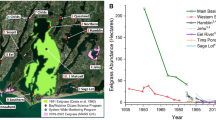
Abstract
Coastal watersheds support more than one half of the world’s human population and are experiencing unprecedented urban, agricultural, and industrial expansion. The freshwater–marine continua draining these watersheds are impacted increasingly by nutrient inputs and resultant eutrophication, including symptomatic harmful algal blooms, hypoxia, finfish and shellfish kills, and loss of higher plant and animal habitat. In addressing nutrient input reductions to stem and reverse eutrophication, phosphorus (P) has received priority traditionally in upstream freshwater regions, while controlling nitrogen (N) inputs has been the focus of management strategies in estuarine and coastal waters. However, freshwater, brackish, and full-salinity components of this continuum are connected structurally and functionally. Intensification of human activities has caused imbalances in N and P loading, altering nutrient limitation characteristics and complicating successful eutrophication control along the continuum. Several recent examples indicate the need for dual N and P input constraints as the only nutrient management option effective for long-term eutrophication control. Climatic changes increase variability in freshwater discharge with more severe storms and intense droughts and interact closely with nutrient inputs to modulate the magnitude and relative proportions of N and P loading. The effects of these interactions on phytoplankton production and composition were examined in two neighboring North Carolina lagoonal estuaries, the New River and Neuse River Estuaries, which are experiencing concurrent eutrophication and climatically driven hydrologic variability. Efforts aimed at stemming estuarine and coastal eutrophication in these and other similarly impacted estuarine systems should focus on establishing N and P input thresholds that take into account effects of hydrologic variability, so that eutrophication and harmful algal blooms can be controlled over a range of current and predicted climate change scenarios.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ache, B.W., K.M. Crossett, P.A. Pacheco, J.E. Adkins, and P.C. Wiley. 2013. “The coast” is complicated: a model to consistently describe the nation’s coastal population. Estuaries and Coasts 1–5. doi:10.1007/s12237-013-9629-9
Ahern, K.S., C.R. Ahern, and J.W. Udy. 2007. Nutrient additions generate prolific growth of Lyngbya majuscula (cyanobacteria) in field and bioassay experiments. Harmful Algae 6: 134–151.
Altman, J.C., and H.W. Paerl. 2012. Composition of inorganic and organic nutrient sources influences phytoplankton community structure in the New River Estuary, North Carolina. Aquatic Ecology 42: 269–282.
Anderson, I.C., M.J. Brush, M.F. Piehler, C.A. Currin, J.W. Stanhope, A.R. Smyth, J.D. Maxey, and M.L. Whitehead. 2013. Impacts of climate-related drivers on the benthic nutrient filter in a shallow photic estuary. Estuaries and Coasts. doi:10.1007/s12237-013-9665-5.
Boesch, D.F., E. Burreson, W. Dennison, E. Houde, M. Kemp, V. Kennedy, R. Newell, K. Paynter, R. Orth, and W. Ulanowicz. 2001. Factors in the decline of coastal ecosystems. Science 293: 629–638.
Borsuk, M.E., C.A. Stow, and K.H. Reckhow. 2004. Confounding effect of flow on estuarine response to nitrogen loading. Journal of Environmental Engineering 130: 605–614.
Boynton, W.R., and W.M. Kemp. 1985. Nutrient regeneration and oxygen consumption by sediments along an estuarine salinity gradient. Marine Ecology Progress Series 23: 45–55.
Bricker, S.B., C.G. Clement, D.E. Pirhalla, S.P. Orlando, and D.R.G. Farrow. 1999. National estuarine eutrophication assessment: effects of nutrient enrichment in the Nation’s estuaries. NOAA, National Ocean Service, Special Projects Office, and the National Centers for Coastal Ocean Science, Silver Spring, MD.
Brown, C.A. 1942. “Justus von Liebig—Man and teacher.” and “Liebig and the Law of the Minimum”. In Liebig and After Liebig: a century of progress in agricultural chemistry. American Association for the Advancement of Science. The Science Press Printing Co., Lancaster, PA.
Capone, D.G., M. Mulholland, and E.J. Carpenter (eds.). 2008. Nitrogen in the marine environment, vol. 2. Orlando: Academic.
Chai, C., Z. Yu, Z. Shen, X. Song, X. Cao, and Y. Yao. 2009. Nutrient characteristics in the Yangtze River Estuary and the adjacent East China Sea before and after impoundment of the Three Gorges Dam. Science of the Total Environment 407: 4687–4695.
Chen, C.T.A., and F. Millero. 1986. Precise thermodynamic properties for natural waters covering only the limnological range. Limnology and Oceanography 31: 657–662.
Cloern, J.E. 2001. Our evolving conceptual model of the coastal eutrophication problem. Marine Ecology Progress Series 210: 223–253.
Conley, D.J., H.W. Paerl, R.W. Howarth, D.F. Boesch, S.P. Seitzinger, K.E. Havens, C. Lancelot, and G.E. Likens. 2009. Controlling eutrophication: nitrogen and phosphorus. Science 323: 1014–1015.
David, M.B., L.E. Drinkwater, and G.F. McIsaac. 2010. Sources of nitrate yields in the Mississippi River Basin. Journal of Environmental Quality 39: 1657–1667.
Diaz, R.J., and R. Rosenberg. 2008. Spreading dead zones and consequences for marine ecosystems. Science 321: 926–929.
Dortch, Q., and T.E. Whitledge. 1992. Does nitrogen or silicon limit phytoplankton production in the Mississippi River plume and nearby regions? Continental Shelf Research 12: 1293–1309.
Elliott, J.A., S.J. Thackeray, C. Huntingford, and R.G. Jones. 2005. Combining a regional climate model with a phytoplankton community model to predict future changes in phytoplankton in lakes. Freshwater Biology 50: 1404–1411.
Elmgren, R., and U. Larsson. 2001. Nitrogen and the Baltic Sea: managing nitrogen in relation to phosphorus. The Scientific World, Special Edition (S2): 371–377. Balkema Publishers.
Elser, J.J., M.E.S. Bracken, E.E. Cleland, D.S. Gruner, W.S. Harpole, H. Hillebrand, J.T. Bgai, E.W. Seabloom, J.B. Shurin, and J.E. Smith. 2007. Global analysis of nitrogen and phosphorus limitation of primary producers in freshwater, marine and terrestrial ecosystems. Ecology Letters 10: 1124–1134.
Emanuel, K., R. Sundararajan, and J. Williams. 2008. Hurricanes and global warming: results from downscaling IPCC AR4 simulations. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society 89: 347–367.
Ensign, S.H., J.N. Halls, and M.A. Mallin. 2004. Application of digital bathymetry data in an analysis of flushing times of two North Carolina Estuaries. Computers and Geosciences 30: 501–511.
Feuchtmayr, H., R. Moran, K. Hatton, L. Conner, T. Heyes, B. Moss, I. Harvey, and D. Atkinson. 2009. Global warming and eutrophication: effects on water chemistry and autotrophic communities in experimental hypertrophic shallow lake mesocosms. Journal of Applied Ecology 46: 713–723.
Finlay, K., A. Patoine, D.B. Donald, M. Bogard, and P.R. Leavitt. 2010. Experimental evidence that pollution with urea can degrade water quality in phosphorus-rich lakes of the northern Great Plains. Limnology and Oceanography 55: 1213–1230.
Fisher, T.R., A.B. Gustafson, K. Sellner, R. Lacuture, L.W. Haas, R. Magnien, R. Karr, and B. Michael. 1999. Spatial and temporal variation in resource limitation in Chesapeake Bay. Marine Biology 133: 763–778.
Galloway, J.N., and E.B. Cowling. 2002. Reactive nitrogen and the world: 200 years of change. Ambio 31: 64–71.
Goldman, C.R. 1981. Lake Tahoe: two decades of change in a nitrogen deficient oligotrophic lake. Verhandlungen Internationale Vereinigung für Theoretische und Angewandte Limnologie 21: 45–70.
Granéli, E.K., U. Wallström, U. Larsson, and R. Elmgren. 1999. Nutrient limitation of the Baltic Sea area. Ambio 19: 142–151.
Hall, N.S., and H.W. Paerl. 2011. Vertical migration patterns of phytoflagellates in relation to light and nutrient availability in a shallow, microtidal estuary. Marine Ecology Progress Series 425: 1–19.
Hall, N.S., R.W. Litaker, E. Fensin, J.E. Adolf, A.R. Place, and H.W. Paerl. 2008. Environmental factors contributing to the development and demise of a toxic dinoflagellate (Karlodinium veneficum) bloom in a shallow, eutrophic, lagoonal estuary. Estuaries and Coasts 31: 402–418.
Hall, N.S., H.W. Paerl, B.L. Peierls, A.C. Whipple, and K.L. Rossignol. 2013. Effects of climatic variability on phytoplankton biomass and community structure in the eutrophic, microtidal, New River Estuary, North Carolina, USA. Estuarine and Coastal Shelf Science 117: 70–82.
Havens, K.E., T. Fukushima, P. Xie, T. Iwakuma, R.T. James, N. Takamura, T. Hanazato, and T. Yamamoto. 2001. Nutrient dynamics and the eutrophication of shallow lakes Kasumigaura (Japan), Donghu (PR China), and Okeechobee (USA). Environmental Pollution 111: 262–272.
Howarth, R.W. 1998. An assessment of human influences on inputs of nitrogen to the estuaries and continental shelves of the North Atlantic Ocean. Nutrient Cycling in Agroecosystems 52: 213–223.
Howarth, R.W., R. Marino, J. Lane, and J.J. Cole. 1988. Nitrogen fixation rates in freshwater, estuarine, and marine ecosystems. Limnology and Oceanography 33: 669–687.
Howarth, R., D. Anderson, J. Cloem, C. Elfring, C. Hopkinson, B. Lapointe, T. Malone, N. Marcus, K. McGlathery, A. Sharpley, and D. Walker. 2000. Nutrient pollution of coastal rivers, bays, and seas. Vol. 7 of issues in ecology. Washington, D.C: Ecological Society of America.
Hudnell, K.H. (ed.). 2008. Cyanobacterial harmful algal blooms. London: Springer. 950p.
Humborg, C., L. Rahm, D.J. Conley, T. Tamminen, and B. von Bodungen. 2007. Silicon in the Baltic Sea: long-term Si decrease in the Baltic Sea—a conceivable ecological risk? Journal of Marine Systems 73: 221–222.
Jeppesen, E., B. Moss, H. Bennion, L. Carvalho, L. De Meester, H. Feuchtmayr, N. Friberg, M.O. Gessner, M. Hefting, T.L. Lauridsen, et al. 2010. Interaction of climate change and eutrophication. In Climate change impacts on freshwater ecosystems, ed. M. Kernan, R.W. Battarbee, and B. Moss, 119–151. Chichester: Wiley-Blackwell.
Jōhnk, K.D., J. Huisman, J. Sharples, B. Sommeijer, P.M. Visser, and J.M. Stroom. 2008. Summer heatwaves promote blooms of harmful cyanobacteria. Global Change Biology 14: 495–512.
Justić, D., N.N. Rabalais, R.E. Turner, and Q. Dortch. 1995. Changes in nutrient structure of river-dominated coastal waters: stoichiometric nutrient balance and its consequences. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 40: 339–356.
Kosten, S., V. Huszar, E. Bécares, L. Costa, E. van Donk, L.-A. Hansson, E. Jeppesen, C. Kruk, G. Lacerot, N. Mazzeo, L. De Meester, B. Moss, M. Lurling, T. Noges, S. Romo, and M. Scheffer. 2012. Warmer climate boosts cyanobacterial dominance in shallow lakes. Global Change Biology 18: 118–126.
Kraberg, A., N. Wasmund, J. Vanaverbeke, D. Schiedek, K.H. Wiltshire, and N. Mieszkowska. 2011. Regime shifts in the marine environment: scientific basis and political context. Marine Pollution Bulletin 62: 7–20.
Kratzer, C.R., and P.L. Brezonik. 1981. A Carlson-type trophic state index for nitrogen in Florida lakes. Journal of the American Water Resources Association 17: 713–715.
Kuffner, I.B., and V.J. Paul. 2001. Effects of nitrate, phosphate and iron on the growth of macroalgae and benthic cyanobacteria from Cocos Lagoon, Guam. Marine Ecology Progress Series 222: 63–72.
Laurent, A., K. Fennel, J. Hu, and R. Hetland. 2012. Simulating the effects of phosphorus limitation in the Mississippi and Atchafalaya River plumes. Biogeosciences Discussion 9: 5625–5657.
Lewis Jr., W.M., and W.A. Wurtsbaugh. 2008. Control of lacustrine phytoplankton by nutrients: erosion of the phosphorus paradigm. Internationale Revue gesamten Hydrobiologie 93: 446–465.
Lewis, W.M., W.A. Wurtsbaugh, and H.W. Paerl. 2011. Rationale for control of anthropogenic nitrogen and phosphorus in inland waters. Environmental Science & Technology 45: 10030–10035.
Likens, G.E. (Ed.). 1972. Nutrients and eutrophication. American Society of Limnology and Oceanography, Special Symposium 1. 328 p.
Mallin, M.A., L.B. Cahoon, M.R. McIver, D.C. Parsons and G.C. Shank. 1997. Nutrient limitation and eutrophication potential in the Cape Fear and New River Estuaries. Report No. 313. Water Resources Research Institute of the University of North Carolina, Raleigh, NC.
Mallin, M.A., M.R. McIver, H.A. Wells, D.C. Parsons, and V.L. Johnson. 2005. Reversal of eutrophication following sewage treatment upgrades in the New River Estuary, North Carolina. Estuaries 28: 750–760.
McCarthy, M.J.P.L., L. Lavrentyev, L. Yang, Y. Zhang, B. Qin Chen, and W.S. Gardner. 2007. Nitrogen dynamics and microbial food web structure during a summer cyanobacterial bloom in a subtropical, shallow, well-mixed, eutrophic lake (Lake Taihu, China). Hydrobiologia 581: 195–207.
Moisander, P.H., L.A. Cheshire, J. Braddy, E.S. Calandrino, M. Hoffman, M.F. Piehler, and H.W. Paerl. 2012. Facultative diazotrophy increases Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii competitiveness under fluctuating nitrogen availability. FEMS Microbiology Ecology 79: 800–811.
Moss, B., S. Kosten, M. Meerhoff, R.W. Battarbee, E. Jeppesen, N. Mazzeo, K. Havens, G. Lacerot, Z. Liu, L. De Meester, H. Paerl, and M. Scheffer. 2011. Allied attack: climate change and eutrophication. Inland Waters 1: 101–105.
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. 2012. Spatial Trends in Coastal Socioeconomics Demographic Trends Database: 1970–2010. http://coastalsocioeconomics.noaa.gov/.
National Research Council. 2000. Clean coastal waters: understanding and reducing the effects of nutrient pollution. Ocean Studies Board and Water Science and Technology Board, Commission on Geosciences, Environment, and Resources. Washington, DC: National Academy Press. 405 p.
Naumann, E. 1921. Einige Grundlinien der regionalen Limnologie. Lunds Universitets Årsskrift N.F. II, 17:1–22.
Nixon, S.W. 1995. Coastal marine eutrophication: a definition, social causes, and future concerns. Ophelia 41: 199–219.
Nixon, S.W., J.W. Ammerman, L.P. Atkinson, V.M. Berounski, G. Billen, W.C. Boicourt, W.R. Boynton, T.M. Church, D.M. Ditoro, R. Elmgren, J.H. Garber, A.E. Giblin, R.A. Jahnke, N.J.P. Owens, M.E.Q. Pilson, and S.P. Seitzinger. 1996. The fate of nitrogen and phosphorus at the land–sea margin of the North Atlantic Ocean. Biogeochemistry 35: 141–180.
North, R.L., S.J. Guildford, R.E.H. Smith, S.M. Havens, and M.R. Twiss. 2007. Evidence for phosphorus, nitrogen, and iron colimitation of phytoplankton communities in Lake Erie. Limnology and Oceanography 52: 315–328.
O’Goman, P. 2012. Sensitivity of tropical precipitation extremes to climate change. Nature Geoscience 5: 697–700.
Padisak, J. 1997. Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii (Woloszynska) Seenaya et Subba Raju, an expanding, highly adaptive cyanobacterium: worldwide distribution and review of its ecology. Archiv für Hydrobiologie, Supplement 107: 563–593.
Paerl, H.W. 1990. Physiological ecology and regulation of N2 fixation in natural waters. Advances in Microbial Ecology 11: 305–344.
Paerl, H.W. 1997. Coastal eutrophication and harmful algal blooms: importance of atmospheric deposition and groundwater as “new” nitrogen and other nutrient sources. Limnology and Oceanography 42: 1154–1165.
Paerl, H.W. 2009. Controlling eutrophication along the freshwater–marine continuum: dual nutrient (N and P) reductions are essential. Estuaries and Coasts 32: 593–601.
Paerl, H.W., and J. Huisman. 2008. Blooms like it hot. Science 320: 57–58.
Paerl, H.W., and D. Justić. 2011. Primary producers: phytoplankton ecology and trophic dynamics in coastal waters. In Treatise on estuarine and coastal science, vol. 6, ed. E. Wolanski and D.S. McLusky, 23–42. Waltham: Academic.
Paerl, H.W., and V. Paul. 2011. Climate change: links to global expansion of harmful cyanobacteria. Water Research 46: 1349–1363.
Paerl, H.W., and M.F. Piehler. 2008. Nitrogen and marine eutrophication. In Nitrogen in the marine environment, vol. 2, ed. D.G. Capone, M. Mulholland, and E. Carpenter, 529–567. Orlando: Academic.
Paerl, H.W., and J. Huisman. 2009. Climate change: a catalyst for global expansion of harmful cyanobacterial blooms. Environmental Microbiology Reports 1(1): 27–37.
Paerl, H.W., and J.T. Scott. 2010. Throwing fuel on the fire: synergistic effects of excessive nitrogen inputs and global warming on harmful algal blooms. Environmental Science & Technology 44: 7756–7758.
Paerl, H.W., M.A. Mallin, C.A. Donahue, M. Go and B.L. Peierls. 1995. Nitrogen loading sources and eutrophication of the Neuse River estuary, NC: direct and indirect roles of atmospheric deposition. UNC Water Resources Research Institute Report No. 291. 119 p.
Paerl, H.W., J.D. Bales, L.W. Ausley, C.P. Buzzelli, L.B. Crowder, L.A. Eby, J.M. Fear, M. Go, B.L. Peierls, T.L. Richardson, and J.S. Ramus. 2001. Ecosystem impacts of 3 sequential hurricanes (Dennis, Floyd and Irene) on the US’s largest lagoonal estuary, Pamlico Sound, NC. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 98(10): 5655–5660.
Paerl, H.W., L.M. Valdes, M.F. Piehler, and M.E. Lebo. 2004. Solving problems resulting from solutions: evolution of a dual nutrient management strategy for the eutrophying Neuse River Estuary, North Carolina, USA. Environmental Science and Technology 38: 3068–3073.
Paerl, H.W., L.M. Valdes, J.E. Adolf, B.M. Peierls, and L.W. Harding Jr. 2006. Anthropogenic and climatic influences on the eutrophication of large estuarine ecosystems. Limnology and Oceanography 51: 448–462.
Paerl, H.W., L.M. Valdes, A.R. Joyner, and V. Winkelmann. 2007. Phytoplankton indicators of ecological change in the nutrient and climatically-impacted Neuse River–Pamlico sound system, North Carolina. Ecological Applications 17(5): 88–101.
Paerl, H.W., J.J. Joyner, A.R. Joyner, K. Arthur, V.J. Paul, J.M. O’Neil, and C.A. Heil. 2008. Co-occurrence of dinoflagellate and cyanobacterial harmful algal blooms in southwest Florida coastal waters: a case for dual nutrient (N and P) input controls. Marine Ecology Progress Series 371: 143–153.
Paerl, H.W., K.L. Rossignol, Nathan S. Hall, B.L. Peierls, and Michael S. Wetz. 2010. Phytoplankton community indicators of short- and long-term ecological change in the anthropogenically and climatically impacted Neuse River Estuary, North Carolina, USA. Estuaries and Coasts 33: 485–497.
Paerl, H.W., N.S. Hall, and E.S. Calandrino. 2011a. Controlling harmful cyanobacterial blooms in a world experiencing anthropogenic and climatic-induced change. Science of the Total Environment 409: 1739–1745.
Paerl, H.W., H. Xu, M.J. McCarthy, G. Zhu, B. Qin, Y. Li, and W.S. Gardner. 2011b. Controlling harmful cyanobacterial blooms in a hyper-eutrophic lake (Lake Taihu, China): the need for a dual nutrient (N & P) management strategy. Water Research 45: 1973–1983.
Paerl, H.W., N.S. Hall, B.L. Peierls, K.L. Rossignol and A.R. Joyner. 2013. Hydrologic variability and its control of phytoplankton community structure and function in two shallow, coastal, lagoonal ecosystems: the Neuse and New River Estuaries, North Carolina, USA. Estuaries and Coasts. DOI:10.1007/s12237-013-9686-0.
Parma, S. 1980. The history of the eutrophication concept and the eutrophication in the Netherlands. Hydrobiological Bulletin 14: 5–11.
Paul, V.J. 2008. Global warming and cyanobacterial harmful algal blooms. In Cyanobacterial harmful algal blooms: state of the science and research needs. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, ed. Hudnell, H.K, vol. 619. Springer, pp. 239–257.
Peeters, J.C.H., and L. Peperzak. 1990. Nutrient limitation in the North Sea: a bioassay approach. Netherlands Journal of Sea Research 26: 61–73.
Peierls, B.L., N.F. Caraco, M.L. Pace, and J.J. Cole. 1991. Human influence on river nitrogen. Nature 350: 386–387.
Peierls, B.L., N.S. Hall, and H.W. Paerl. 2012. Non-monotonic responses of phytoplankton biomass accumulation to hydrologic variability: a comparison of two coastal plain North Carolina estuaries. Estuaries and Coasts 35: 1376–1392.
Rabalais, N.N. 2002. Nitrogen in aquatic ecosystems. Ambio 16: 102–112.
Rabalais, N.N., and R.E. Turner (eds.). 2001. Coastal hypoxia: consequences for living resources and ecosystems. Coastal and Estuarine Studies 58. Washington, DC: American Geophysical Union. 454p.
Redfield, A.C. 1958. The biological control of chemical factors in the environment. American Scientist 46: 205–222.
Redfield, A.C., B.H. Ketchum, and F.A. Richards. 1963. The influence of organisms on the composition of sea-water. In The sea, vol. 2, ed. N.M. Hill, 26–77. New York: Wiley-Interscience.
Reynolds, C.S. 2006. Ecology of phytoplankton (ecology, biodiversity and conservation). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Rudek, J., H.W. Paerl, M.A. Mallin, and P.W. Bates. 1991. Seasonal and hydrological control of phytoplankton nutrient limitation in the lower Neuse River Estuary, North Carolina. Marine Ecology Progress Series 75: 133–142.
Ryther, J., and W. Dunstan. 1971. Nitrogen, phosphorus, and eutrophication in the coastal marine environment. Science 171: 1008–1013.
Scheffer, M., D. Straile, E.H. van Nes, and H. Hosper. 2001. Climatic warming causes regime shifts in lake food webs. Limnology and Oceanography 46: 1780–1783.
Schindler, D.W. 1975. Whole-lake eutrophication experiments with phosphorus, nitrogen and carbon. Verhandlungen Internationale Vereinigung für Theoretische und Angewandte Limnologie 19: 3221–3231.
Schindler, D.W. 2012. The dilemma of controlling cultural eutrophication of lakes. Proceedings of the Royal Society B. doi:10.1098/rspb.2012.1032.
Schindler, D.W., and J.R. Vallentyne. 2008. The algal bowl: overfertilization of the world’s freshwaters and estuaries. Edmonton: University of Alberta Press.
Schindler, D.W., R.E. Hecky, D.L. Findlay, M.P. Stainton, B.R. Parker, M. Paterson, K.G. Beaty, M. Lyng, and S.E.M. Kasian. 2008. Eutrophication of lakes cannot be controlled by reducing nitrogen input: results of a 37 year whole ecosystem experiment. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 105: 11254–11258.
Scott, J.T., and M.J. McCarthy. 2010. Nitrogen fixation may not balance the nitrogen pool in lakes over timescales relevant to eutrophication management. Limnology and Oceanography 55: 1265–1270.
Scott, J.T., R.D. Doyle, S.J. Prochnow, and J.D. White. 2008. Are watershed and lacustrine controls on planktonic N2 fixation hierarchically structured? Ecological Applications 18: 805–819.
Scott, J.T., J.K. Stanley, R.D. Doyle, M.G. Forbes, and B.W. Brooks. 2009. River–reservoir transition zones are nitrogen fixation hot spots regardless of ecosystem trophic state. Hydrobiologia 625: 61–68.
Seitzinger, S.P. 1988. Denitrification in freshwater and coastal marine systems: ecological and geochemical significance. Limnology and Oceanography 33: 702–724.
Smith, V.H., and D.W. Schindler. 2009. Eutrophication science: where do we go from here? Trends in Ecology and Evolution 24(4): 201–207.
Spivak, A.C., M.J. Vanni, and E.M. Mette. 2011. Moving on up: can results from simple aquatic mesocosm experiments be applied across broad spatial scales? Freshwater Biology 56: 279–291.
Sprengel, C.P. 1839. Die Lehre vom Dünger oder Beschreibung aller bei der Landwirthschaft gebräuchlicher vegetablilischer, animalischer und mineralischer Düngermaterialien, nebst Erklärung ihrer Wirkungsart. Leipzig.
Steffen, M.M., B.S. Belisle, S.B. Watson, G.L. Boyer, and S.W. Wilhelm. 2014. Review: status, causes and controls of cyanobacterial blooms in Lake Erie. Journal of Great Lakes Research. doi:10.1016/j.jglr.2013.12.012.
Sterner, R. 2008. On the phosphorus limitation paradigm for lakes. International Review of Hydrobiology 93: 433–445.
Stüken, A., J. Rücker, T. Endrulat, K. Preussel, M. Hemm, B. Nixdorf, U. Karsten, and C. Wiedner. 2006. Distribution of three alien cyanobacterial species (Nostocales) in northeast Germany: Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii, Anabaena bergii and Aphanizomenon aphanizomenoides. Phycologia 45: 696–703.
Suikkanen, S., M. Laamanen, and M. Huttunen. 2007. Long-term changes in summer phytoplankton communities of the open northern Baltic Sea. Estuarine and Coastal Shelf Science 71: 580–592.
Sylvan, J.B., Q. Dortch, D.M. Nelson, A.F. Maier Brown, W. Morrison, and J.W. Ammerman. 2006. Phosphorus limits phytoplankton growth on the Louisiana shelf during the period of hypoxia formation. Environmental Science & Technology 40: 7548–7553.
Thienemann, A. 1915. Physikalische und chemische Untersuchungen in den Maaren der Eifel. Verein der preussischen Rheinlande und Westfalens 70: 250–302.
Tomas, C.R., J. Peterson, and A.O. Tatters. 2007. Harmful algal species from Wilson Bay, New River, North Carolina: composition, nutrient bioassay and HPLC pigment analyses. North Carolina Water Resources Research Institute Report number 369 (31 pages). Available at http://repository.lib.ncsu.edu/dr/bitstream/1840.4/2002/1/NC.
Trenberth, K.E. 2005. The impact of climate change and variability on heavy precipitation, floods, and droughts. In Encyclopedia of hydrological sciences, ed. M.G. Anderson, 1–11. Hoboken: Wiley.
US Environmental Protection Agency. 2011. Reactive nitrogen in the United States: an analysis of inputs, flows, consequences, and management options. Scientific Advisory Board Publication No. EPA-SAB-11-013. Washington, DC.
Vitousek, P.M., H.A. Mooney, J. Lubchenko, and J.M. Mellilo. 1997. Human domination of Earth’s ecosystem. Science 277: 494–499.
Vollenweider, R A. 1968. Scientific fundamentals of the eutrophication of lakes and flowing waters, with particular reference to nitrogen and phosphorus as factors in eutrophication. Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development, Paris. Technical Report DAS/CS 1/68.27. 250 p.
Watkinson, A.J., J.M. O’Neil, and W.C. Dennison. 2005. Ecophysiology of the marine cyanobacterium Lyngbya majuscula (Oscillatoriaceae) in Moreton Bay, Australia. Harmful Algae 4: 697–715.
Webster, P.J., G.J. Holland, J.A. Curry, and H.R. Chang. 2005. Changes in tropical cyclone number, duration, and intensity in a warming environment. Science 309: 1844–1846.
Wetz, M.S., and H.W. Paerl. 2008. Estuarine phytoplankton responses to hurricanes and tropical storms with different characteristics (trajectory, rainfall, winds). Estuaries and Coasts 31: 419–429.
Wetzel, R.G. 2001. Limnology, third edition: lake and river ecosystems. Orlando: Academic.
Wiedner, C., J. Rücker, R. Brüggemann, and B. Nixdorf. 2007. Climate change affects timing and size of populations of an invasive cyanobacterium in temperate regions. Oecologia 152: 473–484.
Xu, H., H.W. Paerl, B. Qin, G. Zhu, and G. Gao. 2010. Nitrogen and phosphorus inputs control phytoplankton growth in eutrophic Lake Taihu, China. Limnology and Oceanography 55: 420–432.
Acknowledgments
We thank co-workers who assisted with field and laboratory work and manuscript preparation, including B. Abare, J, Braddy, A. Joyner, L. Kelly, and R. Sloup. The editorial input from I. Anderson and W. Gardner and review provided by K. McGlathery are appreciated. This research was funded by the Strategic Environmental Research and Developmental Program (SERDP)–Defense Coastal/Estuarine Research Program, Project SI-1413, The Lower Neuse Basin Association/Neuse River Compliance Association, the North Carolina Department of Environment and Natural Resources (ModMon Program), and National Science Foundation Projects OCE 0825466, OCE 0812913, ENG/CBET0826819 and 1230543, and DEB 1119704 and 1240851.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Iris C. Anderson
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Paerl, H.W., Hall, N.S., Peierls, B.L. et al. Evolving Paradigms and Challenges in Estuarine and Coastal Eutrophication Dynamics in a Culturally and Climatically Stressed World. Estuaries and Coasts 37, 243–258 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12237-014-9773-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12237-014-9773-x