Abstract
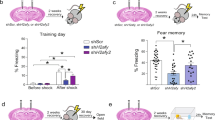
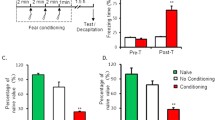
Gene transcription and new protein synthesis regulated by epigenetics play integral roles in the formation of new memories. However, as an important part of epigenetics, the function of chromatin remodeling in learning and memory has been less studied. Here, we showed that SMARCA5 (SWI/SNF related, matrix-associated, actin-dependent regulator of chromatin, subfamily A, member 5), a critical chromatin remodeler, was responsible for hippocampus-dependent memory maintenance and neurogenesis. Using proteomics analysis, we found protein expression changes in the hippocampal dentate gyrus (DG) after the knockdown of SMARCA5 during contextual fear conditioning (CFC) memory maintenance in mice. Moreover, SMARCA5 was revealed to participate in CFC memory maintenance via modulating the proteins of metabolic pathways such as nucleoside diphosphate kinase-3 (NME3) and aminoacylase 1 (ACY1). This work is the first to describe the role of SMARCA5 in memory maintenance and to demonstrate the involvement of metabolic pathways regulated by SMARCA5 in learning and memory.








Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
31 March 2023
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12264-023-01051-8
References
Marco A, Meharena HS, Dileep V, Raju RM, Davila-Velderrain J, Zhang AL. Mapping the epigenomic and transcriptomic interplay during memory formation and recall in the hippocampal engram ensemble. Nat Neurosci 2020, 23: 1606–1617.
Xu XF, Jing X, Ma HX, Yuan RR, Dong Q, Dong JL, et al. MiR-181a participates in contextual fear memory formation via activating mTOR signaling pathway. Cereb Cortex 2018, 28: 3309–3321.
Zovkic IB, Sweatt JD. Epigenetic mechanisms in learned fear: Implications for PTSD. Neuropsychopharmacology 2013, 38: 77–93.
Dias BG, Maddox S, Klengel T, Ressler KJ. Epigenetic mechanisms underlying learning and the inheritance of learned behaviors. Trends Neurosci 2015, 38: 96–107.
Cui X, Zhang R, Yang Y, Wu E, Tang Y, Zhao Z, et al. Identification and characterization of long non-coding RNA Carip in modulating spatial learning and memory. Cell Rep 2022, 38: 110398.
Yoon G, Lim YH, Jo D, Ryu J, Song J, Kim YK. Obesity-linked circular RNA circTshz2-2 regulates the neuronal cell cycle and spatial memory in the brain. Mol Psychiatry 2021, 26: 6350–6364.
Griggs EM, Young EJ, Rumbaugh G, Miller CA. MicroRNA-182 regulates amygdala-dependent memory formation. J Neurosci 2013, 33: 1734–1740.
Vergallo A, Lista S, Zhao Y, Lemercier P, Teipel SJ, Potier MC, et al. MiRNA-15b and miRNA-125b are associated with regional Aβ-PET and FDG-PET uptake in cognitively normal individuals with subjective memory complaints. Transl Psychiatry 2021, 11: 78.
Zhao C, Zhou B, Cao J, Zhang Y, Li W, Wang M, et al. MiR-187-3p participates in contextual fear memory formation through modulating SATB2 expression in the hippocampus. Neuroreport 2020, 31: 909–917.
Jarome TJ, Lubin FD. Histone lysine methylation: Critical regulator of memory and behavior. Rev Neurosci 2013, 24: 375–387.
Gupta S, Kim SY, Artis S, Molfese DL, Schumacher A, Sweatt JD, et al. Histone methylation regulates memory formation. J Neurosci 2010, 30: 3589–3599.
González-Rodríguez P, Cheray M, Füllgrabe J, Salli M, Engskog-Vlachos P, Keane L, et al. The DNA methyltransferase DNMT3A contributes to autophagy long-term memory. Autophagy 2021, 17: 1259–1277.
Jarome TJ, Perez GA, Webb WM, Hatch KM, Navabpour S, Musaus M, et al. Ubiquitination of histone H2B by proteasome subunit RPT6 controls histone methylation chromatin dynamics during memory formation. Biol Psychiatry 2021, 89: 1176–1187.
Kim S, Yu NK, Shim KW, Kim JI, Kim H, Han DH, et al. Remote memory and cortical synaptic plasticity require neuronal CCCTC-binding factor (CTCF). J Neurosci 2018, 38: 5042–5052.
Schoberleitner I, Mutti A, Sah A, Wille A, Gimeno-Valiente F, Piatti P, et al. Role for chromatin remodeling factor Chd1 in learning and memory. Front Mol Neurosci 2019, 12: 3.
Zhao XC, An P, Wu XY, Zhang LM, Long B, Tian Y, et al. Overexpression of hSNF2H in glioma promotes cell proliferation, invasion, and chemoresistance through its interaction with Rsf-1. Tumour Biol 2016, 37: 7203–7212.
Sheu JJ, Choi JH, Yildiz I, Tsai FJ, Shaul Y, Wang TL, et al. The roles of human sucrose nonfermenting protein 2 homologue in the tumor-promoting functions of Rsf-1. Cancer Res 2008, 68: 4050–4057.
Alvarez-Saavedra M, Yan K, De Repentigny Y, Hashem LE, Chaudary N, Sarwar S, et al. Snf2h drives chromatin remodeling to prime upper layer cortical neuron development. Front Mol Neurosci 2019, 12: 243.
Alvarez-Saavedra M, De Repentigny Y, Lagali PS, Raghu Ram EVS, Yan K, Hashem E, et al. Snf2h-mediated chromatin organization and histone H1 dynamics govern cerebellar morphogenesis and neural maturation. Nat Commun 2014, 5: 4181.
Alvarez-Saavedra M, De Repentigny Y, Yang D, O’Meara RW, Yan K, Hashem LE, et al. Voluntary running triggers VGF-mediated oligodendrogenesis to prolong the lifespan of Snf2h-null ataxic mice. Cell Rep 2016, 17: 862–875.
Wille A, Amort T, Singewald N, Sartori SB, Lusser A. Dysregulation of select ATP-dependent chromatin remodeling factors in high trait anxiety. Behav Brain Res 2016, 311: 141–146.
Païzanis E, Renoir T, Lelievre V, Saurini F, Melfort M, Gabriel C, et al. Behavioural and neuroplastic effects of the new-generation antidepressant agomelatine compared to fluoxetine in glucocorticoid receptor-impaired mice. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 2010, 13: 759–774.
Jing X, Sui WH, Wang S, Xu XF, Yuan RR, Chen XR, et al. HDAC7 ubiquitination by the E3 ligase CBX4 is involved in contextual fear conditioning memory formation. J Neurosci 2017, 37: 3848–3863.
O’Leary OF, O’Connor RM, Cryan JF. Lithium-induced effects on adult hippocampal neurogenesis are topographically segregated along the dorso-ventral axis of stressed mice. Neuropharmacology 2012, 62: 247–255.
Papatheodoropoulos C. Higher intrinsic network excitability in ventral compared with the dorsal hippocampus is controlled less effectively by GABAB receptors. BMC Neurosci 2015, 16: 75.
Xue B, Qu Y, Zhang X, Xu XF. miRNA-126a-3p participates in hippocampal memory via alzheimer’s disease-related proteins. Cereb Cortex 2022, 32: 4763–4781.
Xu XF, Wang YC, Zong L, Chen ZY, Li Y. Elevating Integrin-linked Kinase expression has rescued hippocampal neurogenesis and memory deficits in an AD animal model. Brain Res 2018, 1695: 65–77.
West MJ, Gundersen HJ. Unbiased stereological estimation of the number of neurons in the human hippocampus. J Comp Neurol 1990, 296: 1–22.
Lybrand ZR, Goswami S, Zhu J, Jarzabek V, Merlock N, Aktar M, et al. A critical period of neuronal activity results in aberrant neurogenesis rewiring hippocampal circuitry in a mouse model of epilepsy. Nat Commun 2021, 12: 1423.
Poot RA, Dellaire G, Hülsmann BB, Grimaldi MA, Corona DF, Becker PB, et al. HuCHRAC, a human ISWI chromatin remodelling complex contains hACF1 and two novel histone-fold proteins. EMBO J 2000, 19: 3377–3387.
Oppikofer M, Bai T, Gan Y, Haley B, Liu P, Sandoval W, et al. Expansion of the ISWI chromatin remodeler family with new active complexes. EMBO Rep 2017, 18: 1697–1706.
Hakimi MA, Bochar DA, Schmiesing JA, Dong Y, Barak OG, Speicher DW, et al. A chromatin remodelling complex that loads cohesin onto human chromosomes. Nature 2002, 418: 994–998.
Loyola A, Huang JY, LeRoy G, Hu S, Wang YH, Donnelly RJ, et al. Functional analysis of the subunits of the chromatin assembly factor RSF. Mol Cell Biol 2003, 23: 6759–6768.
Frankland PW, Köhler S, Josselyn SA. Hippocampal neurogenesis and forgetting. Trends Neurosci 2013, 36: 497–503.
Ko HG, Jang DJ, Son J, Kwak C, Choi JH, Ji YH, et al. Effect of ablated hippocampal neurogenesis on the formation and extinction of contextual fear memory. Mol Brain 2009, 2: 1.
Zhuo JM, Tseng HA, Desai M, Bucklin ME, Mohammed AI, Robinson NT, et al. Young adult born neurons enhance hippocampal dependent performance via influences on bilateral networks. eLife 2016, 5: e22429.
Clelland CD, Choi M, Romberg C, Clemenson GD Jr, Fragniere A, Tyers P, et al. A functional role for adult hippocampal neurogenesis in spatial pattern separation. Science 2009, 325: 210–213.
Xu XF, Li T, Wang DD, Chen B, Wang Y, Chen ZY. Integrin-linked kinase is essential for environmental enrichment enhanced hippocampal neurogenesis and memory. Sci Rep 2015, 5: 11456.
Sahay A, Scobie KN, Hill AS, O’Carroll CM, Kheirbek MA, Burghardt NS, et al. Increasing adult hippocampal neurogenesis is sufficient to improve pattern separation. Nature 2011, 472: 466–470.
Creer DJ, Romberg C, Saksida LM, van Praag H, Bussey TJ. Running enhances spatial pattern separation in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2010, 107: 2367–2372.
Cook RM, Burke BJ, Buchhagen DL, Minna JD, Miller YE. Human aminoacylase-1. Cloning, sequence, and expression analysis of a chromosome 3p21 gene inactivated in small cell lung cancer. J Biol Chem 1993, 268: 17010–17017.
Sass JO, Vaithilingam J, Gemperle-Britschgi C, Delnooz CC, Kluijtmans LA, van de Warrenburg BP, et al. Expanding the phenotype in aminoacylase 1 (ACY1) deficiency: Characterization of the molecular defect in a 63-year-old woman with generalized dystonia. Metab Brain Dis 2016, 31: 587–592.
Tylki-Szymanska A, Gradowska W, Sommer A, Heer A, Walter M, Reinhard C, et al. Aminoacylase 1 deficiency associated with autistic behavior. J Inherit Metab Dis 2010, 33: 211–214.
Chen CW, Tsao N, Zhang W, Chang ZF. NME3 regulates mitochondria to reduce ROS-mediated genome instability. Int J Mol Sci 2020, 21: 5048.
Chen CW, Wang HL, Huang CW, Huang CY, Lim WK, Tu IC, et al. Two separate functions of NME3 critical for cell survival underlie a neurodegenerative disorder. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2019, 116: 566–574.
Wertz MH, Mitchem MR, Pineda SS, Hachigian LJ, Lee H, Lau V, et al. Genome-wide in vivo CNS screening identifies genes that modify CNS neuronal survival and mHTT toxicity. Neuron 2020, 106: 76-89.e8.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Youth Program of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32000788); Shandong Province Natural Science Foundation (ZR2019 BC097); Key Project from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81830035); the Major program of National Natural Science Foundation of China (82090033); the Major Basic research program of Shandong Province Natural Science Foundation (ZR2019ZD35); The Major program of Technological innovation 2030 “Brain science and brain-inspired research” (2021ZD0203002); Shandong Taishan Scholar Award; and the Fundamental Research Funds of Qingdao University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Qu, Y., Zhou, N., Zhang, X. et al. Chromatin Remodeling Factor SMARCA5 is Essential for Hippocampal Memory Maintenance via Metabolic Pathways in Mice. Neurosci. Bull. 39, 1087–1104 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12264-023-01032-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12264-023-01032-x