Abstract
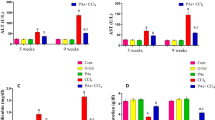
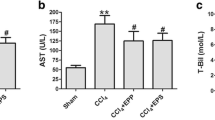
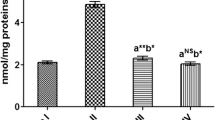
Proanthocyanidins are naturally occurring compounds widely available in fruits, vegetables, nuts and seeds. They are a class of phenolic compounds and have been reported to exhibit a wide range of biological effects. In this study, we investigated the protective effect of grape seed proanthocyanidins on hepatic injury induced by dimethylnitrosamine (DMN) in rats. Treatment with DMN caused a significant increase in levels of serum alanine transaminase, aspartate transaminase, alkaline phosphatase, and bilirubin. Oral administration of proanthocyanidins (20 mg/kg daily for 4 weeks) remarkably prevented these elevations. Proanthocyanidins also restored serum albumin and total protein levels, and reduced the hepatic level of malondialdehyde. Furthermore, DMN-induced collagen accumulation, as estimated by histological analysis of liver tissue stained with Sirius red, was reduced in the proanthocyanidinstreated rats. A reduction in hepatic stellate cell activation, as assessed by α-smooth muscle actin staining, was associated with proanthocyanidins treatment. In conclusion, these results demonstrate that proanthocyanidins exhibited in vivo hepatoprotective and anti-fibrogenic effects against DMN-induced liver injury. It suggests that grape seed proanthocyanidins may be useful in preventing the development of hepatic fibrosis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albanis, E. and Friedman, S. L., Antifibrotic agents for liver disease. Am. J. Transplant., 6, 12–19 (2006).
Bagchi, D., Bagchi, M., Stohs, S. J., Das, D. K., Ray, S. D., Kuszynski, C. A., Joshi, S. S., and Pruess, H. G., Free radicals and grape seed proanthocyanidins extract: importance in human health and disease prevention, Toxicology, 148, 187–197 (2000).
Bagchi, D., Bagchi, M., Stohs, S., Ray, S. D., Sen, C. K., and Preuss, H. G., Cellular protection with proanthocyanidins derived from grape seeds. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci., 957, 260–270 (2002).
Broadhust, R. B. and Jones, W. T., Analysis of condensed tannin using acidified vanillin. J. Sci. Food Agri., 29, 788–794 (1978).
Bruck, R., Ashkenazi, M., Weiss, S., Goldiner, I., Shapiro, H., Aeed, H., Genina, O., Helpern, Z., and Pines, M., Prevention of liver cirrhosis in rats by curcumin. Liver Int., 27, 373–383 (2007).
Buege, J. A. and Aust, S. D., Microsomal lipid peroxidation. Methods Enzymol., 52, 302–310 (1978).
Chen, W. H., Liu, P., Xu, G. F., Lu, W., Xiong, W. G., Li, F. H., and Liu, C. H., Role of lipid peroxidation liver fibrogenesis induced by dimethylnitrosamine in rats. Shijie Huaren Xiaohua ZaZhi, 9, 645–648 (2001).
Dryden, G. W. Jr., Deaciuc, I., Arteel, G., and McClain, C. J., Clinical implications of oxidative stress and antioxidant therapy. Curr. Gastroenterol. Rep., 7, 308–316 (2005).
Dulundu, E., Ozel, Y., Topaloglu, U., Ercan, F., Gedik, N., and Sener, G., Grape seed extract reduces oxidative stress and fibrosis in experimental biliary obstruction. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol., 22, 885–892 (2007).
Friedman, S. L., Molecular regulation of hepatic fibrosis, an integrated cellular response to tissue injury. J. Biol. Chem., 275, 2247–2250 (2000).
Friedman, S. L., Hepatic stellate cells: protean, multifunctional, and enigmatic cells of the liver. Physiol. Rev., 88, 125–172 (2008).
Friedman, S. L., Mechanism of hepatic fibrogenesis. Gastroenterol., 134, 1655–1669 (2008)
Gabetta, B., Fuzzati, N., Griffini, A., Lolla, E., Pace, R., Ruffilli, T., and Peterlongo, F., Characterization of proanthocyanidins from grape seeds. Fitoterapia, 71, 162–175 (2000).
Haggerty H. G. and Holsapple M. P., Role of metabolism in dimethylnitrosamine-induced immunosupression: a review. Toxicology, 63, 1–23 (1990).
Jezequel, A. M., Mancini, R., Ranaldesi, M. L., Balllardini, G., Fallani, M., Bianchi, F., and Orlandi, F., Dimethylnitrosamine-induced cirrhosis. Evidence for an immunological mechanism. J. Hepatol., 8, 42–52 (1989).
Junqueira, L. C., Bignolas, G., and Brentani, R. R., Picrosirius staining plus polarization microscopy, a specific method for collagen detection in tissue sections. J. Histochem., 11, 447–455 (1979).
Karaa, A., Thompson, K. J., McKillop, I. H., Clemens, M. G., and Schrum, L. W., S-adenosyl-L-methionine attenuates oxidative stress and hepatic stellate cell activation in an ethanol-LPS-induced fibrotic rat model. Shock, 30, 197–205 (2008).
Kolios, G., Valatas, V., and Kouroumalis, E., Role of Kupffer cells in the pathogenesis of liver disease. World J. Gastroenterol., 14, 7413–7420 (2006).
Lee, E. S., Lee, H. E., Shin, J. Y., Yoon, S., and Moon, J. O., The flavonoid quercetin inhibits dimethylnitrosamineinduced liver damage in rats, J. Pharm. Pharmacol., 55, 1169–1174 (2003).
Lowry, O. H., Rosebrough, N. J., Farr, A. L., and Randal, R. J., Protein measurement with the Folin phenol regent. J. Biol. Chem., 193, 265–275 (1951).
Maher, J. J. and Bissell D. M., Cell-matrix interations in liver. Semin. Cell Biol., 4, 189–201 (1993).
McMullen, M. R, Pritchard, M. T., and Nagy L. E., Isolation of Kupffer cells from rats fed chronic ethanol. Methods Mol. Biol., 447, 199–212 (2008)
Medina, J. and Moreno-Otero, R., Pathophysiological basis for antioxidant therapy. Drugs, 65, 2445–2461 (2005).
Moon, J. O., Park, S. K., and Nagano, T., Hepatoprotective effect of Fe-TPEN on carbon tetrachloride induced liver injury in rats. Biol. Pharm. Bull., 21, 284–288 (1998).
Moreira, R. K., Hepatic stellate cells and liver fibrosis. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med., 131, 1728–1734 (2007).
Nakamura, T., Ueno, T., Sakamoto, M., Sakata, R., Torimura, T., Hashimoto, O., Ueno, H., and Sata, M., Suppression of transforming growth factor-beta results in upregulation of transcription of regeneration factors after chronic liver injury. J. Hepatol., 41, 974–982 (2004).
Nieto, N. and Cederbaum, A. I., S-adenosylmethionine blocks collagen I production by preventing transforming growth factor-beta induction of the COL1A2 promoter. J. Biol. Chem., 280, 30963–30974 (2005).
Parola, M., Pinzani, M., Casini, A., Albano, E., Poli, G., Gentilini, A., Gentilini, M., and Dianzani, U., Stimulation of lipid peroxidation or 4-hydrononenal treatment increase procollagen alpha 1 (1) gene expression in human liver fat-storing cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 194, 1004–1050 (1993).
Pinzani, M., Marra, F., and Carloni, V., Signal transduction in hepatic stellate cells. Liver, 18, 2–13 (1998).
Terracini, B., Magee, P. N., and Barnes, J. M., Hepatic pathology in rats on dietary levels of dimethylnitrosamine. Br. J. Cancer, 61, 559–565 (1967).
Vendemiale, G., Grattagliano, I., Caruso, M. L., Serviddio, G., Valentini, A. M., Pirrelli, M., and Altomare, E., Increased oxidative stress in dimethylnitrosamine-induced liver fibrosis in the rat: Effect of N-acethylcysteine and interferon-α, Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol., 175, 130–139 (2001).
Weng, H., L., Cai, W. M., and Liu, R. H., Animal experiment and clinical study of effect of gamma-interferon on hepatic fibrosis. World J. Gastroenterol., 7, 42–48 (2001).
Zhu, W. and Fung, P. C., The roles played by crucial free radicals like lipid free radicals nitric oxide, and enzymes NOS and NADPH in CCl4-induced acute liver injury of mice. Free Radic. Biol. Med., 29, 870–880 (2000).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shin, MO., Yoon, S. & Moon, JO. The proanthocyanidins inhibit dimethylnitrosamine-induced liver damage in rats. Arch. Pharm. Res. 33, 167–173 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-010-2239-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-010-2239-1