Abstract
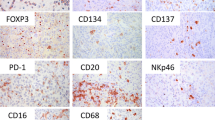
Regulatory T cells (Tregs) have been implicated as inhibitors of antitumor immune reactions. However, data on the relevance of their prevalence at tumor sites in influencing disease outcome are controversial. The aim of our study was to investigate the role in tumor progression and the prognostic impact of the density of lymphocytes expressing FOXP3, a transcription factor expressed predominantly by CD4+CD25+ Tregs, in primary cutaneous melanoma. We examined the infiltration of FOXP3+ cells by immunohistochemistry in tumor samples from 97 patients and evaluated in relation to patient and tumor parameters. The degree of infiltration by FOXP3+ cells did not show correlation with the thickness of melanomas. Moreover, no associations were found with metastasis formation during the 5-year follow-up period, patient survival, or any other clinicopathologic parameters studied. These results suggest that the presence of FOXP3+ lymphocytes in primary tumors is not of prognostic importance in human cutaneous melanoma.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Paschen A, Eichmüller S, Schadendorf D (2004) Identification of tumor antigens and T-cell epitopes, and its clinical application. Cancer Immunol Immunother 53:196–203
Marincola FM, Jaffee EM, Hicklin DJ, Ferrone S (2000) Escape of human solid tumors from T-cell recognition: molecular mechanisms and functional significance. Adv Immunol 74:181–273
Zou W (2005) Immunosuppressive networks in the tumour environment and their therapeutic relevance. Nat Rev Cancer 5:263–274
Knutson KL, Disis ML, Salazar LG (2007) CD4 regulatory T cells in human cancer pathogenesis. Cancer Immunol Immunother 56:271–285
Curiel TJ, Coukos G, Zou L et al (2004) Specific recruitment of regulatory T cells in ovarian carcinoma fosters immune privilege and predicts reduced survival. Nat Med 10:942–949
Hiraoka N, Onozato K, Kosuge T, Hirohashi S (2006) Prevalence of FOXP3+ regulatory T cells increases during the progression of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma and its premalignant lesions. Clin Cancer Res 12:5423–5434
Bates GJ, Fox SB, Han C et al (2006) Quantification of regulatory T cells enables the identification of high-risk breast cancer patients and those at risk of late relapse. J Clin Oncol 24:5373–5380
Kobayashi N, Hiraoka N, Yamagami W et al (2007) FOXP3+ regulatory T cells affect the development and progression of hepatocarcinogenesis. Clin Cancer Res 13:902–911
Gao Q, Qiu S-J, Fan J et al (2007) Intratumoral balance of regulatory and cytotoxic T cells is associated with prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma after resection. J Clin Oncol 25:2586–2593
Fox SB, Launchbury R, Bates GJ et al (2007) The number of regulatory T cells in prostate cancer is associated with the androgen receptor and hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-2α but not HIF-1α. Prostate 67:623–629
Siddiqui SA, Frigola X, Bonne-Annee S et al (2007) Tumor-infiltrating Foxp3−CD4+CD25+ T cells predict poor survival in renal cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 13:2075–2081
Badoual C, Hans S, Rodriguez J et al (2006) Prognostic value of tumor-infiltrating CD4+ T-cell subpopulations in head and neck cancer. Clin Cancer Res 12:465–472
Salama P, Phillips M, Grieu F et al (2009) Tumor-infiltrating FOXP3+ T regulatory cells show strong prognostic significance in colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol 27:186–192
Álvaro T, Lejeune M, Salvadó MT et al (2005) Outcome in Hodgkin’s lymphoma can be predicted from the presence of accompanying cytotoxic and regulatory T cells. Clin Cancer Res 11:1467–1473
Carreras J, Lopez-Guillermo A, Fox BC et al (2006) High numbers of tumor-infiltrating FOXP3-positive regulatory T cells are associated with improved overall survival in follicular lymphoma. Blood 108:2957–2964
Gjerdrum LM, Woetmann A, Odum N et al (2007) FOXP3+ regulatory T cells in cutaneous T-cell lymphomas: association with disease stage and survival. Leukemia 21:2512–2518
Lee NR, Song EK, Jang KY et al (2008) Prognostic impact of tumor infiltrating FOXP3 positive regulatory T cells in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma at diagnosis. Leuk Lymphoma 49:247–256
Mourmouras V, Fimiani M, Rubegni P et al (2007) Evaluation of tumour-infiltrating CD4+CD25+FOXP3+ regulatory T cells in human cutaneous benign and atypical naevi, melanomas and melanoma metastases. Br J Dermatopathol 157:531–539
De Panfilis G, Campanini N, Santini M et al (2008) Phase- and stage-related proportions of T cells bearing the transcription factor FOXP3 infiltrate primary melanoma. J Invest Dermatol 128:676–684
Miracco C, Mourmouras V, Biagioli M et al (2007) Utility of tumour-infiltrating CD25+FOXP3+ regulatory T cell evaluation in predicting local recurrence in vertical growth phase cutaneous melanoma. Oncol Rep 18:1115–1122
Hillen F, Baeten CIM, van de Winkel A et al (2008) Leukocyte infiltration and tumor cell plasticity are parameters of aggressiveness in primary cutaneous melanoma. Cancer Immunol Immunother 57:97–106
Ladányi A, Somlai B, Gilde K et al (2004) T-cell activation marker expression on tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes as prognostic factor in cutaneous malignant melanoma. Clin Cancer Res 10:521–530
Ladányi A, Kiss J, Somlai B et al (2007) Density of DC-LAMP+ mature dendritic cells in combination with activated T lymphocytes infiltrating primary cutaneous melanoma is a strong independent prognostic factor. Cancer Immunol Immunother 56:1459–1469
Balch CM, Buzaid AC, Soong S-J et al (2001) Final version of the American Joint Committee on Cancer staging system for cutaneous melanoma. J Clin Oncol 19:3635–3648
Ebert LM, Tan BS, Browning J et al (2008) The regulatory T cell-associated transcription factor FOXP3 is expressed by tumor cells. Cancer Res 68:3001–3009
Morgan ME, van Bilsen JH, Bakker AM et al (2005) Expression of FOXP3 mRNA is not confined to CD4+CD25+ T regulatory cells in humans. Hum Immunol 66:13–20
Roncador G, Brown PJ, Maestre L et al (2005) Analysis of FOXP3 protein expression in human CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells at the single-cell level. Eur J Immunol 35:1681–1691
Wang J, Ioan-Facsinay A, van der Voort EI et al (2007) Transient expression of FOXP3 in human activated nonregulatory CD4+ T cells. Eur J Immunol 37:129–138
Fontenot JD, Gavin MA, Rudensky AY (2003) Foxp3 programs the development and function of CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells. Nat Immunol 4:330–336
Fontenot JD, Rasmussen JP, Williams LM et al (2005) Regulatory T cell lineage specification by the forkhead transcription factor Foxp3. Immunity 22:329–341
Hori S, Nomura T, Sakaguchi S (2003) Control of regulatory T cell development by the transcription factor Foxp3. Science 299:1057–1061
Yagi H, Nomura T, Nakamura K et al (2004) Crucial role of FOXP3 in the development and function of human CD25+CD4+ regulatory T cells. Int Immunol 16:1643–1656
Walker MR, Kasprowicz DJ, Gersuk VH et al (2003) Induction of FoxP3 and acquisition of T regulatory activity by stimulated human CD4+CD25− T cells. J Clin Invest 112:1437–1443
Allan SE, Passerini L, Bacchetta R et al (2005) The role of 2 FOXP3 isoforms in the generation of human CD4+ Tregs. J Clin Invest 115:3276–3284
Allan SE, Crome SQ, Crellin NK et al (2007) Activation-induced FOXP3 in human T effector cells does not suppress proliferation or cytokine production. Int Immunol 19:345–354
Ziegler SF (2006) FOXP3: of mice and men. Annu Rev Immunol 24:209–226
Kryczek I, Liu R, Wang G et al (2009) FOXP3 defines regulatory T cells in human tumor and autoimmune disease. Cancer Res 69:3995–4000
Acknowledgements
We thank Katalin Derecskei, Ibolya Sinka and Miklós Kónya (National Institute of Oncology) for their excellent technical assistance. The study was supported by Hungarian Ministry of Health grant ETT 308/2003 (AL), Hungarian Scientific Research Fund grant OTKA K 72836 (AL), and NKFP1a-0024-05 (JT).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ladányi, A., Mohos, A., Somlai, B. et al. FOXP3+ Cell Density in Primary Tumor Has No Prognostic Impact in Patients with Cutaneous Malignant Melanoma. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 16, 303–309 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-010-9254-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-010-9254-x