Abstract
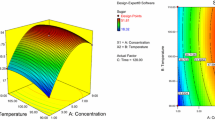
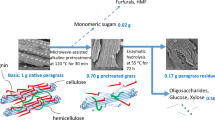
Paulownia, a fast-growing and high-fiber plant (cellulose: 41.66% and hemicellulose: 19.61%), has the potential to serve as an interesting source for production of bioethanol. The aim of this paper is to study and compare the kinetics of enzymatic hydrolysis of Paulownia pretreated by dilute acid (DA), alkali (AL) and ultrasonic-assisted alkali (UA). The enzymatic hydrolysis was performed at 50°C, atmospheric pressure with 40 FPU/g-cellulose cellulase and 80 CBU/g-cellulose cellobiase. The hydrolysis process can be successfully described by the Michaelis-Menten model under the three pretreatment conditions. Due to the high removal of lignin and increased porosity of the substrate, UA pretreatment is proved to be the most effective method in improving enzymatic saccharification, followed by DA pretreatment and alkali (AL) pretreatment. Inhibition constant K I of all experiments (DA: 2.16 g/L, AL: 3.12 g/L and UA: 1.83 g/L) suggests that glucose has a strong inhibition for enzymatic hydrolysis, for lower K I is proportional to higher inhibition performance. The experimental date fits well with kinetics model. This indicates that the model is suitable for performance monitoring, conditions optimization and process control at full-scale studies.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Curreli, N. and M. Agelli (2002) Complete and efficient enzymatic hydrolysis of pretreated wheat straw. Proc. Biochem. 37: 937–941.
Intanakul, P., M. Krairiksh, and Dr. P. Kitchaiya (2003) Enhancement of enzymatic hydrolysis of lignocellulosic wastes by microwave pretreatment under atmospheric pressure. J. Wood Chem. Technol. 23: 217–225.
Phothisantikul, P. P. and R. Tuanpusa (2013) Effect of CH3COOH and K2CO3 on hydrothermal pretreatment of water hyacinth (eichhornia crassipes). I&EC Res. 52: 5009–5015.
Sambusiti, C., E. Ficara, and F. Malpei (2013) Effect of sodium hydroxide pretreatment on physical, chemical characteristics and methane production of five varieties of sorghum. Energy 55: 449–456.
Ayrilmis, N. and A. Kaymakci (2013) Fast growing biomass as reinforcing filler in thermoplastic composites: Paulownia elongata wood. Ind. Crop. Prod. 43: 457–464.
Cheng, J., Y. Sun, and Y. Chen (2012) Optimization of dilute acid pretreatment of Paulownia for the production of bioethanol by respond surface methodology. Adv. Mat. Res. 2012: 250–553.
Alvira, P., E. Tomás-Pejó, M. Ballesteros, and M. J. Negro (2010) Pretreatment technologies for an efficient bioethanol production process based on enzymatic hydrolysis: A review. Bioresource Technol. 101: 4851–4861.
Kumar, R., G. Mago, V. Balan, and C. E. Wyman (2009) Physical and chemical characterizations of corn stover and poplar solidsresulting from leading pretreatment technologies. Bioresource Technol. 100: 3948–3962.
Lee, D. H., E. Y. Cho, C.-J. Kim, and S. B. Kim (2010) Pretreatment of waste newspaper using ethylene glycol for bioethanol production. Biotechnol. Bioproc. Eng. 15: 1094–1101.
Aguiar, R. S., M. H. L. Silveira, and A. P. Pitarelo (2013) Kinetics of enzyme-catalyzed hydrolysis of steam-exploded sugarcane bagasse. Bioresource Technol. 147: 416–423.
Timothy, D. H. B., M. Ahmad, E. M. Hardiman, and R. Rahmanpour (2011) Pathways for degradation of lignin in bacteria and fungi. Nat. Prod. Rep. 28: 1871–1960.
Timothy, D. H. B., M. Ahmad, E. M. Hardiman, and R. Singh (2011) The emerging role for bacteria in lignin degradation and bio-product formation. Curr. Opin. Biotec. 22: 394–400.
Sun, Y. and J. J. Cheng (2005) Dilute acid pretreatment of rye straw and bermudagrass for ethanol production. Bioresour. Technol. 96: 1599–1606.
Chen, M., J. Zhao, and L. Xia (2009) Comparison of four different chemical pretreatments of corn stover for enhancing enzymatic digestibility. Biomass Bioenerg. 33: 1381–1385.
Grohmann, K., R. Torget, and M. Himmel (1985) Optimization of dilute acid pretreatment of biomass. Biotechnol. Bioeng. Symp. 15: 59–80.
Avci, A., B. C. Saha, G. J. Kennedy, and M. A. Cotta (2013) Dilute sulfuric acid pretreatment of corn stover for enzymatic hydrolysis and efficient ethanol production by recombinant Escherichia coli FBR5 without detoxification. Bioresource Technol. 142: 312–319.
Hernández, E., A. Garcí, M. Lópe, J. Puls, J. C. Parajó, and C. Martín (2013) Dilute sulphuric acid pretreatment and enzymatic hydrolysis of Moringa oleifera empty pods. Ind. Crop. Prod. 44: 227–231.
Rajan, K. and D. J. Carrier (2014) Effect of dilute acid pretreatment conditions and washing on the production of inhibitors and on recovery of sugars during wheat straw enzymatic hydrolysis. Biomass Bioenerg 62: 222–227.
Azizul Haque, M., D. N. Barman, T. H. Kang, M. K. Kim, J. Kim, H. Kim, and H. D. Yun (2013) Effect of dilute alkali pretreatment on structural features and enhanced enzymatic hydrolysis of Miscanthus sinensis at boiling temperature with low residence time. Biosyst. Eng. 114: 294–305.
Yueshu, G.., J. Xu, Y. Zhang, Q. Yu, Z. Yuan, and Y. Liu (2013) Effects of different pretreatment methods on chemical composition of sugarcane bagasse and enzymatic hydrolysis. Bioresour. Technol. 144: 396–400.
González, López-Santín, Caminal, and Sola (1986) Dilute acid hydrolysis of wheat straw hemicellulose at moderate temperature: a simplified kinetic model. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 28: 288–293.
Saha, B. C., L. B. Iten, M. A. Cotta, and Y. V. Wu (2005) Dilute acid pretreatment, enzymatic saccharification, and fermentation of rice hulls to ethanol. Biotechnol. Prog. 21: 816–822.
Bezerra, R. M. F. and A. A. Dias (2004) Discrimination among eight modified Michaelis-Menten kinetics models of cellulose hydrolysis with a large range of substrate/enzyme ratios. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 112: 173–184.
Lopez, F., M. T. Garcia, M. J. Feria, and J. C. Garcia (2014) Optimization of furfural production by acid hydrolysis of Eucalyptus globulus in two stages. Chem. Eng. J. 204: 195–201.
Wei, G.-Y., Y.-J. Lee, Y. J. Kim, I.-H. Jin, J.-H. Lee, C.-H. Chung, and J.-W. Lee (2010) Kinetic study on the pretreatment and enzymatic saccharification of rice Hull for the production of fermentable sugars. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 162:1471–1482.
Zhao, X., L. Zhang, and D. Liu (2008) Comparative study on chemical pretreatment methods for improving enzymatic digestibility of crofton weed stem. Bioresour. Technol. 99: 3729–3736.
Laine, J. E. and D. A. I. Goring (1977) Influence of ultrasonic irradiation on the properties of cellulosic fibers. Cell Chem. Technol. 11: 561–567.
Seino, T., A. Yoshioka, M. Fujiwara, K.-L. Chen, T. Erata, M. Tabata, and M. Takai (2001) ESR studies of radicals generated by ultrasonic irradiation of lignin solution. Anapplication of the spin trapping method. Wood Sci. Technol. 35: 97–106.
Gupta, R. and Y. Y. Lee (2009) Mechanism of cellulase reaction on pure cellulosic substrates. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 102: 1570–1581.
Nazhad, M. M., L. P. Ramos, L. Paszner, and J. N. Saddler (1995) Structural constraints affecting the initial enzymatic-hydrolysis of recycled paper. Enz. Microb. Technol. 17: 68–74.
Teeri, T. T. (1997) Crystalline cellulose degradation: New insight into the function of cellobiohydrolases. Trends Biotechnol. 15: 160–167.
Ahmad Ziad Sulaiman and Azilah Ajit (2013) Ultrasound mediated enzymatic hydrolysis of cellulose and carboxymethyl cellulose. Biotechnol. Prog. 9: 1448–1457.
Carrillo, F., M. J. Lis, X. Colom, M. López-Mesas, and J. Valldeperas (2005) Effect of alkali pretreatment on cellulase hydrolysis of wheat straw: Kinetic study. Proc. Biochem. 40: 3360–3364.
Carvalho, M. L., R. Sousa Jr, U. F. Rodríguez-Zúñiga Suarez, CAG, Rodrigues, R. C. Giordano, and R. L. C. Gi ordano (2013) Kinetic study of the enzymatic hydrolysis of sugarcane bagasse. Braz. J. Chem. Eng. 30: 437–447.
Toquero, C. and S. Bolado (2014) Effect of four pretreatments on enzymatic hydrolysis and ethanol fermentation of wheat straw. Influence of inhibitors and washing. Bioresour. Technol. 157: 68–76.
Andri, P., A. S. Mayer, P. A. Jensen, and Dam-Johansen (2010) Reactor design for minimizing product inhibition during enzymatic lignocellulose hydrolysis: I. Significance and mechanism of cellobiose and glucose inhibition on cellulolytic enzymes. Biotechnol. Adv. 28: 308–324.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ye, Xk., Chen, Y. Kinetics study of enzymatic hydrolysis of Paulownia by dilute acid, alkali, and ultrasonic-assisted alkali pretreatments. Biotechnol Bioproc E 20, 242–248 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-014-0490-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-014-0490-x