Abstract
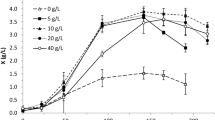
This study is the first to describe the evolution of both hydrodynamic and oxygen transfer conditions during the submerged culture of the entomopathogenic nematode, Steinernema carpocapsae CABA01 (an indigenous strain isolated within the State of Hidalgo, Mexico), and its symbiotic bacterium, Xenorhabdus nematophila, using an internal-loop mechanically agitated bioreactor of 4.5 L of liquid volume. Concentrations up to 217,306 viable nematodes per mL, with 94% in infective juvenile (IJ) stage (i.e., 204,444 IJ/mL), were achieved in 16 days of bioprocess. The Reynolds number (Re) was used as an index of the actual hydrodynamic conditions, and it varied within the interval 5,150 < Re (dimensionless) < 9,440, involving apparent culture broth viscosity changes from 3 to 5.4 mPa s during the processing. The aeration efficiency was expressed on the basis of the volumetric oxygen transfer coefficient, k L a, which varied within the range 0.026 to 0.170 s−1.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kiely, T., D. Donaldson, and A. Grube (2004) Pesticides industry sales and usage. 2000 and 2001 market estimates. pp. 8–9. USEPA, Washington DC, USA.
Wood, S. and S. Ehui (2005) Food. pp. 209–241. In: R. Hassan, R. Scholes, and N. Ash (eds.). Ecosystems and Human Wellbeing: Current State and Trends, Volume 1. Island Press, Washington DC, USA.
Van-Bortel, W., H. D. Trung, L. K. Thuan, T. Sochantha, D. Socheat, C. Sumrandee, V. Baimai, K. Keokenchanh, P. Samlane, P. Roelants, L. Denis, K. Verhaeghen, V. Obsomer, and M. Coosemans (2008) The insecticide resistance status of malaria vectors in the Mekong region. Malaria J. 7: 102.
Hajek, A. E. (2004) Natural enemies: An introduction to biological control. pp. 3–17. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK.
Ehlers, R. U. (2001) Mass production of entomopathogenic nematodes for plant protection. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 56: 623–633.
Shapiro-llan, D. I. and R. Gaugler (2002) Production technology for entomopathogenic nematodes and their bacterial symbionts. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 28: 137–146.
Forst, S. and D. Clarke (2002) Bacteria-nematode symbiosis. pp. 57–77. In: R. Gaugler (ed.). Entomopathogenic Nematology. CABI Publishing, Cambridge MA, USA.
ChavarrÍa-Hernández, N., M. A. Islas-López, G. Maciel-Vergara, M. Gayosso-Canales, and A. I. RodrÍguez-Hernández (2008) Kinetics of infective juvenile production of the entomopathogenic nematode Steinernema carpocapsae in submerged monoxenic culture. Bioproc.Biosyst. Eng. 31: 419–426.
Chavarría-Hernández, N., R. Sanjuan-Galindo, L. Medina-Torres, and A. I. Rodríguez-Hernández (2007) Submerged monoxenic culture of the entomopathogenic nematode Steinernema carpocapsae in an internal-loop airlift bioreactor using two configurations of the inner tube. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 98: 167–176.
Pace, G. W., W. Grote, D. E. Pitt, and J. M. Pitt (1986) Liquid culture of nematodes. International Patent Application, WO 86/01074.
Friedman, M. J., S. E. Langston, and S. Pollitt (1989) Mass production in liquid culture of insect-killing nematodes. International Patent Application, WO 89/04602.
Surrey, M. R. and R. J. Davies (1996) Pilot-scale liquid culture and harvesting of an entomopathogenic nematode, Heterorhabditis bacteriophora. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 67: 92–99.
Ehlers, R. U., S. Lunau, K. Krasomil-Osterfeld, and K. H. Osterfeld (1998) Liquid culture of the entomopathogenic nematode bacterium-complex Heterorhabditis megidis/Photorhabdus luminescens. Biocontrol 43: 77–86.
Strauch, O. and R. U. Ehlers (2000) Influence of the aeration rate on the yields of the biocontrol nematode Heterorhabditis megidis in monoxenic liquid cultures. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 54: 9–13.
Neves, J. M., J. A. Teixeira, N. Simöes, and M. Mota (2001) Effect of airflow rate on yields of Steinernema carpocapsae Az 20 in liquid culture in an external-loop airlift bioreactor. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 72: 369–373.
Johnigk, S. A., F. Ecke, M. Poehling, and R. U. Ehlers (2004) Liquid culture mass production of biocontrol nematodes, Heterorhabditis bacteriophora (Nematoda: Rhabditida): Improved timing of dauer juvenile inoculation. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 64: 651–658.
Pérez-Santos, U. (2009) Aislamiento de nematodos nativos del estado de Hidalgo con potencial para el control de plagas agrÍcolas. BE Thesis. Universidad Autónoma del Estado de Hidalgo, México.
Akhurst, R. J. (1980) Morphological and functional dimorphism in Xenorhabdus spp., Bacteria symbiotically associated with the insect pathogenic nematodes Neoaplectana and Heterorhabditis. J. Gen. Microbiol. 121: 303–309.
Woodring, J. L. and H. K. Kaya (1988) Steinernematid and Heterorhabditid nematodes: A handbook of biology and techniques. pp. 9–10. Arkansas Agric. Exp. Stn. USA.
Martínez-Rodríguez, A. (2008) Aislamiento y producción masiva de simbiontes bacterianos de nematodos nativos del estado de Hidalgo con potencial para el control de plagas agrícolas. BE Thesis. Universidad Autónoma del Estado de Hidalgo, México.
Buecher, E. J. and I. Popiel (1989) Liquid culture of the entomogenous nematode Steinernema feltiae with its bacterial symbiont. J. Nematol. 21: 500–504.
Chisti, Y. and U. J. Jauregui-Haza (2002) Oxygen transfer and mixing in mechanically agitated airlift bioreactors. Biochem. Eng. J. 10: 143–153.
Hemrajani, R. R. and G. B. Tatterson (2004) Mechanically stirred vessels. pp. 345–390. In: E. L. Paul, V. A. Atiemo-Obeng, and S. M. Kresta (eds.). Handbook of Industrial Mixing: Science and Practice. John Wiley & Sons, NJ, USA.
Nagata, S. (1975) Mixing: Principles and applications. pp. 20–22. Wiley, NY, USA.
Young, J. M., P. Dunnill, and J. D. Pearce (1998) Physical properties of liquid nematode cultures and the design of recovery operations. Bioproc. Eng. 19: 121–127.
Chavarría-Hernández, N., A. I. Rodríguez-Hernández, F. Pérez-Guevara, and M. de la Torre (2003) Evolution of culture broth rheological properties during propagation of the entomopathogenic nematode, Steinernema carpocapsae, in submerged monoxenic culture. Biotechnol. Prog. 19: 405–409.
Vrábel, P., R. G. J. M. van der Lans, F. N. van der Schot, K. Ch. A. M. Luyben, B. Xu, and S. O. Enfors (2001) CMA: Integration of fluid dynamics and microbial kinetics in modelling of largescale fermentations. Chem. Eng. J. 84: 463–474.
Felse, A. and T. Panda (2000) Submerged culture production of chitinase by Trichoderma harzianum in stirred tank bioreactors: The influence of agitator speed. Biochem. Eng. J. 4: 115–120.
Garcia-Ochoa, F. and E. Gomez (2009) Bioreactor scale-up and oxygen transfer rate in microbial processes: An overview. Biotechnol. Adv. 27: 153–176.
Atkinson, B. and F. Mavituna (1991) Biochemical engineering and biotechnology handbook. pp. 732–733. Stockton Press, NY, USA.
Bang, W., I. Nikov, H. Delmas, and A. Bascoul (1998) Gas-liquid mass transfer in a new three-phase stirred airlift reactor. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 72: 137–142.
Lindegren, J. E., R. E. Rij, S. R. Ross, and D. C. Fouse (1986) Respiration rate of Steinernema feltiae infective juveniles at several constant temperatures. J. Nematol. 18: 221–224.
Suárez-Sánchez, J. (2002) Evaluación de la demanda específica de oxígeno en cultivo sumergido del nematodo entomopatógeno Steinernema feltiae y de su bacteria simbionte Xenorhabdus nematophilus. MSc Thesis. CINVESTAV-IPN, México.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chavarría-Hernández, N., Ortega-Morales, E., Vargas-Torres, A. et al. Submerged monoxenic culture of the entomopathogenic nematode, Steinernema carpocapsae CABA01, in a mechanically agitated bioreactor: Evolution of the hydrodynamic and mass transfer conditions. Biotechnol Bioproc E 15, 580–589 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-009-3107-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-009-3107-z