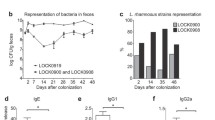
Abstract
Three Lactobacillus strains (LOCK 0900, LOCK 0908, LOCK 0919) out of twenty-four isolates were selected according to their antagonistic activity against pathogenic bacteria, resistance to low pH and milieu of bile salts. Intragastric administration of a mixture of these strains to Balb/c mice affected cytokine TH1-TH2 balance toward nonallergic TH1 response. Spleen cells, isolated from lactobacilli-treated mice and re-stimulated in vitro with the mixture of heat-inactivated tested strains, produced significantly higher amounts of anti-allergic tumor necrosis factor- and interferon-γ than control animals whereas the level of pro-allergic interleukin-5 was significantly lower. Lactobacillus cells did not translocate through the intestinal barrier into blood, liver and spleen; a few Lactobacillus cells found in mesenteric lymph nodes could create antigenic reservoir activating the immune system. The mixture of Lactobacillus LOCK 0900, LOCK 0908 and LOCK 0919 strains represents a probiotic bacterial preparation with possible use in prophylaxis and/or therapy of allergic diseases.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CFU:
-
colony forming units
- Con:
-
A concanavalin A
- IFN:
-
interferon
- IL:
-
interleukin
- MLN:
-
mesenteric lymph nodes
- PBS:
-
phosphate-buffered saline
- TH :
-
T helper (lymphocytes)
- TGF:
-
transforming growth factor
- TNF:
-
tumor necrosis factor
References
Fedorak R.N., Madsen K.L.: Probiotics and prebiotics in gastrointestinal disorders. Curr.Opin.Gastroenterol.20, 146–155 (2004).
Isolauri E., Arvola T., Sutas Y., Moilanen E., Salminen S.: Probiotics in the management of atopic eczema. Clin.Exp.Allergy30, 1604–1610 (2000).
Kalliomaki M., Salminen S., Arvilommi H., Koro P., Koskinen P., Isolauri E.: Probiotics in primary prevention of atopic disease: a randomized placebo-controlled trial. Lancet357, 1076–1079 (2001a).
Kalliomaki M., Kirjavainen P., Eerola E., Kero P., Salminen S., Isolauri E.: Distinct patterns of neonatal gut microflora in infants in whom atopy was and was not developing, J.Allergy Clin.Immunol.107, 129–134 (2001b).
Kocourkova I., Zadnikova R., Zizka J., Rosova V.: Effect of oral application of a probiotic E. coli strain on the intestinal microflora of children of allergic mothers during the first year of life. Folia Microbiol.52, 189–193 (2007).
Kokesova A., Frolova L., Kverka M., Sokol D., Rossmann O., Bartova J., Tlaskalova-Hogenova H.: Oral administration of probiotic bacteria (E. coli Nissle, E. coli O83, Lactobacillus casei) influences the severity of dextran sodium sulfate-induced colitis in BALB/c mice. Folia Microbiol.51, 478–484 (2006).
Krauthammer M., Rzhetsky A., Morozov P., Friedman C.: Using BLAST for identifying gene and protein names in journal articles. Gene23, 245–252 (2000).
Kurman J.A.: Starters with selected intestinal bacteria. Bulletin IDF227, 41–55 (1988).
Ljungh A., Wadstrom T.: Lactic acid bacteria as probiotics. Curr.Issues Intest.Microbiol.7, 73–89 (2006).
Lodinova-Zadnikova R., Cukrowska B., Tlaskalova-Hogenova H.: Oral administration of probiotic Escherichia coli after birth reduces frequency of allergies and repeated infections later in life (after 10 and 20 years). Internat.Arch.Allergy Immunol.131, 209–211 (2003).
Macpherson A.J., Uhr T.: Induction of protective IgA by intestinal dendritic cells carrying commensal bacteria. Science303, 1662–1665 (2004).
Marewicz E., Moneta J., Motyl I., Heczko P.B., Libudzisz Z.: Comparison of adherence to Caco-2 human epithelial cell line of Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium strains of various origin: human, animal and vegetal. Med.Sci.Mon. Internat.Med.J.Exp. Clin.Res.6(Suppl. 3), 34 (2000).
Mowat A.M.: Anatomical basis of tolerance and immunity to intestinal antigens. Nat.Rev.Immunol.3, 331–341 (2003).
Ostad S.N., Salarian A.A., Ghahramani M.H., Fazeli M.R., Samadi N., Jamalifar H.: Live and heat-inactivated lactobacilli from feces inhibit Salmonella typhi and Escherichia coli adherence to Caco-2 cells. Folia Microbiol.54, 157–160 (2009).
Pohjavuori E., Viljanen M., Korpela R.: Lactobacillus GG effect in increasing IFN-production in infants with cow’s milk allergy. J.Allergy Clin.Immunol.114, 131–136 (2004).
Salama M., Sandine W., Giovannoni S.: Development and application of oligonucleotide probes for identification of Lactococcus lactis subsp. cremoris. Appl.Environ.Microbiol.57, 1313–1318 (1991).
Schrezenmeier J., De Vrese M.: Probiotics, probiotics and synbiotics — approaching a definition. Am.J.Nutr.73(Suppl. 2), 361S–364S (2001).
Tailliez P., Tremblay J., Ehrlich S.D., Chopin A.: Molecular diversity and relationship with in Lactococcus lactis, as revealed by randomly amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD). Syst.Appl.Microbiol.21, 530–538 (1998).
Umetsu D.T., Dekruyff R.H.: The regulation of allergy and asthma. Immunol.Rev.212, 238–255 (2006).
Vancikova Z., Lodinova-Zadnikova R., Radl J., Tlaskalova-Hogenova H.: The early postnatal development of salivary antibody and immunoglobulin response in children orally colonized with a nonpathogenic, probiotic strain of E. coli. Folia Microbiol.48, 281–287 (2003).
Walencka E., Rozalska S., Sadowska B., Rozalska B.: The influence of Lactobacillus acidophilus-derived surfactants on staphylococcal adhesion and biofilm formation. Folia Microbiol.53, 61–66 (2008).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
These authors contributed equally to the work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cukrowska, B., Motyl, I., Kozáková, H. et al. Probiotic Lactobacillus strains: in vitro and in vivo studies. Folia Microbiol 54, 533–537 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-009-0077-7
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-009-0077-7