Abstract
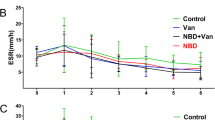
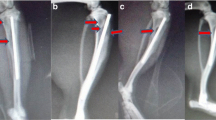
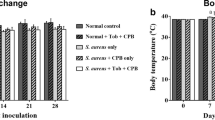
Joint replacement infections and osteomyelitis are among the most serious complications in orthopaedics and traumatology. The risk factors for these infections are often bacterial resistance to antimicrobials. One of the few solutions available to control bacterial resistance involves antimicrobials, which have a different mechanism of action from traditional antibiotics. Antimicrobial peptides (AMP) appear to be highly promising candidates in the treatment of resistant infections. We have identified several AMP in the venom of various wild bees and designed analogues that show potent antimicrobial activity and low toxicity against eukaryotic cells. The aim of the present study was to test the efficacy of one of those synthetic peptide analogues for the treatment of acute osteomyelitis invoked in laboratory rats. Femoral cavities of 20 laboratory Wistar rats were infected with Staphylococcus aureus. After 1 week, eight rats received an injectable calcium phosphate carrier alone, another eight rats were treated with a calcium phosphate mixed with AMP, and four rats were left without any further treatment. After another week, all rats were euthanized and radiographs were made of both the operated and healthy limbs. The animals with the carrier alone exhibited more severe acute osteomyelitis on radiographs in comparison to the recipients of the calcium phosphate carrier loaded AMP and untreated infected individuals. Based on the results of the above mentioned experiment, it was concluded that when injected directly into the site of femoral acute osteomyelitis, the calcium phosphate carrier mixed with AMP reduced osteomyelitis signs visible on radiographs.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arciola CR, Campoccia D, Ehrlich GD, Montanaro L (2015) Biofilm-based implant infections in orthopaedics. Adv Exp Med Biol 830:29–46. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-11038-7_2
Baltzer SA, Brown MH (2011) Antimicrobial peptides— promising alternatives to conventional antibiotics. J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol 20:228–235. doi:10.1159/000331009
Biavasco F, Vignaroli C, Varaldo PE (2000) Glycopeptide resistance in coagulase-negative staphylococci. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 19:403–417. doi:10.1007/s100960000299
Brogden NK, Brogden KA (2011) Will new generations of modified antimicrobial peptides improve their potential as pharmaceuticals? Int J Antimicrob Agents 38:217–225. doi:10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2011.05.004
Campoccia D, Montanaro L, Speziale P, Arciola CR (2010) Antibiotic-loaded biomaterials and the risks for the spread of antibiotic resistance following their prophylactic and therapeutic clinical use. Biomaterials 31:6363–6337. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2010.05.005
Čeřovský V (2014) Antimicrobial peptides isolated from insects (in Czech, abstract in English). Chem List 108:344–353
Čeřovský V, Nešuta O, Dudková V, Melicherčík P (2016) Antimicrobial peptides for topical treatment of osteomyelitis and prevention of implant related infections in orthopedics. J Pept Sci 22:157–158
Cetinkaya Y, Falk P, Mayhall CG (2000) Vancomycin-resistant enterococci. Clin Microbiol Rev 13:686–607. doi:10.1128/CMR.13.4.686-707.2000
Cierny G, Mader JT, Pennick H (1985) A clinical staging system of adult osteomyelitis. Contemp Orthop 10:17–37. doi:10.1097/01.blo. 0000088564.81746.62
Costerton JW (2005) Biofilm theory can guide the treatment of device-related orthopaedic infections. Clin Orthop Rel Res 437:7–11. doi:10.1097/00003086-200508000-00003
Ehrlich GD, Stoodley P, Kathju S, Zhao Y, McLeod BR, Balaban N, Hu FZ, Sotereanos NG, Costerton JW, Stewart PS, Post JC, Lin Q (2005) Engineering approaches for the detection and control of orthopaedic biofilm infections. Clin Orthop Rel Res 437:59–66
Faber C, Hoogendoorn RJW, Stallmann HP, Lyaruu DM, van Nieuw AA, Wuisman PIJM (2004) In vivo comparison of Dhvar-5 and gentamicin in MRSA osteomyelitis prevention model. J Antimicrob Chemother 54:1078–1084. doi:10.1093/jac/dkh441
Faber C, Stallmann HP, Lyaruu DM, Joosten U, Eiff C, van Nieuw AA, Wuisman PIJM (2005) Comparable efficacies of the antimicrobial peptide human lactoferrin 1-11 and gentamicin in a chronic methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus osteomyelitis model. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 49:2438–2444. doi:10.1128/AAC.49.6.2438-2444.2005
Fischer B, Vaudaux P, Mangin M (1996) Novel animal model for studying the molecular mechanisms of bacterial adhesion to bone-implanted metallic devices. Role of fibronectin in Staphylococcus aureus adhesion. J Orthop Res 14:914–920. doi:10.1002/jor.1100140611
Giuliani A, Pirri G, Nicoletto SF (2007) Antimicrobial peptides. An overview of a promising class of therapeutics. Centr Eur J Biol 2:1–33. doi:10.2478/s11535-007-0010-5
Hancock REW, Sahl H-G (2006) Antimicrobial and host-defense peptides as new anti-infective therapeutic strategies. Natur Biotech 24:1551–1557. doi:10.1038/nbt1267
Hanssen AD, Osmon DR, Patel R (2005) Local antibiotic delivery systems: where are we and where are we going? Clin Orthop Rel Res 437:111–114. doi:10.1097/01.blo.0000175122.50804
Jacoby GA, Archer GL (1991) New mechanisms of bacterial resistance to antimicrobial agents. New Engl J Med 324:601–612. doi:10.1056/NEJM199102283240906
Jahoda D, Nyč O, Pokorný D, Landor I, Sosna A (2006) Antibiotic treatment for prevention of infectious complications in joint replacement. Acta Chir Orthop Traum Cech 73:108–114
Jahoda D, Nyč O, Šimša J, Kučera E, Hanek P, Chrz P, Pokorný D, Tawa N, Landor I, Sosna A (2008a) Late hematogenous infection of prosthetic joint. Acta Chir Ortop Traum Čech 75:88–92
Jahoda D, Sosna A, Nyč O et al (2008b) Infectious complications of joint replacement. Triton, Praha
Jahoda D, Landor I, Benedík J, Pokorný D, Judl T, Barták V, Jahodová I, Fulín P, Síbek M (2015) PCR diagnostic system in the treatment of prosthetic joint infections. Folia Microbiol 60:385–391. doi:10.1007/s12223-014-0370-y
Mader JT, Shirtliff M, Calhoun JH (1997) Staging and staging application in osteomyelitis. Clin Infect Dis 25:1303–1309. doi:10.1086/516149
Meani E, Romanò C, Crosby L, Hofmann G (2007) Infection and local treatment in orthopedic surgery, first edition. Springer, US
Melichercik P, Jahoda D, Landor I et al (2011) Local carrier of antibiotics. Ortopedie 4:36–39
Monincová L, Buděšinský M, Slaninová J, Hovorka O, Cvačka J, Voburka Z, Fučík V, Borovičková L, Bednárová L, Straka J, Čeřovský V (2010) Novel antimicrobial peptides from the venom of the eusocial bee Halictus sexcinctus (hymenoptera: Halictidae) and their analogs. Amino Acids 39:763–775. doi:10.1007/s00726-010-0519-1
Nešuta O, Hexnerová R, Buděšínský M, Slaninová J, Bednárová L, Hadravová R, Straka J, Veverka V, Čeřovský V (2016) Antimicrobial peptide from the wild bee Hylaeus signatus venom and its analogues: structure-activity study and synergistic effect with antibiotics. J Nat Prod 79:1073–1083. doi:10.1021/acs.jnatprod.5b01129
Nguyen LT, Haney EF, Vogel HJ (2011) The expanding scope of antimicrobial peptide structures and their modes of action. Trends Biotech 29:464–471 doi.org/10.1016/j.tibtech.2011.05.001
Oren Z, Shai Y (1998) Mode of action of linear amphipathic alpha-helical antimicrobial peptides. Biopolymers 47:451–463. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-0282
Oyston PCF, Fox MA, Richards SJ, Clark GC (2009) Novel peptide therapeutics for treatment of infections. J Med Microbiol 58:977–987. doi:10.1099/jmm.0.011122-0
R Core Team (2014) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. Vienna, Austria: the R Foundation for Statistical Computing. http://www.R-project.org/. Accessed 25 Sept 2015
Reizner W, Hunter JG, O’Malley NT, Southgate RD, Schwarz EM, Kates SL (2014) Systematic review of animals models for Staphylococcus aureus osteomyelitis. Eur Cells Mater 27:196–212. doi:10.22203/eCM.v027a15
Ribeiro M, Monteiro FJ, Ferraz MP (2012) Infection of orthopedic implants with emphasis on bacterial adhesion process and techniques used in studying bacterial-material interactions. Biomatter 2:176–194. doi:10.4161/biom.22905
Romano CL, Toscano M, Romano D, Drago L (2013) Antibiofilm agents and implant-related infections in orthopaedics: where are we? J Chemother 25:67–80. doi:10.1179/1973947812Y.0000000045
Schindler J (2001) Microbial biofilm (in Czech, abstract in English). Vesmír 4:203–206
Stallmann HP, Faber C, Bronckers ALJJ, Nieuw Amerongen AV, Wuisman PIJM (2004) Osteomyelitis prevention in rabbits using antimicrobial peptide hLF1-11- or gentamicin-containing calcium phosphate cement. J Antimicrob Chemother 54:472–476. doi:10.1093/jac/dkh346
Stoodley P, Kathju S, Hu FZ, Erdos G, Levenson JE, Mehta N, Dice B, Johnson S, Hall-Stoodley L, Nistico L, Sotereanos N, Sewecke J, Post JC, Ehrlich GD (2005) Molecular and imaging techniques for bacterial biofilms in joint arthroplasty infections. Clin Orthop Relat Res 437:31–40. doi:10.1097/01.blo.0000175129.83084.d5
Toke O (2005) Antimicrobial peptides: new candidates in the fight against bacterial infection. Biopolymers. Pept Sci 80:717–735. doi:10.1002/bip.20286
Trampuz A, Zimmerli W (2005) Prosthetic joint infections: update in diagnosis and treatment. Swiss Med Wkly 30:243–251
Winkler H, Haiden P (2016) Treatment of chronic bone infection. Oper Tech Orthop 26:2–11. doi:10.1053/j.oto.2016.01.002
Winkler H, Kaudela K, Stoiber A, Menschik F (2006) Bone grafts impregnated with antibiotics as a tool for treating infected implants in orthopedic surgery—one stage revision results. Cell Tissue Bank 7:319–323. doi:10.1007/s10561-006-9010-3
Wisniewska M, Babiak I, Palczewski PD, Swiatkowski J,Golebiowski M (2009) Cierny-Mader calssification of chronic osteomyelitis: Preoperative evaluation with cross-sectional imaging. E-Poster: C-590, Congress: ECR
Yeaman MR, Yount NY (2003) Mechanisms of antimicrobial peptide action and resistance. Pharm Rev 55:27–55. doi:10.1124/pr.55.1.2
Yeung ATY, Gellatly SL, Hancock REW (2011) Multifunctional cationic host defence peptides and their clinical applications. Cell Mol Life Sci 68:2161–2176. doi:10.1007/s00018-011-0710-x
Zaiou M (2007) Multifunctional antimicrobial peptides: therapeutic targets in several human diseases. J Mol Med 85:317–329. doi:10.1007/s00109-006-0143-4
Zasloff M (2002) Antimicrobial peptides of multicellular organisms. Nature 415:389–395. doi:10.1038/415389a
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Czech Health Research Council (AZV ČR, grant number 16-27726A), by the Technology Agency of the Czech Republic (grant number TA04010638), by research project RVO 61388963 of the Institute of Organic Chemistry and Biochemistry, Academy of Sciences of the Czech Republic, and by internal grant numbers 9777 (Advanced therapies) and 6010 of the Motol University Hospital. We thank Dr. Radek Šerý from the National Institute of Public Health for his help with the experiments on laboratory animals and for performing radiography. We also thank to Mr. Tim Lioyd for assistance with the English.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
All applicable international, national, and institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed. The experiments with animals were carried out in the research and breeding facility of the National Institute of Public Health in Prague, under conditions that comply with Regulation No. 419/2012 of the Ministry of Health as last amended. All procedures performed in studies were in accordance with the ethical standards of this institute.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Melicherčík, P., Čeřovský, V., Nešuta, O. et al. Testing the efficacy of antimicrobial peptides in the topical treatment of induced osteomyelitis in rats. Folia Microbiol 63, 97–104 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-017-0540-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-017-0540-9