Abstract
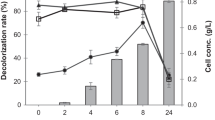
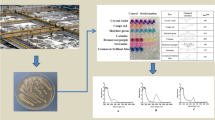
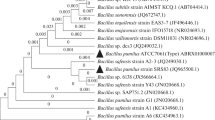
Efficient bacterial strain was isolated from the dye contaminated area and identified as Bacillus stratosphericus SCA1007 based on 16S rRNA gene sequence (GenBank under accession number KY992944). This isolate was selected based on its potential to efficiently decolorize reactive orange 16 dye which is extensively used in textile industries. Various culture conditions like dye concentration, temperature, pH, salinity, and additional nitrogen source were optimized in the present study. The optimal conditions for decolorization of reactive orange 16 was found to be: dye concentration 150 mg/L, pH 7, temperature 35 °C, and yeast extract as nitrogen source. The isolate was also resistant to 4% saline culture condition. Decolorization and degradation of dye were confirmed through UV–visible spectroscopy, Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) and liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry analysis (LC–MS). Toxicity studies were performed on Escherichia coli and Vigna radiata to confirm the non-toxic nature of the degraded metabolites. This is the first study demonstrating complete decolorization of reactive orange 16 dye by Bacillus stratosphericus SCA1007 at high salinity within 10 h of incubation under optimized conditions.









Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Ajaz M, Rehman A, Khan Z et al (2019) Degradation of azo dyes by Alcaligenes aquatilis 3c and its potential use in the wastewater treatment. AMB Express 9:64. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13568-019-0788-3
Ali H (2010) Biodegradation of synthetic dyes—a review. Water Air Soil Pollut 213:251–273. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-010-0382-4
Asses N, Ayed L, Hkiri N, Hamdi M (2018) Congo Red Decolorization and detoxification by Aspergillus niger : removal mechanisms and dye degradation pathway. Biomed Res Int 2018:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/3049686
Bhatia D, Sharma NR, Singh J, Kanwar RS (2017) Biological methods for textile dye removal from wastewater: a review. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 47:1836–1876. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643389.2017.1393263
Breed RS, Murray EGD, Smith NR (1957) Bergey’s manual of systematic bacteriology
Breijyeh Z, Jubeh B, Rafi K (2020) Resistance of gram negative bacteria to current antibacterial agent and approaches to resolve it. Molecules 25:1340. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25061340
Chang J, Lin C (2001) Decolorization kinetics of a recombinant Escherichia coli strain harboring azo-dye-decolorizing determinants from Rhodococcus sp. Biotechnol Lett 23:631–636. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010306114286
Chen K-C, Huang W-T, Wu J-Y, Houng J-Y (1999) Microbial decolorization of azo dyes by Proteus mirabilis. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 23:686–690. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jim.2900689
Chen KC, Wu JY, Liou DJ, Hwang SCJ (2003) Decolorization of the textile dyes by newly isolated bacterial strains. J Biotechnol 101:57–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0168-1656(02)00303-6
Cui D, Li G, Zhao M, Han S (2014) Decolourization of azo dyes by a newly isolated Klebsiella sp. strain Y3, and effects of various factors on biodegradation. Biotechnol Biotechnol Equip 28:478–486. https://doi.org/10.1080/13102818.2014.926053
Deng D, Guo J, Zeng G, Sun G (2008) Decolorization of anthraquinone, triphenylmethane and azo dyes by a new isolated Bacillus cereus strain DC11. Int Biodeterior Biodegradation 62:263–269. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2008.01.017
Dos SA, Cervantes F, Van LJ (2007) Review paper on current technologies for decolourisation of textile wastewaters: perspectives for anaerobic biotechnology. Bioresour Technol 98:2369–2385. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2006.11.013
Elango G, G R, Elango S, (2017) Physico-chemical parameters of textile dyeing effluent and its impacts with case study. Int J Res Chem Env 7:17–24
Gao T, Qin D, Zuo S et al (2020) Decolorization and detoxification of triphenylmethane dyes by isolated endophytic fungus, Bjerkandera adusta SWUSI4 under non-nutritive conditions. Bioresour Bioprocess 7:53. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40643-020-00340-8
Geetha K, Velmani N (2015) Diverse technology and methods for dye treatment. Asian J Chem 27:1177–1184. https://doi.org/10.14233/ajchem.2015.17804
Habib S, Ahmad SA, Johari WLW et al (2018) Evaluation of conventional and response surface level optimisation of n-dodecane (n-C12) mineralisation by psychrotolerant strains isolated from pristine soil at Southern Victoria Island. Antarctica Microb Cell Fact 17:44. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-018-0889-8
Eslami H, Shariatifar A, Rafiee E, Shiranian M, Salehi Sadat Saeede F, Hosseini S, Eslami G, Ghanbari R, Ebrahimi AA (2019) Decolorization and biodegradation of reactive Red 198 Azo dye by a new Enterococcus faecalis–Klebsiella variicola bacterial consortium isolated from textile wastewater sludge. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 35(3) https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-019-2608-y
Haque M, Haque A, Mosharaf k, Marcus PK, (2021) Decolorization, degradation and detoxification of carcinogenic sulfonated azo dye methyl orange by newly developed biofilm consortia. Saudi J Biol Sci 28:793–804. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjbs.2020.11.012
Kalyani DC, Telke AA, Govindwar SP et al (2009) Biodegradation and detoxification of reactive textile dye by isolated Pseudomonas sp SUK1. Water Environ Res 81:298-307.
Kapdan IK, Oztekin R (2003) Decolorization of textile dyestuff reactive orange 16 in fed-batch reactor under anaerobic condition. Enzyme Microb Technol 33:231–235. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0141-0229(03)00128-5
Karim ME, Dhar K, Hossain MT (2018) Decolorization of textile reactive dyes by bacterial monoculture and Consortium screened from textile dyeing effluent. J Genet Eng Biotechnol 16:375–380. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jgeb.2018.02.005
Khehra MS, Saini HS, Sharma DK et al (2006a) Biodegradation of azo dye C.I. Acid Red 88 by an anoxic–aerobic sequential bioreactor. Dye Pigment 70:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dyepig.2004.12.021
Khehra MS, Saini HS, Sharma DK et al (2006b) Biodegradation of azo dye C.I. Acid Red 88 by an anoxic - Aerobic sequential bioreactor. Dye Pigment 70:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dyepig.2004.12.021
Kiiskinen LL, Rättö M, Kruus K (2004) Screening for novel laccase-producing microbes. J Appl Microbiol 97:640-646
Kolekar YM, Pawar SP, Gawai KR et al (2008) Decolorization and degradation of disperse blue 79 and acid orange 10, by Bacillus fusiformis KMK5 isolated from the textile dye contaminated soil. Bioresour Technol 99:8999–9003. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2008.04.073L
López MJ, Guisado G, Vargas-García MC et al (2006) Decolorization of industrial dyes by ligninolytic microorganisms isolated from composting environment. Enzyme Microb Technol 40:42–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enzmictec.2005.10.035
Mabrouk ME, Yusef H (2008) Decolorization of fast red by Bacillus subtilis HM. J Applies Sci Res 4:262–269
Masarbo RS, Ismailsab M, Monisha TR et al (2018) Enhanced decolorization of sulfonated azo dye methyl orange by single and mixed bacterial strains AK1, AK2 and VKY1. Bioremediat J 22:136–146. https://doi.org/10.1080/10889868.2018.1516612
Megha V, Meenakshi S, Jpn R (2015) Optimization of different parameters on synthetic dye decolorization by free and immobilized Mucor hiemalis MV04 (KR078215). Res J Chem Sci Res J Chem Sci 5:2231–2606
Ojekunle OZ, Lateef S (2017) Environmental impact of abattoir waste discharge on the quality of surface water and ground water in Abeokuta. J Environ Anal Toxicol 07:1–10. https://doi.org/10.4172/2161-0525.1000509
Park C, Lee M, Lee B et al (2007) Biodegradation and biosorption for decolorization of synthetic dyes by Funalia trogii. Biochem Eng J 36:59–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2006.06.007
Patel K, Shah M, Darji A, Nair S (2013) Exploiting application of Pseudomonas spp. ETL-2013 in microbial degradation and decolorization of disperse orange 3. J Bioremediation Biodegrad 04:1–7. https://doi.org/10.4172/2155-6199.1000193
Patil PS, Phugare SS, Jadhav SB, Jadhav JP (2010) Communal action of microbial cultures for Red HE3B degradation. J Hazard Mater 181:263–270. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.05.006
Pillai HPJS (2017) Optimization of process conditions for effective degradation of azo blue dye by streptomyces DJP15. J Pure Appl Microbiol 11:1757–1765. https://doi.org/10.22207/JPAM.11.4.14
Popli S, Patel UD (2015) Destruction of azo dyes by anaerobic–aerobic sequential biological treatment: a review. Int J Environ Sci Technol 12:405–420. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-014-0499-x
Pritchard PH, Costa CF (1991) EPA’s Alaska oil spill bioremediation project. Part 5. Environ Sci Technol 25:372–379. https://doi.org/10.1021/es00015a002
Rudakiya DM, Pawar KS (2013) Optimization of culture condition for enhanced decolorization of reactive orange 16 by Comamonas acidovorans MTCC 3364. Int J Microbiol Appl Sci 2:467–476
Saha P, Rao KVB (2019) Biotransformation of Reactive Orange 16 by alkaliphilic bacterium Bacillus flexus VITSP6 and toxicity assessment of biotransformed metabolites. Int J of Environ Sci and Technol 5:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-019-02256-z
Shahi D, Sapkota R (2018) A comparative study on dye degradation by leaf and root extracts of Parthenium hysterophorus L. Int J Appl Sci Biotechnol 6:327–331. https://doi.org/10.3126/ijasbt.v6i4.22110
Sharma S, Roy S (2015) Biodegradation of dye reactive black - 5 by a novel bacterial endophyte. Int Res J Environ Sci 4:44–53
Shobana S, Hangam BT (2012) biodegradation and decolorization of reactive orange 16 by Nocardiopsis alba soil isolate. J Bioremediation Biodegrad 03:1–7. https://doi.org/10.4172/2155-6199.1000155
Soni RK, Acharya PB, Modi HA (2015) Elucidation of biodegradation mechanism of reactive red 35 by Pseudomonas aeruginosa ARSKS20. IOSR J Environ Sci Ver I 9:31–40. https://doi.org/10.9790/2402-09813140
Telke AA, Kalyani DC, Dawkar VV, Govindwar SP (2009) Influence of organic and inorganic compounds on oxidoreductive decolorization of sulfonated azo dye C.I. Reactive Orange 16. J Hazard Mater 172:298–309. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.07.008
Tomczak WE, Gorecki L (2012) Azo dyes - Biological activity and synthetic strategy. Chemik 66:1298–1307
Wood JM (2015) Bacterial responses to osmotic challenges. J Gen Physiol 145:381–388. https://doi.org/10.1085/jgp.201411296
Yadav AN, Sachan SG, Verma P, Saxena AK (2016) Bioprospecting of plant growth promoting psychrotrophic bacilli from the cold desert of north western Indian Himalayas. Indian J Exp Biol 54:142–150
Yaseen DA, Scholz M (2018) Treatment of synthetic textile wastewater containing dye mixtures with microcosms. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:1980–1997. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0633-7
Yoo ES, Libra J, Adrian L (2001) Mechanism of decolorization of azo dyes in anaerobic mixed culture. J Environ Eng 127:844–849. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9372(2001)127:9(844)
Zhou W, Zimmermann W (1993) Decolorization of industrial effluents containing reactive dyes by actinomycetes. FEMS Microbiol Lett 107:157–161. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6968.1993.tb06023.x
Zin KM, Effendi Halmi MI, Abd Gani SS et al (2020) Microbial decolorization of triazo dye, direct blue 71: an optimization approach using response surface methodology (RSM) and artificial neural network (ANN). Biomed Res Int 2020:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/2734135
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the Central Instrumentation Facility and Department of Bioengineering and Biotechnology, BIT, Mesra, Ranchi for providing the infrastructure and laboratory facilities. The authors are also thankful to the Department of Chemistry, Indian Institute of Technology, Patna for providing the facilities for research work. A special thanks to Amar Nath sir for their valuable suggestions for MS analysis.
Funding
This study is funded by BIT, Mesra for seed money scheme (DSR/SMS-2015/2015–2016(3122)).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, methodology, original draft preparation, and review and editing: Kriti Akansha. Liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry analysis (LC–MS): Manish Kumar. Figures: Ajar Nath Yadav. Supervision: Shashwati Ghosh Sachan and Debashis Chakraborty.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Akansha, K., Yadav, A.N., Kumar, M. et al. Decolorization and degradation of reactive orange 16 by Bacillus stratosphericus SCA1007. Folia Microbiol 67, 91–102 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-021-00914-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-021-00914-9