/poloxamer 188 system confirmed that there were intermolecular interactions between tanshinone IIA and poloxamer 188 and no conversion to crystalline material. Tanshinone IIA existed in a microcrystalline form in the system. These results suggested that improvement of the dissolution rate could be correlated to the formation of a eutectic mixture between the drug and the carrier. After 60 days the solid dispersion samples were chemically and physically stable. The present studies indicated that the planetary ball mill technique could be considered as a novel and efficient method to prepare solid dispersion formulations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ali, W., Williams, A. C., and Rawlinson, C. F., Stochiometrically governed molecular interactions in drug: poloxamer solid dispersions. Int. J. Pharm., 391, 162–168 (2010).
Arima, H., Yunomae, K., Miyake, K., Irie, T., Hirayama, F., and Uekama, K., Comparative studies of the enhancing effects of cyclodextrins on the solubility and oral bioavailability of tacrolimus in rats. J. Pharm. Sci., 90, 690–701 (2001).
Balani, P. N., Wong, S. Y., Ng, W. K., Widjaja, E., Tan, R. B. H., and Chan, S. Y., Influence of polymer content on stabilizing milled amorphous salbutamol sulphate. Int. J. Pharm., 391, 125–136 (2010).
Chen, Y., Zhang, G. G., Neilly, J., Marsh, K., Mawhinney, D., and Sanzgiri, Y. D., Enhancing the bioavailability of ABT-963 using solid dispersion containing Pluronic F-68. Int. J. Pharm., 286, 69–80 (2004).
Chiou, W. L. and Riegelman, S., Pharmaceutical applications of solid dispersion systems. J. Pharm. Sci., 60, 1281–1302 (1971).
Chutimaworapan, S., Ritthidej, G. C., Yonemochi, E., Oguchi, T., and Yamamoto, K., Effect of water soluble carriers on dissolution characteristics of nifedipine solid dispersions. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm., 26, 1141–1150 (2000).
Craig, D. Q. M., The mechanisms of drug release from solid dispersions in water-soluble polymers. Int. J. Pharm., 231, 131–144 (2002).
Fu, J., Huang, H., Liu, J., Pi, R., Chen, J., and Liu, P., Tanshinone IIA protects cardiac myocytes against oxidative stress-triggered damage and apoptosis. Eur. J. Pharmacol., 568, 213–221 (2007).
Gao, J., Yang, G., Pi, R., Li, R., Wang, P., Zhang, H., Le, K., Chen, S., and Liu, P., Tanshinone IIA protects neonatal rat cardiomyocytes from adriamycin-induced apoptosis. Transl. Res., 151, 79–87 (2008).
Hancock, B. C. and Zografi, G., Characteristics and significance of the amorphous state in pharmaceutical systems. J. Pharm. Sci., 86, 1–12 (1997).
Jiang, B., Zhang, L., Wang, Y., Li, M., Wu, W., Guan, S., Liu, X., Yang, M., Wang, J., and Guo, D.-a., Tanshinone IIA sodium sulfonate protects against cardiotoxicity induced by doxorubicin in vitro and in vivo. Food Chem. Toxicol., 47, 1538–1544 (2009).
Lam, B. Y., Lo, A. C., Sun, X., Luo, H. W., Chung, S. K., and Sucher, N. J., Neuroprotective effects of tanshinones in transient focal cerebral ischemia in mice. Phytomedicine, 10, 286–291 (2003).
Leuner, C. and Dressman, J., Improving drug solubility for oral delivery using solid dispersions. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm., 50, 47–60 (2000).
Li, J., Wang, G., Li, P., and Hao, H., Simultaneous determination of tanshinone IIA and cryptotanshinone in rat plasma by liquid chromatography-electrospray ionizationmass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci., 826, 26–30 (2005).
Mao, S. J., Hou, S. X., Liang, Z., Bi, Y. Q., Wu, Y., Li, H., and Jin, H., Ion-pair reversed-phase HPLC: assay validation of sodium tanshinone IIA sulfonate in mouse plasma. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci., 831, 163–168 (2006).
Miller, D. A., McConville, J. T., Yang, W., Williams, R. O. III, and McGinity, J. W., Hot-melt extrusion for enhanced delivery of drug particles. J. Pharm. Sci., 96, 361–376 (2007).
Newa, M., Bhandari, K. H., Li, D. X., Kim, J. O., Yoo, D. S., Kim, J.-A., Yoo, B.-K., Woo, J.-S., Choi, H.-G., and Yong, C.-S., Preparation and evaluation of immediate release ibuprofen solid dispersions using polyethylene glycol 4000. Biol. Pharm. Bull., 31, 939–945 (2008).
Ozeki, T., Yuasa, H., and Kanaya, Y., Application of the solid dispersion method to the controlled release of medicine IX. Difference in the release of flurbiprofen from solid dispersions with poly (ethylene oxide) and hydroxypropylcellulose and the interaction between medicine and polymers. Int. J. Pharm., 155, 209–217 (1997).
Passerini, N., Albertini, B., González-Rodríguez, M. L., Cavallari, C., and Rodriguez, L., Preparation and characterization of ibuprofen-poloxamer 188 granules obtained by melt granulation. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci., 15, 71–78 (2002).
Seo, A., Holm, P., Kristensen, H. G., and Schaefer, T., The preparation of agglomerates containing solid dispersions of diazepam by melt agglomeration in a high shear mixer. Int. J. Pharm., 259, 161–171 (2003).
Serajuddin, A. T. M., Solid dispersion of poorly water-soluble drugs: early promises, subsequent problems, and recent breakthroughs. J. Pharm. Sci., 88, 1058–1066 (1999).
Sonoda, R., Horibe, M., Oshima, T., Iwasaki, T., and Watano, S., Improvement of dissolution property of poorly water-soluble drug by novel dry coating method using planetary ball mill. Chem. Pharm. Bull., 56, 1243–1247 (2008).
Sun, J., Huang, S. H., Tan, B. K., Whiteman, M., Zhu, Y. C., Wu, Y. J., Ng, Y., Duan, W., and Zhu, Y. Z., Effects of purified herbal extract of Salvia miltiorrhiza on ischemic rat myocardium after acute myocardial infarction. Life Sci., 76, 2849–2860 (2005).
The Pharmacopoeia Committee of China: China Pharmacopeia 2010 ed., part I. The Chemical Industry Publishing House, Beijing, (2010).
Tian, B. P., Yuan, Z. F., and Zhang, L. T., The review: pharmacokinetic studies in vivo for Danshen and its preparations. China Pharmacy, 6, 375–376 (2003).
Yamashita, K., Nakate, T., Okimoto, K., Ohike, A., Tokunaga, Y., Ibuki, R., Higaki, K., and Kimura, T., Establishment of new preparation method for solid dispersion formulation of tacrolimus. Int. J. Pharm., 267, 79–91 (2003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, X., Liu, X., Gan, L. et al. Preparation and physicochemical characterizations of tanshinone IIA solid dispersion. Arch. Pharm. Res. 34, 949–959 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-011-0612-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-011-0612-3