Abstract
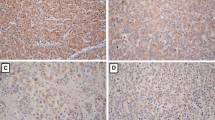
Claudins have been reported to be differentially regulated in malignancies and implicated in the process of carcinogenesis and tumor progression. Claudin-1 has been described as key factor in the entry of hepatitis C virus (HCV) into hepatocytes and as promoter of epithelial-mesenchymal transition in liver cells. The objective of the current study was to characterize claudin expression in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) as well as HCC-surrounding and normal liver samples with respect to cirrhosis and HCV infection. Expression of claudin-1, -2, -3, -4, and −7 was measured by morphometric analysis of immunohistochemistry, and Western blotting in 30 HCCs with 30 corresponding non-tumorous tissues and 6 normal livers. Claudin-1 and −7 protein expression was found significantly elevated in cirrhosis when compared with non-cirrhotic liver. HCCs developed in cirrhotic livers showed even higher expression of claudin-1 contrary to decreased claudin-7 expression when compared with cirrhosis. With reference to HCV status, HCCs or surrounding livers of HCV-infected samples did not show significant alterations in claudin expression when compared with HCV-negative specimens. Cirrhotic transformation associates with elevated claudin-1 and -7 expressions in both non-tumorous liver and HCC. The fact that no significant differences in claudin expression were found regarding HCV-positivity in our sample set suggests that HCV infection alone does not induce a major increase in the total amount of its entry co-factor claudin-1. Increased expression of claudin-1 seems to be a consequence of cirrhotic transformation and might contribute to a more effective HCV entry and malignant transformation.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ferenci P, Fried M, Labrecque D, Bruix J, Sherman M, Omata M, Heathcote J, Piratsivuth T, Kew M, Otegbayo JA, Zheng SS, Sarin S, Hamid SS, Modawi SB, Fleig W, Fedail S, Thomson A, Khan A, Malfertheiner P, Lau G, Carillo FJ, Krabshuis J, Le Mair A (2010) Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC): a global perspective. J Clin Gastroenterol 44(4):239–245. doi:10.1097/MCG.0b013e3181d46ef2
Bosch FX, Ribes J, Diaz M, Cleries R (2004) Primary liver cancer: worldwide incidence and trends. Gastroenterology 127(5 Suppl 1):S5–S16
Furuse M, Sasaki H, Fujimoto K, Tsukita S (1998) A single gene product, claudin-1 or -2, reconstitutes tight junction strands and recruits occludin in fibroblasts. J Cell Biol 143(2):391–401
Furuse M, Sasaki H, Tsukita S (1999) Manner of interaction of heterogeneous claudin species within and between tight junction strands. J Cell Biol 147(4):891–903
Morita K, Furuse M, Fujimoto K, Tsukita S (1999) Claudin multigene family encoding four-transmembrane domain protein components of tight junction strands. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96(2):511–516
Pileri P, Uematsu Y, Campagnoli S, Galli G, Falugi F, Petracca R, Weiner AJ, Houghton M, Rosa D, Grandi G, Abrignani S (1998) Binding of hepatitis C virus to CD81. Science 282(5390):938–941
Scarselli E, Ansuini H, Cerino R, Roccasecca RM, Acali S, Filocamo G, Traboni C, Nicosia A, Cortese R, Vitelli A (2002) The human scavenger receptor class B type I is a novel candidate receptor for the hepatitis C virus. EMBO J 21(19):5017–5025
Evans MJ, von Hahn T, Tscherne DM, Syder AJ, Panis M, Wolk B, Hatziioannou T, McKeating JA, Bieniasz PD, Rice CM (2007) Claudin-1 is a hepatitis C virus co-receptor required for a late step in entry. Nature 446(7137):801–805. doi:10.1038/nature05654
Ploss A, Evans MJ, Gaysinskaya VA, Panis M, You H, de Jong YP, Rice CM (2009) Human occludin is a hepatitis C virus entry factor required for infection of mouse cells. Nature 457(7231):882–886. doi:10.1038/nature07684
Harris HJ, Davis C, Mullins JG, Hu K, Goodall M, Farquhar MJ, Mee CJ, McCaffrey K, Young S, Drummer H, Balfe P, McKeating JA (2010) Claudin association with CD81 defines hepatitis C virus entry. J Biol Chem 285(27):21092–21102. doi:10.1074/jbc.M110.104836
Krieger SE, Zeisel MB, Davis C, Thumann C, Harris HJ, Schnober EK, Mee C, Soulier E, Royer C, Lambotin M, Grunert F, Dao Thi VL, Dreux M, Cosset FL, McKeating JA, Schuster C, Baumert TF (2010) Inhibition of hepatitis C virus infection by anti-claudin-1 antibodies is mediated by neutralization of E2-CD81-claudin-1 associations. Hepatology 51(4):1144–1157. doi:10.1002/hep.23445
Fofana I, Krieger SE, Grunert F, Glauben S, Xiao F, Fafi-Kremer S, Soulier E, Royer C, Thumann C, Mee CJ, McKeating JA, Dragic T, Pessaux P, Stoll-Keller F, Schuster C, Thompson J, Baumert TF (2010) Monoclonal anti-claudin 1 antibodies prevent hepatitis C virus infection of primary human hepatocytes. Gastroenterology 139 (3):953–964, 964 e951-954. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2010.05.073
Mensa L, Crespo G, Gastinger MJ, Kabat J, Perez-del-Pulgar S, Miquel R, Emerson SU, Purcell RH, Forns X (2011) Hepatitis C virus receptors claudin-1 and occludin after liver transplantation and influence on early viral kinetics. Hepatology 53(5):1436–1445. doi:10.1002/hep.24110
Reynolds GM, Harris HJ, Jennings A, Hu K, Grove J, Lalor PF, Adams DH, Balfe P, Hubscher SG, McKeating JA (2008) Hepatitis C virus receptor expression in normal and diseased liver tissue. Hepatology 47(2):418–427. doi:10.1002/hep.22028
Holczbauer A, Gyongyosi B, Lotz G, Szijarto A, Kupcsulik P, Schaff Z, Kiss A (2013) Distinct claudin expression profiles of hepatocellular carcinoma and metastatic colorectal and pancreatic carcinomas. J Histochem Cytochem: Off J Histochem Soc 61(4):294–305. doi:10.1369/0022155413479123
Yoon CH, Kim MJ, Park MJ, Park IC, Hwang SG, An S, Choi YH, Yoon G, Lee SJ (2010) Claudin-1 acts through c-Abl-protein kinase Cdelta (PKCdelta) signaling and has a causal role in the acquisition of invasive capacity in human liver cells. J Biol Chem 285(1):226–233. doi:10.1074/jbc.M109.054189
Suh Y, Yoon CH, Kim RK, Lim EJ, Oh YS, Hwang SG, An S, Yoon G, Gye MC, Yi JM, Kim MJ, Lee SJ (2012) Claudin-1 induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition through activation of the c-Abl-ERK signaling pathway in human liver cells. Oncogene 32:4873–4882. doi:10.1038/onc.2012.505
Ishak K, Baptista A, Bianchi L, Callea F, De Groote J, Gudat F, Denk H, Desmet V, Korb G, MacSween RN et al (1995) Histological grading and staging of chronic hepatitis. J Hepatol 22(6):696–699
Lodi C, Szabo E, Holczbauer A, Batmunkh E, Szijarto A, Kupcsulik P, Kovalszky I, Paku S, Illyes G, Kiss A, Schaff Z (2006) Claudin-4 differentiates biliary tract cancers from hepatocellular carcinomas. Mod Pathol: Off J U S Can Acad Pathol, Inc 19(3):460–469. doi:10.1038/modpathol.3800549
Grotegut S, von Schweinitz D, Christofori G, Lehembre F (2006) Hepatocyte growth factor induces cell scattering through MAPK/Egr-1-mediated upregulation of Snail. EMBO J 25(15):3534–3545. doi:10.1038/sj.emboj.7601213
Kojima T, Takano K, Yamamoto T, Murata M, Son S, Imamura M, Yamaguchi H, Osanai M, Chiba H, Himi T, Sawada N (2008) Transforming growth factor-beta induces epithelial to mesenchymal transition by down-regulation of claudin-1 expression and the fence function in adult rat hepatocytes. Liver Int: Off J Int Assoc Stud Liver 28(4):534–545. doi:10.1111/j.1478-3231.2007.01631.x
Takaki Y, Hirai S, Manabe N, Izumi Y, Hirose T, Nakaya M, Suzuki A, Mizuno K, Akimoto K, Tsukita S, Shuin T, Ohno S (2001) Dynamic changes in protein components of the tight junction during liver regeneration. Cell Tissue Res 305(3):399–409
Kominsky SL, Argani P, Korz D, Evron E, Raman V, Garrett E, Rein A, Sauter G, Kallioniemi OP, Sukumar S (2003) Loss of the tight junction protein claudin-7 correlates with histological grade in both ductal carcinoma in situ and invasive ductal carcinoma of the breast. Oncogene 22(13):2021–2033. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1206199
Tokes AM, Kulka J, Paku S, Mathe M, Paska C, Lodi C, Kiss A, Schaff Z (2005) The expression of five different claudins in invasive breast carcinomas: comparison of pT1pN1 and pT1pN0 tumors. Pathol Res Pract 201(8–9):537–544
Michl P, Barth C, Buchholz M, Lerch MM, Rolke M, Holzmann KH, Menke A, Fensterer H, Giehl K, Lohr M, Leder G, Iwamura T, Adler G, Gress TM (2003) Claudin-4 expression decreases invasiveness and metastatic potential of pancreatic cancer. Cancer Res 63(19):6265–6271
Korompay A, Borka K, Lotz G, Somoracz A, Torzsok P, Erdelyi-Belle B, Kenessey I, Baranyai Z, Zsoldos F, Kupcsulik P, Bodoky G, Schaff Z, Kiss A (2012) Tricellulin expression in normal and neoplastic human pancreas. Histopathology 60(6B):E76–E86. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2559.2012.04189.x
Sobel G, Paska C, Szabo I, Kiss A, Kadar A, Schaff Z (2005) Increased expression of claudins in cervical squamous intraepithelial neoplasia and invasive carcinoma. Hum Pathol 36(2):162–169. doi:10.1016/j.humpath.2004.12.001
Schmelzer E, Wauthier E, Reid LM (2006) The phenotypes of pluripotent human hepatic progenitors. Stem Cells 24(8):1852–1858. doi:10.1634/stemcells.2006-0036
Schmelzer E, Zhang L, Bruce A, Wauthier E, Ludlow J, Yao HL, Moss N, Melhem A, McClelland R, Turner W, Kulik M, Sherwood S, Tallheden T, Cheng N, Furth ME, Reid LM (2007) Human hepatic stem cells from fetal and postnatal donors. J Exp Med 204(8):1973–1987. doi:10.1084/jem.20061603
Yovchev MI, Grozdanov PN, Joseph B, Gupta S, Dabeva MD (2007) Novel hepatic progenitor cell surface markers in the adult rat liver. Hepatology 45(1):139–149. doi:10.1002/hep.21448
Gonzalez-Mariscal L, Lechuga S, Garay E (2007) Role of tight junctions in cell proliferation and cancer. Prog Histochem Cytochem 42(1):1–57. doi:10.1016/j.proghi.2007.01.001
Hirohashi S, Kanai Y (2003) Cell adhesion system and human cancer morphogenesis. Cancer Sci 94(7):575–581
Lal-Nag M, Morin PJ (2009) The claudins. Genome Biol 10(8):235. doi:10.1186/gb-2009-10-8-235
Harris HJ, Farquhar MJ, Mee CJ, Davis C, Reynolds GM, Jennings A, Hu K, Yuan F, Deng H, Hubscher SG, Han JH, Balfe P, McKeating JA (2008) CD81 and claudin 1 coreceptor association: role in hepatitis C virus entry. J Virol 82(10):5007–5020. doi:10.1128/JVI.02286-07
Orban E, Szabo E, Lotz G, Kupcsulik P, Paska C, Schaff Z, Kiss A (2008) Different expression of occludin and ZO-1 in primary and metastatic liver tumors. Pathol Oncol Res POR 14(3):299–306. doi:10.1007/s12253-008-9031-2
Schluter H, Wepf R, Moll I, Franke WW (2004) Sealing the live part of the skin: the integrated meshwork of desmosomes, tight junctions and curvilinear ridge structures in the cells of the uppermost granular layer of the human epidermis. Eur J Cell Biol 83(11–12):655–665. doi:10.1078/0171-9335-00434
Higashi Y, Suzuki S, Sakaguchi T, Nakamura T, Baba S, Reinecker HC, Nakamura S, Konno H (2007) Loss of claudin-1 expression correlates with malignancy of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Surg Res 139(1):68–76. doi:10.1016/j.jss.2006.08.038
Acknowledgments
We would like to express our gratitude to Magdolna Pekar for her precious help in tissue processing and performing immunohistochemistry. This work was supported by grants from the Hungarian Scientific Research Found (OTKA)# K101435.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Ágnes Holczbauer and Benedek Gyöngyösi equally contributed to the paper.
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 70 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Holczbauer, Á., Gyöngyösi, B., Lotz, G. et al. Increased Expression of Claudin-1 and Claudin-7 in Liver Cirrhosis and Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 20, 493–502 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-013-9683-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-013-9683-4